SYNTHAMINE LP 12™ Synthagea
1-IDENTIFIER
1.1
1.1.1-Description
Synthamine LP12™ as a Yeastbased biomass are a kind of biostimulant extracted from Yeast Massive’s that can promote crop growth, improve crop quality, and enhance crop stress resistance SYNTHAMINE LP12™ have been widely used as biostimulants in crop management due to their growth-promoting and stress-resistant effects.
1.1.2-Names
L-alpha amino acids mix with 20 proteinogenic amino
1.1.3-Supplier
Fermo Crysta fermantasyon ürünleri Ltd. Şti.
Saray osmangazi mahallesi sarsılmaz caddesi no :2 daire 6 Pursaklar Ankara
0-312 5143724
www.fermocrysta.com
1.2-IDENTIFY NUMBERS
1.2.1 -Milicard number : 110.239.009
1.2.2 -EA Codex number : 89-4005-2021
1.2.3 -Cas number : 74-79-3
1.2.4 -EC number : 200-811-1
1.2.5 -Permit License number : 200-811-1
1.2.6 -Patent and License number : 200-811-1
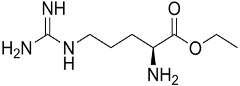
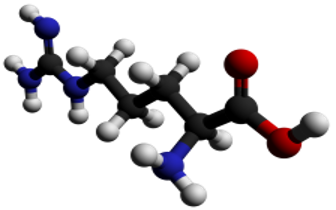
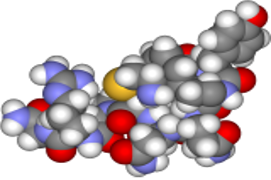
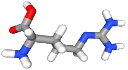
1.3-STRUCTURE
1.3.1-Linear 2D Structure
1.3.2-Ball&Stick Model Structure
1.3.3-Space Filling Model
1.3.4-Stick Model
1.4-CHEMICAL&PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| 1.4.1-CHEMICAL FORMULA | : CnHnNnOnS |
| 1.4.2-TYPE/STATE/FORM | : Liquid |
| 1.4.3-COLOUR | : Dark Brown |
| 1.4.4-ODOUR | : Typical molasses and ferments |
| 1.4.5-TASTE | : Bitter |
| 1.4.6-PARTICLE SIZE | : D10:11.16µm, D50=56.59µm, D90=158.83µm |
| The fraction <10 µm was determined to be ca. % 8.8 by volume | |
| 1.4.7-DENSITY | : 1.46 g/cm³, Bulk: 640 kg/m³ |
| 1.4.8-MELTING POINT | : 223°C |
| 1.4.9-BOILING POINT | : 368°C |
| 1.4.10-FLASH POINT | : 176.1±30.7 °C |
| 1.4.11-VAPOUR PRESSURE | : < 0,1 Pa nin 25 °C |
| 1.4.12-VISCOSITY | : Not available |
| 1.4.13-REFRACTIVE IDEX | : Not available |
| 1.4.14-IGNITION TEMP | : Not available |
| 1.4.15-DISSOCIATION CONSTANTS | : 2.17 at 20 °C |
| 1.4.16-SOLUBILITY | : Soluble in H2O 1000 g/L at 25 °C |
| 1.4.17-pH VALUE | : 5.4-6.4 (100 g/L ,H2O,20 °C) |
| 1.4.18-ACIDITY pKa | : 2.24 |
| 1.4.19-Log P | : log P :-4.20 |
| 1.4.20-CHIRAL ROTATION | : [α]20/D +27°, c = 8, 6 M HCl’de |
| 1.4.21-MOLAR MASS | : avarage 174.2 g/mol |
| 1.4.22-PURIFY | : % 12 free |
| 1.4.22.1-CARRIER | : NA |
| 1.4.23-METALS | : Chloride <%0,02,Sulphate <%0.01 Heavy Metals <%0.0001 Arsenic <%0.00001 |
| Calcium <%0.001 Cobalt< %0.000001 Fe <%0.0005 K <%0.0003 Mg <%0.0002 | |
| Amonium N<%0.01 Na <%0.01 | |
| 1.4.24-LD 50 ORAL RAT | : > 5110 mg/kg |
| 1.4.25-GHS | : H315 (% 15.35): Causes skin irritation |
| H319 (% 99.6): Causes serious eye irritation | |
| 1.4.26-WGK | : Not available |
| 1.4.27-OTHER DETAILS | : Not available |
1.5-CONTENT PROPERTIES
1.5.1-CHEMICAL COMPOSITION
| 1.5.1.1-DRY MATTER | 56% |
| 1.5.1.2-ORGANIC MATTER | 45% |
| 1.5.1.3-TOTAL AMINO ACIDS | 22% |
| 1.5.1.4-FREE AMINO ACIDS | 10% |
| 1.5.1.5-POLYSACCHARIDES | 5% |
| 1.5.1.6-LIPID&FATTY ACID | 2% |
| 1.5.1.7-POLYPHENOL,FLAVONOID | 4% |
| 1.5.1.8-ORGANIC ACID | 6% |
| 1.5.1.9-NUCLEOTIDES | 1,20% |
| 1.5.1.10-POLYOLS | 0,66% |
| 1.5.1.11-VITAMIN | 5,78% |
| 1.5.1.14-BIOACTIVE AND MOLECULES | 1,95% |
| 1.5.1.15-BIOSTIMULANT & ELICITORS | 1,34% |
| 1.5.1.16-ANTIBIOSIS,METABOLITES | 1,34% |
1.5.1.30-TOTAL MINERAL
| 1.5.1.30-TOTAL MINERAL | 6% |
| 1.5.30.1-TOTAL NITROGEN | 3% |
| 1.5.30.1.1-CHEMICAL NITROGEN | 0,20% |
| 1.5.30.1.2-ORGANIC NITROGEN | 2,80% |
| 1.5.30.2-PHOSPHATE TOTAL | 2% |
| 1.5.30.2.1-P2O5 | 1,84% |
| 1.5.30.2.2-ORGANIC PHOSPHATE | 0,16% |
| 1.5.30.3-POTASSIUM | 3% |
| 1.5.30.4-SULFUR TOTAL | 1,12% |
| 1.5.30.4.1-CHEMICAL SULFUR | 0,22% |
| 1.5.30.4.2-ORGANIC SULFUR | 0,90% |
| 1.5.30.5-MAGNESIUM | 1,08% |
| 1.5.30.6-CALCIUM | 0,11% |
| 1.5.30.7-ZINC | 1,95% |
| 1.5.30.8-FERROUS | 1,34% |
| 1.5.30.9-MANGANASE | 1,34% |
| 1.5.30.10-COPPER | 1,34% |
| 1.5.30.11-CHLORE | 1,34% |
| 1.5.30.12-BORON | 1,34% |
| 1.5.30.13-COBALT | 1,34% |
| 1.5.30.14-SELENIUM | 1,34% |
| 1.5.30.15-VANADIUM | 1,34% |
| 1.5.30.16-SODIUM | 1,34% |
1.5.1.3-TOTAL AMINO ACID
| 1.5.1.3-AMINO ACID-Total | %22-26 |
| 1.5.1.3.1-L-ALANINE | 4,78% |
| 1.5.1.3.2-L-ARGININE | 6,70% |
| 1.5.1.3.3-L-ASPARAGINE | 0,77% |
| 1.5.1.3.4-L-ASPARTIC ACID | 3,00% |
| 1.5.1.3.5-L-CYSTEINE | 0,30% |
| 1.5.1.3.6-L-GLUTAMIC ACID | 12,09% |
| 1.5.1.3.7-L-GLUTAMINE | 1,22% |
| 1.5.1.3.8-GLYCINE | 6,74% |
| 1.5.1.3.9-L-HISTIDINE | 0,56% |
| 1.5.1.3.10-L-ISOLEUCINE | 4,92% |
| 1.5.1.3.11-L-LEUCINE | 3,91% |
| 1.5.1.3.12-L-LYSINE | 3,24% |
| 1.5.1.3.13-L-METHIONINE | 0,42% |
| 1.5.1.3.14-L-PHENYALANINE | 3,93% |
| 1.5.1.3.15-L-PROLINE | 4,05% |
| 1.5.1.3.16-L-SERINE | 2,70% |
| 1.5.1.3.17-L-THREONINE | 2,89% |
| 1.5.1.3.18-L-TRYPTOPHAN | 0,11% |
| 1.5.1.3.19-L-TYROSINE | 0,24% |
| 1.5.1.3.20-L-VALINE | 2,76% |
1.5.1.4-FREE AMINO ACID
| 1.5.1.4-AMINO ACID-Free | %10-12 |
| 1.5.1.4.1-L-ALANINE | 2,30% |
| 1.5.1.4.2-L-ARGININE | 4,51% |
| 1.5.1.4.3-L-ASPARAGINE | 0,13% |
| 1.5.1.4.4-L-ASPARTIC ACID | 1,95% |
| 1.5.1.4.5-L-CYSTEINE | 0,22% |
| 1.5.1.4.6-L-GLUTAMIC ACID | 8,95% |
| 1.5.1.4.7-L-GLUTAMINE | 0,40% |
| 1.5.1.4.8-GLYCINE | 5,89% |
| 1.5.1.4.9-L-HISTIDINE | 0,46% |
| 1.5.1.4.10-L-ISOLEUCINE | 2,80% |
| 1.5.1.4.11-L-LEUCINE | 3,40% |
| 1.5.1.4.12-L-LYSINE | 2,88% |
| 1.5.1.4.13-L-METHIONINE | 0,33% |
| 1.5.1.4.14-L-PHENYALANINE | 1,64% |
| 1.5.1.4.15-L-PROLINE | 3,20% |
| 1.5.1.4.16-L-SERINE | 1,95% |
| 1.5.1.4.17-L-THREONINE | 2,04% |
| 1.5.1.4.18-L-TRYPTOPHAN | 0,08% |
| 1.5.1.4.19-L-TYROSINE | 0,19% |
| 1.5.1.4.20-L-VALINE | 1,72% |
1.5.1.5- POLYSACCHARIDE CONTENT
| 1.5.1.5.1-Total Polysaccharides | |
| 1.5.1.5.1.1-Polysaccharides | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.5.1.2-Oligosaccharides | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.5.1.3-Monosaccharides | 0,00% |
1.5.1.6- FATTY ACID LIPID AND STEROLS
| 1.5.1.6.1-Total Fatty Acid | |
| 1.5.1.6.1.1-Alpha Linolenic Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.2-Arachidic Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.3-Arachidonic Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.4-Behenic Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.5-Caproic Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.6-Caprylic Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.7-Capric Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.8-Docosadienoic Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.9-Docosahexaenoic Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.10-Docosapentaenoic Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.11-Eicosadienoic Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.12-Eicosenic Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.13-Eicosapentaenoic Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.14-Eicosatrienoic Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.15-Elaidic Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.16-Erucic Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.17-Gamma Linelonic Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.18-Heneicosanoic Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.19-Heptanoic Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.20-Homo-gamma-Linelenic Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.21-Lauric Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.22-Ligneceric Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.23-Linoleic Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.24-Linolelaidic Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.25-Margaric Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.26-Margaroleic Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.27-Myristic Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.28-Myristoleic Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.29-Nervonic Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.30-Nonadecanoic Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.31-Nonanoic Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.32-Palmitic Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.33-Palmitoleic Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.34-Pentadecanoic Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.35-Oleic Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.36-Stearic Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.37-Tricosanoic Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.38-Tridecanoic Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.39-Vaccenic Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.40-Undecanoic Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.6.2-Total