Seavital 4000 p
1-IDENTIFIER
1.1-Description
1.1.1-Description
SeaVital 4000 as a Seaweed extracts (SEs) are a kind of biostimulant extracted from seaweed (especially green&brown algae)
that can promote crop growth, improve crop quality, and enhance crop stress resistance SeaVital 2000 have been widely
used as biostimulants in crop management due to their growth-promoting and stress-resistant effects.
1.1.2-Names
Seavital 4000 p™
1.1.3-Supplier
SEAWEAN ™ Makroalg ve marin bitkileri özütleri GM
Saray osmangazi mahallesi sarsılmaz caddesi no :2 daire 6 Pursaklar Ankara
0-312 5143724 www.seawean.com
1.2-IDENTIFY NUMBERS
1.2.1 -Milicard number : 868182336-02508
1.2.2 -EA Codex number : 8681823363200
1.2.3 -Cas number :
1.2.4 -EC number :
1.2.5 -Permit License number :
1.2.6 -Patent and License number :
1.3-STRUCTURE
1.3.1-Powder form

1.3.2-Liquid form

1.3.3
1.3.4-Granul form

1.4-CERTIFICATE OF ANALYSIS AND TDS
| 1.4.1-CHEMICAL FORMULA | : CHNOSPK | |||
| 1.4.2-TYPE/STATE/FORM | : Powder, Flake | |||
| 1.4.3-COLOUR | : Black | |||
| 1.4.4-ODOUR | : Characteristic Marine | |||
| 1.4.5-TASTE | : Marine | |||
| 1.4.6-PARTICLE SIZE | : 200 mesh | |||
| 1.4.7-DENSITY | : 1.22 g/L. Bulk: 640 kg/m³ | |||
| 1.4.8-MELTING POINT | : Avarage 145 °C | |||
| 1.4.9-BOILING POINT | : Not available | |||
| 1.4.10-FLASH POINT | : Not available | |||
| 1.4.11-VAPOUR PRESSURE | : < 0.1 hPa nin 25 °C | |||
| 1.4.12-VISCOSITY | : A8-1.26 gm | |||
| 1.4.13-REFRACTIVE IDEX | : Not available | |||
| 1.4.14-IGNITION TEMPURATURE | : Not available | |||
| 1.4.15-DISSOCIATION CONSTANTS | : pK1= 5.18; pK2= 9.09; pK3= 13.2 | |||
| 1.4.16-SOLUBILITY | : 225 g/L H2O at 25 °C | |||
| 1.4.17-pH VALUE | : 8.90 (100 g/L H2O at 20 °C) | |||
| 1.4.18-ACIDITY pKa | : 12.488 | |||
| 1.4.19-Log P | : -1.652 | |||
| 1.4.20-CHIRAL ROTATION | : +25 to 26 ° | |||
| 1.4.21-MOLAR MASS | : 174.2 g/mol | |||
| 1.4.22-PURIFY | : % 97.75 | |||
| 1.4.22.1-CARRIER | : Not available. | |||
| 1.4.23-METALS | : Chloride <%0.02, OG_Sulphate <%0.01, Heavy Metals <%0.0001, Arsenic <%0.00001 | |||
| 1.4.24-LD 50 ORAL RAT | : >6700 mg/Kg | |||
| 1.4.25-GHS | : H315 (%14.52): Causes skin irritation [Warning Skin corrosion/irritation] | |||
H319 (%99.6): Causes serious eye irritation [Warning Serious eye damage/eye irritation]
| 1.4.26-WGK | : None | ||
| 1.4.27-OTHER DETAILS | : Not available | ||
1.5-CONTENT PROPERTIES
| 1.5.1.1-DRY MATTER | 100% |
| 1.5.1.1.1-ORGANIC MATTER | 59,20% |
| 1.5.1.1.2-TOTAL MINERALS | 40,31% |
| 1.5.1.2-H20 or HUMIDITY | 0,49% |
| 1.5.1.3-TOTAL AMINO ACIDS | 7,86% |
| 1.5.1.4-FREE AMINO ACIDS | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.5-POLY,OLIGO,MONO SACCHARIDE | 18,45% |
| 1.5.1.5.1-TOTAL POLYSACCHARIDES | 12,45% |
| 1.5.1.5.1.1-ALGINIC ACID | 2,00% |
| 1.5.1.5.1.2-ALGURONIC ACID | 0,45% |
| 1.5.1.5.1.3-SULFATED POLYSACCHARIDES | 8,00% |
| 1.5.1.6-LIPID&FATTY ACID | 1,54% |
| 1.5.1.7-POLYPHENOL,FLAVONOID | 19,33% |
| 1.5.1.8-ORGANIC ACID | 4,00% |
| 1.5.1.9-NUCLEOTIDES | 0,10% |
| 1.5.1.10-POLYOLS | 5,98% |
| 1.5.1.11-VITAMIN | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.14-BIOACTIVE AND MOLECULES | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.15-BIOSTIMULANT & ELICITORS | 0,59% |
| 1.5.1.16-ANTIBIOSIS,METABOLITES | 1,35% |
| 1.5.1.30-TOTAL MINERAL | |
| 1.5.1.30-Total Minerals | 40,31% |
| 1.5.30.1-TOTAL NITROGEN | 2,00% |
| 1.5.30.1.1-CHEMICAL NITROGEN | 0,00% |
| 1.5.30.1.2-ORGANIC NITROGEN | 2,00% |
| 1.5.30.2-PHOSPHATE TOTAL | 4,00% |
| 1.5.30.2.1-P2O5 | 0,33% |
| 1.5.30.2.2-ORGANIC PHOSPHATE | 1,67% |
| 1.5.30.3-POTASSIUM | 16,00% |
| 1.5.30.4-SULFUR TOTAL | 8,00% |
| 1.5.30.4.1-CHEMICAL SULFUR | 5,30% |
| 1.5.30.4.2-ORGANIC SULFUR | 2,70% |
| 1.5.30.5-MAGNESIUM | 1,70% |
| 1.5.30.6-CALCIUM | 2,20% |
| 1.5.30.7-ZINC | 0,65% |
| 1.5.30.8-FERROUS | 0,14% |
| 1.5.30.9-MANGANASE | 1,05% |
| 1.5.30.10-COPPER | 0,32% |
| 1.5.30.11-CHLORE | 0,17% |
| 1.5.30.12-BORON | 0,00% |
| 1.5.30.13-COBALT | 0,04% |
| 1.5.30.14-SELENIUM | 0,02% |
| 1.5.30.15-VANADIUM | 0,02% |
| 1.5.30.16-SODIUM | 4,00% |
| 1.5.1.3-TOTAL AMINO ACID | |
| 1.5.1.3-AMINO ACID-Total | 7,86% |
| 1.5.1.3.1-L-ALANINE | 0,65% |
| 1.5.1.3.2-L-ARGININE | 0,83% |
| 1.5.1.3.3-L-ASPARAGINE | 0,03% |
| 1.5.1.3.4-L-ASPARTIC ACID | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.3.5-L-CYSTEINE | 0,44% |