Lipids | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.6.2.1-Phospholipids | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.6.2.2-Glyceropholipids | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.6.2.3-Betainelipids | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.6.2.4-Galactolipids | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.6.2.5-Sulpholipids | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.6.2.6-Glycolipids | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.6.2.7-Chlorolipids | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.6.2.8-Long chain alkene | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.6.2.9-Trigalactosyldiacylglycerol | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.6.2.10-Mannose Glycolipid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.6.2.11-Rhamnose Glycolipid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.6.3-Total Sterols | 0,00% |
| 2.10.1-Clionasterol | 0,00% |
| 2.10.2-Clerosterol | 0,00% |
| 2.10.3-Fucosterol | 0,00% |
| 2.10.4-B-Sitosterol | 0,00% |
| 2.10.5-Cholesterol | 0,00% |
| 2.10.6-Brassinolide | 0,00% |
| 2.10.7-Stigmasterol | 0,00% |
| 2.10.8-Ergosterol | 0,00% |
| 2.10.9-Metylenecholesterol | 0,00% |
1.5.1.7 -POLYPHENOL,FLAVONOID AND PIGMENTS
| 1.5.1.7.1-Total Polyphenols | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.7.1.1-Phenolic acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.7.1.2-Coumaric acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.7.1.3-Caffeic acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.7.1.4-Benzoic acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.7.1.5-Cinnamic | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.7.1.6-Phenylpropanoic acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.7.1.7-Curcuminoids | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.7.1.8-Hydroxybenzoketones | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.7.1.9-Methoxyphenols | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.7.1.10-Hydroxyphenlypropenes | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.7.1.11-Tyrosols | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.7.1.12-Naphtoquinones | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.7.1.13-Phenolic terpenes | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.7.2-Total Flavonoid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.7.2.1-Anthocyanins | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.7.2.2-Chalcones | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.7.2.3-Flavanols | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.7.2.4-Flavanones | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.7.2.5-Isaflavonoids | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.7.3-Pigments | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.7.3.1-Chlororophyll-a | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.7.3.2-Chlororophyll-b | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.7.3.3-Trans-B-carotene | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.7.3.4-Cis-B-carotene | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.7.3.5-Allophycocyanin | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.7.3.6-Fucoxanthin | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.7.3.7-Astaxhantin | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.7.3..8-Violaxanthin | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.7.3.9-Zeaxanthin | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.7.3.10-Tocopherol | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.7.3.11-Cantaxanthin | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.7.3.12-Phycocyanin | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.7.3.13-B-phycoerythrobilin | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.7.4-Stilbenes | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.7.5-Lignans | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.7.6-Isoprene,terpenes | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.7.7-Lignin | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.7.8-Humic acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.7.9-Fulvic acid | 0,00% |
1.5.1.8 -ORGANIC ACIDS
| 1.5.1.8.1-Acetic Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.8.2-Lactic Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.8.3-Propionic Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.8.4-Butyric Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.8.5-Succinic acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.8.6-Malic acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.8.7-Tartaric acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.8.8-Glycolic acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.8.9-Alpha hydroxy acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.8.10-Citric acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.8.11.Gluconic acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.8.12-Uronic acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.8.12-Pyruvic acid | 0,00% |
1.5.1.9 -NUCLEOBASES
| 1.5.1.9.1-Adenine | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.9.2-Guanine | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.9.3-Cytosine | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.9.4-Thymine | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.9.5-Uracil | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.9.6-Inosine | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.9.7-3’5’AMP | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.9.10-3’5’GMP | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.9.11-3’5’IMP | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.9.12-cGMP | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.9.13-ATP | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.9.14-Xhantine | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.9.15-Methylguanine | 0,00% |
1.5.1.10 -POLYOLS
| 1.5.1.10.1-Mannitol | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.10.2-Sorbitol | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.10.3-Galactitol | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.10.4-Eryththiotol | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.10.5-Glycerol | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.10.6-Ethylen glycol | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.10.7-Inositol | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.10.8-Xylitol | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.10.9-Maltitol | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.10.10-Lactitol | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.10.11-Maltitol | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.10.12-Ribitol | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.10.13-Fucitol | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.10.14-Isomalt | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.10.15-Iditol | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.10.16-Volemitol | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.10.17-Polyglycitol | 0,00% |
1.5.1.11 -VITAMIN
| 1.5.1.11.1-Vitamin A | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.2-Vitamin B1 Thiamine | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.3-Vitamin B2-Riboflavin | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.4-Vitamin B3-Niacinamide | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.5-Vitamin B5-Pantothenic acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.6-Vitamin B6 Pyridoxine | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.7-Vitamin B7 -Biotin | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.8-Vitamin B9-Folic Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.9-Vitamin B12-Cyanocobalamin | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.10-Vitamin B14-Inosine | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.11-Ascorbic Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.12-Vitamin D2 | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.13-Vitamin D3 | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.14-Vitamin K | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.15-Vitamin E | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.15-Vitamin Pc | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.16-Vitamin Pb | 0,00% |
1.5.1.12 -BIOACTIVE AND BIOMOLECULE
| 1.5.1.11.1-Coenzyme | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.2-Cofactor | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.3-Metabolic enyzmes | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.4-Signalling molecules | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.5-Apoenzymes | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.6-Isoenzymes | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.7-Enzymes,industrial | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.7.1-Endoprotease | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.7.2-Endopeptidase | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.7.3-Serine protease | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.7.4-Cysteine protease | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.7.5-Alpha Amylase | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.7.6-Exopeptidase | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.7.7-Arabanase | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.7.8-Cellulase | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.9-B-Glucanase | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.10-Hemi-cellulase | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.11-Xylanase | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.12-Cellobiose | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.13-Lipase | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.14-Endonuclease | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.15-Glucoamylase | 0,00% |
1.5.1.13 -BIOSTIMULANTS
| 1.5.1.13.1-Plant Biostimulants | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.1-Plant Hormones | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.1.1-Abscisic acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.1.2-Auixine | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.1.2.1-Indole 3 Acetic Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.1.2.1-Indole 3 Butyric Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.1.3-Cytokine | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.1.3.1-Kinetin N6 | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.1.3.1-Kinetin 9 riboside | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.1.4-Gibberellins | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.1.4.1-Gibberellic Acid GA3 | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.1.4.1-Gibberellic Acid GA4 | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.1.4.1-Gibberellic Acid GA7 | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.1.5-Ethylene | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.2-Plant Growth Regulators | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.2.1-Bransterroids | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.2.2-Strigo Lactone | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.2.3-S-Adeonosyl L-Methionine | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.2.4-Super oxide distumase | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.2.5-N-methyl transferase | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.2.6-Melatonin | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.2.7-NAD+ | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.2.8-Alguronic acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.2.9-Ulvabionic acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.2.10-Phosphocholine | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.2.11-Phosphobetaine | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.2.12-Gaba | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.2.13-Baba | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.2.14-B-Glucans | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.2.15-Chitin | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.2.16-Methyl jasmonate | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.2.17-Cerevasine | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.2.18-Elongation factors | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.2.19-Peptidoglycan | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.2.20-Type 3 Secreted effector | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.2.21-Calmadulin | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.2.22-Cerebroside A | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.2.23-Lysophosphatidyl ethanolamine | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.2.24-Small chain peptides | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.2.25-Pseudobactin | 0,00% |
2-ORO
3-TOT
4-DOCUMENTER
4.1-MSDS
4.1.1-MSDS Material Info
| Product Name | : SYNTHAMINE LP 12 ™ |
| Producer Name | : Fermo Crysta™ Fermantasyon Kristalleri Üretim Gıda San. Ve Tic. LTD. ŞTİ. |
| Saray Osmangazi Mahallesi Sarsılmaz Cad.No: 2/15 Pursaklar/ANKARA 0312 5143724 | |
| MILICARD NO | |
| CODEX NUMBER | |
| CAS NUMBER | : 74-79-3 |
Acil durum telefon numarası Ulusal Zehir Danışma Merkezi (UZEM):
114 CHEMTREC Turkey (Istanbul): +(90)-212-7055340
4.1.2-Hazard Identification
Toxicological Data on Ingredients: L-Arginine LD50: >5.110mg/kg. LC50: = Not available.
Potential Acute Health Effects: Slightly hazardous in case of skin contact, of eye contact (irritant), of ingestion, of inhalation.
Potential Chronic Health Effects: CARCINOGENIC EFFECTS: Not . MUTAGENIC EFFECTS: Mutagenic for mammalian somatic CELLS
TERATOGENIC EFFECTS: Not DEVELOPMENTAL TOXICITY: Not. Prolonged exposure is not known to aggravate medical condition.
GHS.Warning,Eye,Irritation,Category 2,H319,P305,P351,P338
4.1.3-First Aid Measurement
EyeContact: Check for and remove any contact lenses. In case of contact,immediately flush eyes with plenty of water for at least
15 minutes Cold water may be used. Get medical attention if irritation occurs.
Skin Contact: Wash with soap and water. Cover the irritated skin with an emollient. Get medical attention if irritation develops.
Cold water may be used.
Serious Skin Contact: Not available.
Inhalation: If inhaled, remove to fresh air. If not breathing, give artificial respiration. If breathing is difficult, give oxygen.
Serious Inhalation: Not available.
Ingestion: DoNOT induce vomiting unless directed to do so by medical personnel. Never give anything by mouth to an
unconscious person. If large quantities of this material are swallowed, call a physician immediately. Loosen tight clothing
such as a collar, tie,belt or waistband.
Serious Ingestion: Not available.
4.1.4-Fire And Explosion Data
Flammability of the Product: May be combustible at high temperature.
Auto-Ignition Temperature: Not available.
Flammable Limits: Not available.
Products of Combustion: These products are carbon oxides (CO, CO2), nitrogen oxides (NO, NO2…).
Fire Hazards in Presence of Various Substances: Slightly flammable to flammable in presence of heat. Non-flammable in
presence of shocks.
Explosion Hazards in Presence of Various Substances: Risks of explosion of the product in presence of mechanical impact: Not
Risks of explosion of the product in presence of static discharge: Not available.
Fire Fighting Media and Instructions: SMALL FIRE: Use DRY chemical powder. LARGE FIRE: Use water spray, fog or foam.
Do Not Use water jet.
Special Remarks on Fire Hazards: Not available.
Special Remarks on Explosion Hazards: Not available.
4.1.5-Accidental Release Measures
Small Spill: Use appropriate tools to put the spilled solid in a convenient waste disposal container.Finish cleaning by
spreading water on the contaminated surface and dispose of according to local and regional authority requirements.
Large Spill: Use a shovel to put the material into a convenient waste disposal container. Finish cleaning by spreading water
on the contaminated surface and allow to evacuate through the sanitary system.