| 1.5.1.3.6-L-GLUTAMIC ACID | 0,90% |
| 1.5.1.3.7-L-GLUTAMINE | 0,01% |
| 1.5.1.3.8-GLYCINE | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.3.9-L-HISTIDINE | 0,32% |
| 1.5.1.3.10-L-ISOLEUCINE | 0,15% |
| 1.5.1.3.11-L-LEUCINE | 0,34% |
| 1.5.1.3.12-L-LYSINE | 0,55% |
| 1.5.1.3.13-L-METHIONINE | 0,09% |
| 1.5.1.3.14-L-PHENYALANINE | 0,77% |
| 1.5.1.3.15-L-PROLINE | 0,95% |
| 1.5.1.3.16-L-SERINE | 0,67% |
| 1.5.1.3.17-L-THREONINE | 0,24% |
| 1.5.1.3.18-L-TRYPTOPHAN | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.3.19-L-TYROSINE | 0,14% |
| 1.5.1.3.20-L-VALINE | 0,78% |
| 1.5.1.4-FREE AMINO ACID | |
| 1.5.1.4-AMINO ACID-Free | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.4.1-L-ALANINE | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.4.2-L-ARGININE | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.4.3-L-ASPARAGINE | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.4.4-L-ASPARTIC ACID | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.4.5-L-CYSTEINE | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.4.6-L-GLUTAMIC ACID | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.4.7-L-GLUTAMINE | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.4.8-GLYCINE | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.4.9-L-HISTIDINE | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.4.10-L-ISOLEUCINE | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.4.11-L-LEUCINE | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.4.12-L-LYSINE | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.4.13-L-METHIONINE | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.4.14-L-PHENYALANINE | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.4.15-L-PROLINE | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.4.16-L-SERINE | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.4.17-L-THREONINE | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.4.18-L-TRYPTOPHAN | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.4.19-L-TYROSINE | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.4.20-L-VALINE | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.5- POLYSACCHARIDE CONTENT | |
| 1.5.1.5.1-Total Poly-Oligo-Mono Saccharides | 18,45% |
| 1.5.1.5.1.1-Total Polysaccharides | 12,45% |
| 1.5.1.5.1.1.1-Alginic Acid | 2,00% |
| 1.5.1.5.1.1.2-Alguronic Acid | 0,45% |
| 1.5.1.5.1.1.3-Sulfated Poylsaccharides ,Ulvans | 8,00% |
| 1.5.1.5.1.1.4-Other Polysaccharides | 2,00% |
| 1.5.1.5.1.2-Total Oligosaccharides | 2,00% |
| 1.5.1.5.1.3-Total Monosaccharides | 4,00% |
| 1.5.1.6- FATTY ACID LIPID AND STEROLS | |
| 1.5.16-Total fatty acid,lipid,sterols | 1,54% |
| 1.5.1.6.1-Total Fatty Acid | 1,14% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.1-Alpha Linolenic Acid | 0,04% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.2-Arachidic Acid | 0,03% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.3-Arachidonic Acid | 0,01% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.4-Behenic Acid | 0,02% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.5-Caproic Acid | 0,01% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.6-Caprylic Acid | 0,02% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.7-Capric Acid | 0,02% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.8-Docosadienoic Acid | 0,03% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.9-Docosahexaenoic Acid | 0,03% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.10-Docosapentaenoic Acid | 0,03% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.11-Eicosadienoic Acid | 0,03% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.12-Eicosenic Acid | 0,03% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.13-Eicosapentaenoic Acid | 0,03% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.14-Eicosatrienoic Acid | 0,03% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.15-Elaidic Acid | 0,03% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.16-Erucic Acid | 0,03% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.17-Gamma Linelonic Acid | 0,03% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.18-Heneicosanoic Acid | 0,03% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.19-Heptanoic Acid | 0,03% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.20-Homo-gamma-Linelenic