4.1.6-Handling And Storage
Regulation (EU) No. 1907/2006 ( regulation on Safety Data Sheets for Hazardous Substances and Mixtures
(R.G 13.12.2014-29204) Preparation Date:12.09.2019 New Arrangemet Date:19.09.2020
Precautions: Keep locked up.. Keep away from heat. Keep away from sources of ignition. Empty containers pose a fire risk,
evaporate the residue under a fume hood. Ground all equipment containing material. Do not breathe dust. Wear suitable
protective clothing.
If you feel unwell, seek medical attention ,show thelabel when possible.Keepaway from incompatibles such as oxidizing agents.
Storage: Light sensitive. Store in light resistant containers. Keep container tightly closed. Keep container in a cool,
well-ventilated area.
Do not store above 24°C (75.2°F).
4.1.7- Exposure Controls/Personal Protection
Engineering Controls: Use process enclosures, local exhaust ventilation,other engineering controls to keep airborne levels
below recommended exposure limits.
If user operations generate dust, fume,mist, use ventilation to keep exposure to airborne contaminants below the exposure
limit.
Personal Protection: Safety glasses. Lab coat. Dust respirator. Be sure to use an approved/certified respirator or equivalent.
Gloves.
PersonalProtection in Case of a LargeSpill:Splash goggles.Full suit.Dust respirator. Boots. Gloves. A self contained breathing
apparatus should be used to avoid inhalation of the product. Suggested protective clothing might not be sufficient; consult a
specialist BEFORE handling this product.
Exposure Limits: Not available.
4.1.8-Physical and Chemical Properties
Physical state and appearance : Liquid
Chemical Formula : CnHnNnOnS
Odor : Odorless
Taste : Not availabe
Molecular Weight : 174.2 g/mol
Cas Number : 74-79-3
EC Number : 200-811-1
Melting Point : 223°C (433°F)
Color : Dark brown
Dispersion Properties : See solubility in water.
Solubility : Soluble in cold water, hot water. Insoluble in diethyl ether. Sparingly soluble in alcohol
4.1.9-Stability and Reactivity Data
Stability: The product is stable.
Instability Temperature: Not available.
Conditions of Instability: Excess heat, light
Incompatibility with various substances: Reactive with oxidizing agents.
Corrosivity: Non-corrosive in presence of glass.
Special Remarks on Reactivity: Light sensitive.
Special Remarks on Corrosivity: Not available.
Polymerization: Will not occur.
4.1.10-Toxicological Information
4.1.10.1-Acute toxicity
LD50 Oral – Rat – male and female – > 5.110 mg/kg Remarks: (ECHA)
Inhalation: No data available
Dermal: No data available
4.1.10.2-Skin corrosion/irritation
Skin – Rabbit
Result: No skin irritation – 4 h (OECD Test Guideline 404)
4.1.10.3-Serious eye damage/eye irritation
Eyes – Rabbit
Result: No eye irritation – 1 h (OECD Test Guideline 405)
4.1.10.4-Respiratory or skin sensitization
No data available
4.1.10.5-Germ cell mutagenicity
Test Type: Mutagenicity (mammal cell test): chromosome aberration. Test system: Human lymphocytes
Metabolic activation: with and without metabolic activation Method: OECD Test Guideline 473
Result: negative
Test Type: Ames test
Test system: Escherichia coli/Salmonella typhimurium Metabolic activation: with and without metabolic activation
Method: OECD Test Guideline 471 Result: negative
4.1.10.6-Carcinogenicity
No data available
4.1.10.7-Reproductive toxicity
No data available
4.1.10.8-Specific target organ toxicity – single exposure
No data available
4.1.10.9-Specific target organ toxicity – repeated exposure
No data available
4.1.10.10-Aspiration hazard
No data available
4.1.11-Ecological Information
Ecotoxicity: Not available.
BOD5 and COD: Not available.
ProductsofBiodegradation:Possibly hazardous shortterm degradation products are not likely.
However,longterm degradation products may arise.
Toxicity of the Products of Biodegradation: The product itself and its products of degradation are not toxic.
Special Remarks on the Products of Biodegradation: Not available.
The test results for acute toxicity of Synthamine LP 12 to fish were: LC50 = 2.8 g/L; LC 100 = 5.6 g/L;
NOEC (mortality) = 1.8 g/L; NOEC (condition) = 1.0 g/L.
4.1.12.-Disposal Considerations
Waste Disposal: Waste must be disposed of in accordance with federal, state and local environmental control regulations.
Identification: Not applicable.
4.1.13-Transpot Information
Land Transport(ADR/RID): According to transportation rules, it is not classified as dangerous goods.
Weather Transport(IATA): According to transportation rules, it is not classified as dangerous goods.
Sea Transport (IMDG): According to transportation rules, it is not classified as dangerous goods.
4.1.14-Regulatory Information
1907/2006 certificate for this product A chemical safety assesment in accordance with EU REACH Regulition
Storage class 10 – 13
EINECS: This product is on the European Inventory of Existing Commercial Chemical Substances.
DSCL (EEC): R40- Possible risks of irreversible effects. S2- Keep out of the reach of children.
S36/37- Wear suitable protective clothing and gloves.
Health Hazard: 1
Fire Hazard: 1
Reactivity: 0
Personal Protection: E
National Fire Protection Association (U.S.A.):
Health: 1
Flammability: 1
Reactivity: 0
Specific hazard:
Protective Equipment: Gloves. Lab coat. Dust respirator. Be sure to use an approved/certified respirator or equivalent.
4.1.15-Safe&Hazard Symbols
4.2-RISK REPORT
4.1.2-Toxıcology Study
Synthamine LP 12™ did not show effects on the reproductive organs in general repeated dose toxicity studies. Moreover, Synthamine LP12
is an amino acid that is required for normal functioning of to humans. The substance is of very low toxicological activity
and subject to homeostasis. Therefore, reprotoxic effects are not expected for Synthamine LP 12 and no test is required for this substance.
Furthermore, a QSAR for the endpoint reproductive toxicity predicts no toxicity to reproduction.
A significant amount of Synthamine LP12 is usually taken up via the food. In usual diet, most amino acids are suppied as constituents of
protein and not as tree amino acid. Protein intake clearly modifies plasma amino acid levels. However, aminoacid
concentrations are sunjects to homeostasis and the plasma concentrarions vary within fixed limits and are tightly regulated.
Several repeated dose toxicity studies consistently indicate the very low toxicity of Synthamine Lp12 Even in very high doses no
toxicity is observed and no adverse effects were reported for the reproductive organs.
There fore it is highly unlikely that L-arginine taken up via any use covered by this registration would result in systemic effects
insluding effects on unborn life.
4.2.2-ECHA.EU Europe
4.2.2.1-Toxicity
A limit test according to OECD 203 did not show any adverse effects to fish at a test concentration of 1 g/L L-arginine.
A subsequent test with L-arginine according to OECD 203 with higher test concentrations showed the following results:
LC50 = 2.8 g/L; LC 100 = 5.6 g/L; NOEC (mortality) = 1.8 g/L; NOEC (condition) = 1.0 g/L.
EC50 was found to be 1.8g/L,EC100 was found to be 5.6 g/L. EC50 for algae was calculated to be ca. 26857mg/L
NOEC(mobility)was estimated to be 1.0 g/L and NOEC (condition)was estimated to be <1.0g/L
L-arginine did not show toxicity to mikroorganisms. The EC10 after 16h was>10g/L
Considering the results from higher trophic levels as well as for microorganisms and an expert statement
(see endpoint summary in IUCLID section 6.1.5) toxicity testing with aquatic algae was not deemed necessary.
Fresh water fish :limit test according to OECD 203 did not show any adverse effects to fish at a test concentration of 1 g/L
Fresh water invertebrates:A limit test according to OECD 202 did not show any adverse effects to Daphnia magna at a test
concentration of 1 g/L L-arginine.
A subsequent test with L-arginine according to OECD 202 with higher test concentrations showed the following results:
EC50 = 1.8 g/L; EC100 = 5.6 g/L; NOEC (mobility) was estimated to be 1.0 g/L and NOEC (condition) was estimated to be < 1.0 g/L.
4.2.2.2-Irratıon-Corrosion
The instillation of L-arginine did not cause any changes at the rabbits eyes. The corneae, irises and conjunctivae were not affected
by instillation of the test item. L-arginine is classified as not-irritating to eyes.
4.2.2.3- Sensitation
There is no human or animal data that indicates L-arginine to be a skin sensitiser. Considering the extensive, widespread dermal
exposure to L-arginine in preparations repeatedly applied to the skin or being in contact with the skin, the absence of case reports
of humans showing skin reactions is consistent with L-arginine having a very low skin sensitisation potential.
4.2.2.4- Repeated dose toxicity
The mean human daily intake of arginine for all life stage and gender groups from food and supplements is approximately 4.2 g/d
(Food and Nutrition Board, 2005). A dietary dose of 5.0% L-arginine is equivalent to about 50 times amount of the mean daily
oral intake for humans.
4.2.2.5- Genetic Toxicity
In a GLP guideline study according to OECD 473 L-arginine did not induce a statistically significant increase in the
frequency of cellswith chromosome aberrations in either the absence or presence of a liver enzyme metabolising system in
either of two separate experiments. The maximum test concentration was 1740 µg/L. The test material was therefore considered
to be non-clastogenic to human lymphocytes in vitro.
4.2.2.6-Toxicity to Reproduction
L-arginine did not show effects on the reproductive organs in general repeated dose toxicity studies. Moreover, L-arginine
is an amino acid that is required for normal functioning of humans. The substance is of very low toxicological activity and
subject to homeostasis. Therefore, reprotoxic effects are not expected for L-arginine and no test is required for this
substance.
5-TEST STANDARTS&RESULTS
5.1-SPECTRAL ANALYSIS
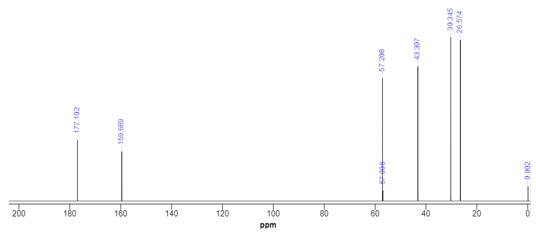
5.1.1- 1H NMR Spectra
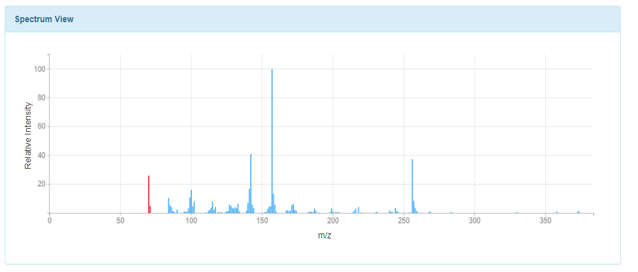
5.1.2- GC-MS Spektra
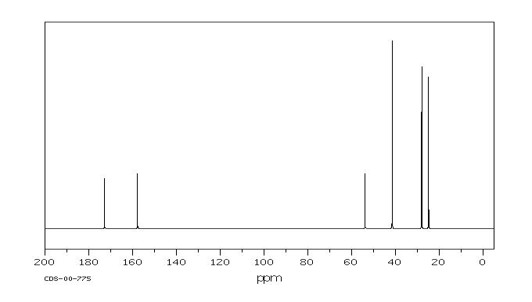
5.1.3- 13C NMR Spektra
6. APPLICATION/PLANT NUTRITION, FERTIGATION, HEALTH AND PESTS
6.2.1-Potato Application /Fertigation,Crop Protection
| 6.2.1.1-Turbo Spray | : Sprays 100-300 g /da |
| 6.2.1.2-Drip Irrıgation | : 1:1000 dilute |
| 6.2.1.3-30 days after planting | : 100 g/d |
| 6.2.1.4-45 days after planting | : 250 g/d |
| 6.2.1.5-90 days after planting | : 100 g/d |
| 6.2.1.6-Aerial Uses | : 200-400g/d |
| 6.2.1.7-Roat Soak | : 200-500 g/d |
| 6.2.1.8-Seed Treatment | : 3-5 g/kg of seed |
| 6.2.1.9-Alternaria diseaes | : 1 kg/ha |
| 6.2.1.10-Dry rot diseaes | : 220 g/d |
| 6.2.1.11-Potato Virus | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.1.12-Verticillium | : 60 g/d |
| 6.2.1.13-Skin Spot | : 80 g /d |
| 6.2.1.14-Powdery Scab | : 110 g/d |
| 6.2.1.15-Gangrene | : 190 g/d |
| 6.2.1.16-Viral and viroid diseaes | : 180 g/d |
| 6.2.1.17-Nematode parasitic | : 380 g/d |
| 6.2.1.18-Miscellaneous diseaes | : 35 g/d |
| 6.2.1.19-Bacterial soft rot | : 80 g/d |
| 6.2.1.20-Botrytis gray mold | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.1.21-Charcoal rot | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.1.22-Fusarium | : 700 g/d |
| 6.2.1.23-Pysyllid yellows | : 210 g/d |
| 6.2.1.24-Air pollution damage | : 130 g/d |
| 6.2.1.25-Fertilizer burn | : 108 g/d |
| 6.2.1.26-Freezing necros | : 190 g/d |
| 6.2.1.27-Hollow heart | : 33 g/d |
| 6.2.1.28-Lightning injury | : 78 g /d |
| 6.2.1.29-Second growth | : 90 g/d |
| 6.2.1.30-Greening | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.1.31-Xylem ring discoloration | : 260 g/d |
| 6.2.1.32-Tipburn | : 25 g/d |
| 6.2.1.33-Sunscald | : 106 g/d |
| 6.2.1.34-Stem streak necrosis | : 188 g/d |
| 6.2.1.35-Sprout tubers | : 102 g/d |
| 6.2.1.36-Spinding sprout | : 180 g/d |
| 6.2.1.37-Internal brown spot | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.1.38-Internal brown spot | : 112 g/d |
| 6.2.1.39-Heat and drought necrosis | : 190 g/d |
| 6.2.1.40-Feather and scald | : 110 g/d |
| 6.2.1.41-Enlarged lenticels | : 40 g/d |
| 6.2.1.42-Rootling | : 290 g/d |
| 6.2.1.43-Rootling | : 130 g/d |
| 6.2.1.44-Maturating | : 70 g/d |
| 6.2.1.45-Maturating | : 100 g/d |
| 6.2.1.46-Antifreezing and preventing cold stress | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.1.47Antifreezing and preventing cold stress | : 400 g/d |
6.2.2-Apple Application /Fertigation,Crop Protection
| 6.2.2.1-Apple Scab-the fungus Venturia inaequalis | : 230 g/d |
| 6.2.2.2-Alternaria leaf and fruit blotch | : 177 g/d |
| 6.2.2.3-Bitter rot | : 55 g/d |
| 6.2.2.4-Powdery mildew | : 102 g/d |
| 6.2.2.5-White root rot-Rosellinia necatrix | : 380 g/d |
| 6.2.2.6-Sclerotium collar root -Sclerotium spp | : 310 g/d |
| 6.2.2.7-Black rot canker | : 74 g/d |
| 6.2.2.8-Collar rot | : 192 g/d |
| 6.2.2.9-Apple virus diseaes | : 450 g/d |
| 6.2.2.10-Brown rot | : 214 g/d |
| 6.2.2.11-Seedling blight | : 190 g/d |
| 6.2.2.12-Fire blight | : 600 g/d |
| 6.2.2.13-Poor Fruiting | : 250-300 g/d |
| 6.2.2.14-Root Decay | : 80-120 g/d |
| 6.2.2.15-Grey-coloured crusty growth | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.2.16-Grey-coloured crusty growth | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.2.17-Bird Damage on Flowers | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.2.18-Waterlogging | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.2.19-Waterlogging | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.2.20-Calcium uptake | : 120-300 g/d |
| 6.2.2.21-Calcium uptake | : 120-300 g/d |