Acid | 0,03% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.21-Lauric Acid | 0,03% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.22-Ligneceric Acid | 0,03% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.23-Linoleic Acid | 0,03% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.24-Linolelaidic Acid | 0,03% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.25-Margaric Acid | 0,03% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.26-Margaroleic Acid | 0,03% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.27-Myristic Acid | 0,03% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.28-Myristoleic Acid | 0,03% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.29-Nervonic Acid | 0,03% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.30-Nonadecanoic Acid | 0,03% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.31-Nonanoic Acid | 0,03% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.32-Palmitic Acid | 0,03% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.33-Palmitoleic Acid | 0,03% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.34-Pentadecanoic Acid | 0,03% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.35-Oleic Acid | 0,03% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.36-Stearic Acid | 0,03% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.37-Tricosanoic Acid | 0,03% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.38-Tridecanoic Acid | 0,03% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.39-Vaccenic Acid | 0,03% |
| 1.5.1.6.1.40-Undecanoic Acid | 0,03% |
| 1.5.1.6.2-Total Lipids | 0,22% |
| 1.5.1.6.2.1-Phospholipids | 0,02% |
| 1.5.1.6.2.2-Glyceropholipids | 0,02% |
| 1.5.1.6.2.3-Betainelipids | 0,02% |
| 1.5.1.6.2.4-Galactolipids | 0,02% |
| 1.5.1.6.2.5-Sulpholipids | 0,02% |
| 1.5.1.6.2.6-Glycolipids | 0,02% |
| 1.5.1.6.2.7-Chlorolipids | 0,02% |
| 1.5.1.6.2.8-Long chain alkene | 0,02% |
| 1.5.1.6.2.9-Trigalactosyldiacylglycerol | 0,02% |
| 1.5.1.6.2.10-Mannose Glycolipid | 0,02% |
| 1.5.1.6.2.11-Rhamnose Glycolipid | 0,02% |
| 1.5.1.6.3-Total Sterols | 0,18% |
| 1.5.1.6.3.1-Clionasterol | 0,02% |
| 1.5.1.6.3.2-Clerosterol | 0,02% |
| 1.5.1.6.3.3-Fucosterol | 0,02% |
| 1.5.1.6.3.4-B-Sitosterol | 0,02% |
| 1.5.1.6.3.5-Cholesterol | 0,02% |
| 1.5.1.6.3.6-Brassinolide | 0,02% |
| 1.5.3.1.3.7-Stigmasterol | 0,02% |
| 1.5.3.1.3.8-Ergosterol | 0,02% |
| 1.5.3.1.3.9-Metylenecholesterol | 0,02% |
| 1.5.1.7 -POLYPHENOL,FLAVONOID AND PIGMENTS | |
| 1.5.1.7-Total Polyphenol,flavonoid,pigments | 19,33% |
| 1.5.1.7.1-Total Polyphenols | 6,64% |
| 1.5.1.7.1.1-Phenolic acid | 2,00% |
| 1.5.1.7.1.2-Coumaric acid | 0,33% |
| 1.5.1.7.1.3-Caffeic acid | 0,40% |
| 1.5.1.7.1.4-Benzoic acid | 0,50% |
| 1.5.1.7.1.5-Cinnamic | 0,34% |
| 1.5.1.7.1.6-Phenylpropanoic acid | 0,29% |
| 1.5.1.7.1.7-Curcuminoids | 0,31% |
| 1.5.1.7.1.8-Hydroxybenzoketones | 0,11% |
| 1.5.1.7.1.9-Methoxyphenols | 0,70% |
| 1.5.1.7.1.10-Hydroxyphenlypropenes | 0,32% |
| 1.5.1.7.1.11-Tyrosols | 0,90% |
| 1.5.1.7.1.12-Naphtoquinones | 0,21% |
| 1.5.1.7.1.13-Phenolic terpenes | 0,23% |
| 1.5.1.7.2-Total Flavonoid | 2,65% |
| 1.5.1.7.2.1-Anthocyanins | 0,23% |
| 1.5.1.7.2.2-Chalcones | 0,54% |
| 1.5.1.7.2.3-Flavanols | 0,89% |
| 1.5.1.7.2.4-Flavanones | 0,55% |
| 1.5.1.7.2.5-Isaflavonoids | 0,44% |
| 1.5.1.7.3-Total Pigments | 3,04% |
| 1.5.1.7.3.1-Chlororophyll-a | 0,13% |
| 1.5.1.7.3.2-Chlororophyll-b | 0,19% |
| 1.5.1.7.3.3-Trans-B-carotene | 0,08% |
| 1.5.1.7.3.4-Cis-B-carotene | 0,04% |
| 1.5.1.7.3.5-Allophycocyanin | 0,17% |
| 1.5.1.7.3.6-Fucoxanthin | 0,77% |
| 1.5.1.7.3.7-Astaxhantin | 0,32% |
| 1.5.1.7.3..8-Violaxanthin | 0,29% |
| 1.5.1.7.3.9-Zeaxanthin | 0,21% |
| 1.5.1.7.3.10-Tocopherol | 0,11% |
| 1.5.1.7.3.11-Cantaxanthin | 0,19% |
| 1.5.1.7.3.12-Phycocyanin | 0,33% |
| 1.5.1.7.3.13-B-phycoerythrobilin | 0,21% |
| 1.5.1.7.4-Total Stilbenes | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.7.5-Total Lignans | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.7.6-Total Isoprene,terpenes | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.7.7-Total Lignin | 2,00% |
| 1.5.1.7.8-Total Humic acid | 3,00% |
| 1.5.1.7.9-Total Fulvic acid | 2,00% |
| 1.5.1.8 -ORGANIC ACIDS | |
| 1.5.1.8-Total Organic Acid | 4,00% |