| 6.2.2.22-Poor growing conditions | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.2.23-Poor growing conditions | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.2.24-Unproductive trees | : 10 g/tree |
| 6.2.2.25-Pollinating Partner | : 80 g/d |
| 6.2.2.26-Mussel Scale | : 340 g/d |
| 6.2.2.27-Aphid Attack | : 280-370 g/d |
| 6.2.2.28-Caterpillars | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.2.29-Capsid Bugs | : 90 g/d |
| 6.2.2.30-Summer pruning | : 230 g/d |
| 6.2.2.31-Blossom wilt | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.2.32-Codling Moth | : 380 g/d |
| 6.2.2.33-Coral Spot | : 160 g/d |
| 6.2.2.34-Silver Leaf | : 100 g/d |
| 6.2.2.35-Flyspeck | : 170 g/d |
| 6.2.2.36-Low N requirement varieties | : 100-200 g/d |
| 6.2.2.37-Low N requirement varieties | : 100-200 g/d |
| 6.2.2.38-High N requirement varieties | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.2.39-High N requirement varieties | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.2.40-Vigor of Shoot Growth | : 240-300 g/d |
| 6.2.2.41-Fruit Size and firmness | : 80-120 g/d |
| 6.2.2.42-Terminal growth | : 230 g/d |
| 6.2.2.43-Leaf size growth | : 300-400 g/d |
| 6.2.2.44-Fruit setting | : 30-110 g/d |
| 6.2.2.45-Fruit setting and maturating | : 30-110 g/d |
| 6.2.2.46-Fruit maturity | : 180-270 g/d |
6.2.3
| 6.2.3.1-Growing Excessively Large Fruit | : 110-205 g/d |
| 6.2.3.2-Growing Excessively Large Fruit | : 110-205 g/d |
| 6.2.3.3-Encouraging Good pollination | : 50-90 g/d |
| 6.2.3.4-Encouraging Good pollination | : 50-90 g/d |
| 6.2.3.5-General Soil Application | : 500-700 g/d |
| 6.2.3.6-General Soil Application | : 500-700 g/d |
| 6.2.3.7-General Foliar Application | : 100-400 g/d |
| 6.2.3.8-General Foliar Application | : 100-400 g/d |
| 6.2.3.9-Pre-Bloom | : 20-60 g/d |
| 6.2.3.10-Pre-Bloom | : 20-60 g/d |
| 6.2.3.11-Post-Bloom | : 30-50 g/d |
| 6.2.3.12-Post-Bloom | : 30-50 g/d |
| 6.2.3.13-Plant Population 60-80 trees /d | : 200-500 g/d |
| 6.2.3.14-Plant Population 60-80 trees /d | : 200-500 g/d |
| 6.2.3.15-Plant Population 140-250 trees/d | : 400-600 g/d |
| 6.2.3.16-Plant Population 140-250 trees/d | : 400-600 g/d |
| 6.2.3.17-Spring to early summer | : 100-300 g/d |
| 6.2.3.18-Spring to early summer | : 100-300 g/d |
| 6.2.3.19-Post Harvest | : 200-250 g/d |
| 6.2.3.20-Post Harvest | : 200-250 g/d |
| 6.2.3.21-Antifreezing and preventing cold stress | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.3.22-Antifreezing and preventing cold stress | : 400 g/d |
6.2.4-Grape Application/ Fertigation
| 6.2.4.1-Soil pH near 6.5 | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.4.2-Soil pH near 6.5 | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.4.3-Soil pH 5.0-6.0 | : 300-500 g/d |
| 6.2.4.4-Soil pH 5.0-6.0 | : 300-500 g/d |
| 6.2.4.5-New plantings | : 100-180 g/d |
| 6.2.4.6-New plantings | : 100-180 g/d |
| 6.2.4.7-Coarse textured ,Acid Soil | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.4.8-Pre-Bloom,upper mature leaf/petiole | : 90-110 g/d |
| 6.2.4.9-Bloom and Fruiting ,leaf /petiole opposite cluster | : 170-220 g/d |
| 6.2.4.10-Fruit maturating | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.4.11-Sandy Soil | : 200-300 g/d |
| 6.2.4.12-Sandy Soil | : 200-300 g/d |
| 6.2.4.13-Beginning 2 weeks before bloom | : 30-60 g/d |
| 6.2.4.14-Beginning 2 weeks before bloom | : 30-60 g/d |
| 6.2.4.15-Root damage | : 250 g/d |
| 6.2.4.16-Bud Burst stage | : 40-70 g/d |
| 6.2.4.17-Bud Burst stage | : 40-70 g/d |
| 6.2.4.18-Early Shoot stage | : 70-110 g/d |
| 6.2.4.19-Early Shoot stage | : 70-110 g/d |
| 6.2.4.20-Mid Shoot stage | : 100 g/d |
| 6.2.4.21-Mid Shoot stage | : 100 g/d |
6.2.5
| 6.2.5.1-Post Harvest | : 90-200 g/d |
| 6.2.5.2-Post Harvest | : 90-200 g/d |
| 6.2.5.3-Downy Mildew | : 130-300 g/d |
| 6.2.5.4-Anthracnose | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.5.5-Grey Mold | : 230-290 g/d |
| 6.2.5.6-Viruses | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.5.7-Greenaria bitter rot | : 90-110 g/d |
| 6.2.5.8-Bacterial leaf spot | : 280 g/d |
| 6.2.5.9-Alternaria blight | : 200-300 g/d |
| 6.2.5.10-Black Rot | : 30-80 g/d |
| 6.2.5.11-Black Rot | : 30-80 g/d |
| 6.2.5.12-Rhizopus rot | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.5.13-Rhizopus rot | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.5.14-Botrytis bunch rot | : 230-290 g/d |
| 6.2.5.15-Color,size,taste improving | : 240-340 g/d |
| 6.2.5.16-Color,size,taste improving | : 240-340 g/d |
| 6.2.5.17-Chemical damage | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.5.18-Nutritional Imbalances | : 100-600 g/d |
| 6.2.5.19-Nutritional Imbalances | : 100-600 g/d |
| 6.2.5.20-Sanitation with biocide | : 20 g/10 L H2O |
| 6.2.5.21-Pruning | : 30 g/100 L H2O |
| 6.2.5.22-Boron deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.23-Boron deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.24-Calcium deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.25-Calcium deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.26-Copper deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.27-Copper deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.28-Iron deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.29-Iron deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.30-Magnesium deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.31-Magnesium deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.32-Manganase deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.33-Manganase deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.34-Zinc deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.35-Zinc deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.36-Antifreezing and preventing cold stress | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.5.37-Antifreezing and preventing cold stress | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.5.38-Flowering | : 60-90 g/d |
| 6.2.5.39-Fruit Set | : 100-240 g/d |
6.2.6-Corn Application /Crop Protection
| 6.2.6.1-Seed rots and seeding blights | : 100-200 g/d |
| 6.2.6.2-Stalk rots | : 120 g/d |