| 1.5.1.8.1-Acetic Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.8.2-Lactic Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.8.3-Propionic Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.8.4-Butyric Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.8.5-Succinic acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.8.6-Malic acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.8.7-Tartaric acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.8.8-Glycolic acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.8.9-Alpha hydroxy acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.8.10-Citric acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.8.11.Gluconic acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.8.12-Uronic acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.8.12-Pyruvic acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.9 -NUCLEOBASES | |
| 1.5.1.9-Total Nucleobases | 0,10% |
| 1.5.1.9.1-Adenine | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.9.2-Guanine | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.9.3-Cytosine | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.9.4-Thymine | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.9.5-Uracil | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.9.6-Inosine | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.9.7-3’5’AMP | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.9.10-3’5’GMP | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.9.11-3’5’IMP | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.9.12-cGMP | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.9.13-ATP | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.9.14-Xhantine | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.9.15-Methylguanine | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.10 -POLYOLS | |
| 1.5.1.10-Total Polyols | 5,98% |
| 1.5.1.10.1-Mannitol | 2,70% |
| 1.5.1.10.2-Sorbitol | 0,65% |
| 1.5.1.10.3-Galactitol | 0,20% |
| 1.5.1.10.4-Eryththiotol | 0,11% |
| 1.5.1.10.5-Glycerol | 0,80% |
| 1.5.1.10.6-Ethylen glycol | 0,15% |
| 1.5.1.10.7-Inositol | 0,37% |
| 1.5.1.10.8-Xylitol | 0,10% |
| 1.5.1.10.9-Maltitol | 0,10% |
| 1.5.1.10.10-Lactitol | 0,10% |
| 1.5.1.10.11-Maltitol | 0,10% |
| 1.5.1.10.12-Ribitol | 0,10% |
| 1.5.1.10.13-Fucitol | 0,10% |
| 1.5.1.10.14-Isomalt | 0,10% |
| 1.5.1.10.15-Iditol | 0,10% |
| 1.5.1.10.16-Volemitol | 0,10% |
| 1.5.1.10.17-Polyglycitol | 0,10% |
| 1.5.1.11 -VITAMIN | |
| 1.5.1.11-Total Vitamins | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.1-Vitamin A | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.2-Vitamin B1 Thiamine | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.3-Vitamin B2-Riboflavin | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.4-Vitamin B3-Niacinamide | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.5-Vitamin B5-Pantothenic acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.6-Vitamin B6 Pyridoxine | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.7-Vitamin B7 -Biotin | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.8-Vitamin B9-Folic Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.9-Vitamin B12-Cyanocobalamin | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.10-Vitamin B14-Inosine | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.11-Ascorbic Acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.12-Vitamin D2 | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.13-Vitamin D3 | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.14-Vitamin K | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.15-Vitamin E | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.15-Vitamin Pc | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.16-Vitamin Pb | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.12 -BIOACTIVE AND BIOMOLECULE | |