| 6.2.6.3-Ear rots | : 130-180 g/d |
| 6.2.6.4-Boil and Head smut | : 200-300 g/d |
| 6.2.6.5-Downy mildew | : 80-130 g/d |
| 6.2.6.6-Fusairum | : 240 g/d |
| 6.2.6.7-Virus | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.6.8-Blanking | : 100-120 g/d |
| 6.2.6.9-Blanking | : 100-120 g/d |
| 6.2.6.10-Boron deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.11-Boron deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.12-Calcium deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.13-Calcium deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.14-Copper deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.15-Copper deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.16-Iron deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.17-Iron deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.18-Magnesium deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.19-Magnesium deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.20-Manganase deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.21-Manganase deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.22-Zinc deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.23-Zinc deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.24-Uneven germination | : 100-300 g/d |
| 6.2.6.25-Uneven germination | : 100-300 g/d |
| 6.2.6.26-Aphid | : 800 g/d |
| 6.2.6.27-Cricket | : 600 g/d |
| 6.2.6.28-Cutworm | : 300-500 g/d |
| 6.2.6.29-Earwig | : 200-500 g/d |
| 6.2.6.30-Mite | : 300-700 g/d |
| 6.2.6.31-Heliothis | : 200-270 g/d |
| 6.2.6.32-Maize leafhopper | : 100-300 g/d |
| 6.2.6.33-Parasitoid wasps | : 100-230 g/d |
| 6.2.6.34-Flies | : 200-300 g/d |
| 6.2.6.35-Fungal Systemic diseaes | : 200-450 g/d |
| 6.2.6.36-Smutting diseaes | : 80-190 g/d |
| 6.2.6.37-Herbicide injury symptoms | : 160-210 g/d |
| 6.2.6.38-Trigger symptoms | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.6.39-Trigger symptoms | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.6.40-Nutrient defiency symptoms | : 40-400 g/d |
| 6.2.6.41-Nutrient defiency symptoms | : 40-400 g/d |
| 6.2.6.42-Leaf Diseaes | : 300-400 g/d |
| 6.2.6.43-Leaf Diseaes | : 300-400 g/d |
| 6.2.6.44-Unfavorable soil conditions | : 200-600 g/d |
| 6.2.6.45-Unfavorable soil conditions | : 200-600 g/d |
| 6.2.6.46-Poor Seed-soil contact | : 130-180 g/d |
| 6.2.6.47-Poor Seed-soil contact | : 130-180 g/d |
| 6.2.6.48-Fertilizer injury | : 220-260 g/d |
| 6.2.6.49-Fertilizer injury | : 220-260 g/d |
6.2.7
| 6.2.7.1-Seed planted to deep | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.7.2-Seed planted to deep | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.7.3-Bird and rodent damage | : 450 g/d |
| 6.2.7.4-Bird and rodent damage | : 450 g/d |
| 6.2.7.5-Insects attacking roots | : 340-380 g/d |
| 6.2.7.6-Insects attacking roots | : 340-380 g/d |
| 6.2.7.7-Nematodes | : 500 g/d |
| 6.2.7.8-Nematodes | : 500 g/d |
| 6.2.7.9-Non-uniform planting | : 200-600 g/d |
| 6.2.7.10-Non-uniform planting | : 200-600 g/d |
| 6.2.7.11-Failure of roots develop | : 300-460 g/d |
| 6.2.7.12-Failure of roots develop | : 300-460 g/d |
| 6.2.7.13-Wind damage | : 50-80 g/d |
| 6.2.7.14-Wind damage | : 50-80 g/d |
| 6.2.7.15-Freeze damage | : 100-120 g/d |
| 6.2.7.16-Freeze damage | : 100-120 g/d |
| 6.2.7.17-Antifreezing and preventing cold stress | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.7.18-Antifreezing and preventing cold stress | : 400 g/d |
6.2.8-Tomato Application/Crop Protection
| 6.2.8.1-Failure to set fruit,poor fruit set | : 120-340 g/d |
| 6.2.8.2-Failure to set fruit,poor fruit set | : 120-340 g/d |
| 6.2.8.3-Cold soil stress | : 40-70 g/d |
| 6.2.8.4-Cold soil stress | : 40-70 g/d |
| 6.2.8.5-Root initiatives | : 50-80 g/d |
| 6.2.8.6-Root initiatives | : 50-80 g/d |
| 6.2.8.7-Early blight | : 90-310 g/d |
| 6.2.8.8-Septoria leaf spot | : 60-100 g/d |
| 6.2.8.9-Bacterial spot and speck | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.8.10-Spider mites | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.8.11-Fusarium & Verticillium | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.8.12-Bacterial canker | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.8.13-Late blight | : 100 g/d |
| 6.2.8.14-Hornworms | : 130 g/d |
| 6.2.8.15-Root-Knot nematodes | : 180-240 g/d |
| 6.2.8.16-Gray Leaf Spot | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.8.17-Anthracnose | : 200-240 g/d |
| 6.2.8.18-Blossom end rot | : 50 g/d |
| 6.2.8.19-Buckeye rot | : 60-90 g/d |
| 6.2.8.20-Buckeye rot | : 60-90 g/d |
| 6.2.8.21-Botrytis Gray Mold | : 230-310 g/d |
| 6.2.8.22-Spotty Leaves | : 290-370 g/d |
| 6.2.8.23-Spotty Leaves | : 290-370 g/d |
| 6.2.8.24-Fixing Fruit | : 300-600 g/d |
| 6.2.8.25-Fixing Fruit | : 300-600 g/d |
6.2.9-Tomato Application/Crop Protection
| 6.2.9.1-Catfacing | : 100-300 g/d |
| 6.2.9.2-Catfacing | : 100-300 g/d |
| 6.2.9.3-Leaf Roll | : 120-340 g/d |
| 6.2.9.4-Leaf Roll | : 120-340 g/d |
| 6.2.9.5-Puffiness | : 80-130 g/d |
| 6.2.9.6-Puffiness | : 80-130 g/d |
| 6.2.9.7-Powdery Mildew | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.9.8-Cutworms | : 80-110 g/d |
| 6.2.9.9-Flea beetles | : 100-130 g/d |
| 6.2.9.10-Tuta Absoluta | : 200-700 g/d |
| 6.2.9.11-Whiteflies | : 100-190 g/d |
| 6.2.9.12-Parasitic plants | : 200-340 g/d |
| 6.2.9.13-Apical Stunt | : 300-500 g/d |
| 6.2.9.14-Hail Damage | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.9.15-Small holes in leaves of seedlings | : 30-50 g/d |
| 6.2.9.16-Small holes in leaves of seedlings | : 30-50 g/d |
| 6.2.9.17-Water-soaked spots on leaves | : 40-80 g/d |
| 6.2.9.18-Water-soaked spots on leaves | : 40-80 g/d |
| 6.2.9.19-Trails and tunnels in leaves | : 40-80 g/d |
| 6.2.9.20-Trails and tunnels in leaves | : 40-80 g/d |
| 6.2.9.21-Small to large holes in fruits | : 100-190 g/d |
| 6.2.9.22-Sunken water-soaked areas on fruit | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.9.23-Worm tunnels into fruit | : 190-230 g/d |
| 6.2.9.24-Fruit is distorted | : 40-90 g/d |
| 6.2.9.25-Fruit is distorted | : 40-90 g/d |
| 6.2.9.26-Psyllids | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.9.27-Roots discolored ,mushy | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.9.28-Roots discolored ,mushy | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.9.29-Ring spots on fruit | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.9.30-Uniforming fruit | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.9.31-Preplant,vegetative growth stage | : 100-400 g/d |
| 6.2.9.32-Preplant,vegetative growth stage | : 100-400 g/d |
| 6.2.9.33-Flowering&Fruit Set | : 80-120 g/d |
| 6.2.9.34-Flowering&Fruit Set | : 80-120 g/d |
| 6.2.9.35-Ripening&Maturity | : 80-140 g/d |
| 6.2.9.36-Ripening&Maturity | : 80-140 g/d |
| 6.2.9.37-Over-pruning | : 120 g/d |
| 6.2.9.38-Fruit cracks | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.9.39-Poor fruit set | : 400-450 g/d |
6.2.10-Cabbage Application/Fertigation
| 6.2.10.1-Adjusting the spacing | : 310-340 g/d |
| 6.2.10.2-Adjusting the spacing | : 310-340 g/d |
| 6.2.10.3-Pre-drilling | : 1000 g/d |
| 6.2.10.4-Pre-drilling | : 1000 g/d |
| 6.2.10.5-Transplanting | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.10.6-Transplanting | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.10.7-4-6 leaf stage | : 80-130 g/d |
| 6.2.10.8-4-6 leaf stage | : 80-130 g/d |
6.2.11
| 6.2.11.1-Cutworms | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.11.2-Cabbage worms | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.11.3-Root maggots | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.11.4-Flea Beetles | : 100-400 g/d |
| 6.2.11.5-Aphids | : 100-200 g/d |
| 6.2.11.6-Slugs and Snails | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.11.7-Damping off seedlings | : 100 g/d |
| 6.2.11.8-Clubroot | : 80-100 g/d |
| 6.2.11.9-Caterpillars | : 230 g/d |
| 6.2.11.10-Downy mildew | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.11.11-Sclerotinia rot | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.11.12-Tipburn | : 100-180 g/d |
| 6.2.11.13-Seedlings fail to emerge from soil | : 200-300 g/d |
| 6.2.11.14-Young sprouts fail to grow | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.11.15-Young plants flower | : 300 g/ d |
| 6.2.11.16-Small holes in leaves | : 200-500 g/d |
| 6.2.11.17-Leaves are pitted | : 100-220 g/d |
| 6.2.11.18-Root nematodes | : 200-300 g/d |
| 6.2.11.19-Bacterial Soft rot | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.11.20-Blackleg | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.11.21-White rust | : 120-220 g/d |
| 6.2.11.22-Yellow patches | : 300-550 g/d |
| 6.2.11.23-Turnip mosaic | : 80-130 g/d |
| 6.2.11.24-Cracking of heads | : 200-290 g/d |
| 6.2.11.25-Cracking of heads | : 200-290 g/d |
| 6.2.11.26-Poor heading | : 120-180 g/d |
| 6.2.11.27-Poor heading | : 120-180 g/d |
| 6.2.11.28-Discolored heads | : 130-180 g/d |
| 6.2.11.29-Discolored heads | : 130-180 g/d |
| 6.2.11.30-V-shaped lesions on leaf margin | : 60-80 g/d |
| 6.2.11.31-V-shaped lesions on leaf margin | : 60-80 g/d |
| 6.2.11.32-Heads soft and rotted | : 90-140 g/d |
| 6.2.11.33-Heads soft and rotted | : 90-140 g/d |
| 6.2.11.34-Bolting | : 200-280 g/d |
| 6.2.11.35-Bolting | : 200-280 g/d |
| 6.2.11.36-Curled leaves | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.11.37-Rough leaves | : 300-450 g/d |
| 6.2.11.38-Rough leaves | : 300-450 g/d |
| 6.2.11.39-Poorly developed roots | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.11.40-Poorly developed roots | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.11.41-Wind damage | : 50-80 g/d |
| 6.2.11.42-Wind damage | : 50-80 g/d |
| 6.2.11.43-Freeze damage | : 100-120 g/d |
| 6.2.11.44-Freeze damage | : 100-120 g/d |
| 6.2.11.45-Antifreezing and preventing cold stress | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.11.46-Antifreezing and preventing cold stress | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.11.47-Breaking the cycle-stage | : 230-290 g/d |
| 6.2.11.48-Breaking the cycle-stage | : 230-290 g/d |
| 6.2.11.49-Vegetative stage | : 120-150 g/d |
| 6.2.11.50-Vegetative stage | : 120-150 g/d |
| 6.2.11.51-Head development | : 100-130 g/d |
| 6.2.11.52-Head development | : 100-130 g/d |
6.2.12-Watermelon Application /Crop Protection
| 6.2.12.1-Bacterial Fruit Blotch | : 100-300 g/d |
| 6.2.12.2-Gummy Stem Blight | : 450 g/d |
| 6.2.12.3-Anthracnose | : 200-280 g/d |
| 6.2.12.4-Alternaria | : 300-400 g/d |
| 6.2.12.5-Cercospora | : 130-190 g/d |
| 6.2.12.6-Myrothecium Leaf Spot | : 300-500 g/d |
| 6.2.12.7-Leaf Mosaic | : 220-280 g/d |
| 6.2.12.8-Tobacco ring spot | : 130-160 g/d |
| 6.2.12.9-Squash Leaf Curl Virus | : 300-450 g/d |
| 6.2.12.10-Fusarium | : 90-170 g/d |
| 6.2.12.11-Bud necrosis | : 300-400 g/d |
| 6.2.12.12-Phytopthora | : 200-340 g/d |
| 6.2.12.13-Root Knot nematodes | : 300-500 g/d |
| 6.2.12.14-Rotting seeds | : 200g/d |
| 6.2.12.15-Stunted growth | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.12.16-Stunted growth | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.12.17-Blossom end-rot | : 200-300 g/d |
| 6.2.12.18-Blossom end-rot | : 200-300 g/d |
| 6.2.12.19-Internal Cracking | : 120-270 g/d |
| 6.2.12.20-Internal Cracking | : 120-270 g/d |
| 6.2.12.21-Spongy end | : 180-220 g/d |
| 6.2.12.22-Spongy end | : 180-220 g/d |
| 6.2.12.23-Sunburn | : 200-270 g/d |
| 6.2.12.24-Sunburn | : 200-270 g/d |
| 6.2.12.25-Thrips | : 300-500 g/d |
| 6.2.12.26-Flea Beetles | : 100-170 g/d |
| 6.2.12.27-Beet armyworms | : 500 g/d |
| 6.2.12.28-Grasshoppers | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.12.29-Melon Aphids | : 500-600 g/d |
| 6.2.12.30-Silverleaf Whiteflies | : 200-250 g/d |
| 6.2.12.31-Mole crickets | : 180-230 g/d |
| 6.2.12.32-White grubs | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.12.33-Germination | : 300-400 g/d |
| 6.2.12.34-Germination | : 300-400 g/d |
| 6.2.12.35-Vining | : 100-400 g/d |
| 6.2.12.36-Vining | : 100-400 g/d |
| 6.2.12.37-Flowering | : 40-120 g/d |
| 6.2.12.38-Flowering | : 40-120 g/d |
| 6.2.12.39-Fruiting | : 80-140 g/d |
| 6.2.12.40-Fruiting | : 80-140 g/d |