| 1.5.1.12-Total Bioactive and biomolecules | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.1-Coenzyme | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.2-Cofactor | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.3-Metabolic enyzmes | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.4-Signalling molecules | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.5-Apoenzymes | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.6-Isoenzymes | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.7-Enzymes,industrial | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.7.1-Endoprotease | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.7.2-Endopeptidase | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.7.3-Serine protease | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.7.4-Cysteine protease | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.7.5-Alpha Amylase | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.7.6-Exopeptidase | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.7.7-Arabanase | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.7.8-Cellulase | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.9-B-Glucanase | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.10-Hemi-cellulase | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.11-Xylanase | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.12-Cellobiose | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.13-Lipase | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.14-Endonuclease | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.11.15-Glucoamylase | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13 -BIOSTIMULANTS | |
| 1.5.1.13-Total biostimulants | 0,59% |
| 1.5.1.13.1-Plant Biostimulants | 0,59% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.1-Plant Hormones | 0,59% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.1.1-Abscisic acid | 0,03% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.1.2-Auixine | 0,06% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.1.2.1-Indole 3 Acetic Acid | 0,05% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.1.2.1-Indole 3 Butyric Acid | 0,01% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.1.3-Cytokine | 0,12% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.1.3.1-Kinetin N6 | 0,05% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.1.3.1-Kinetin 9 riboside | 0,05% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.1.4-Gibberellins | 0,15% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.1.4.1-Gibberellic Acid GA3 | 0,02% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.1.4.1-Gibberellic Acid GA4 | 0,02% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.1.4.1-Gibberellic Acid GA7 | 0,02% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.1.5-Ethylene | 0,01% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.2-Plant Growth Regulators | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.2.1-Bransterroids | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.2.2-Strigo Lactone | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.2.3-S-Adeonosyl L-Methionine | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.2.4-Super oxide distumase | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.2.5-N-methyl transferase | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.2.6-Melatonin | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.2.7-NAD+ | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.2.8-Alguronic acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.2.9-Ulvabionic acid | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.2.10-Phosphocholine | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.2.11-Phosphobetaine | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.2.12-Gaba | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.2.13-Baba | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.2.14-B-Glucans | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.2.15-Chitin | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.2.16-Methyl jasmonate | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.2.17-Cerevasine | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.2.18-Elongation factors | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.2.19-Peptidoglycan | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.2.20-Type 3 Secreted effector | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.2.21-Calmadulin | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.2.22-Cerebroside A | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.2.23-Lysophosphatidyl ethanolamine | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.2.24-Small chain peptides | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.13.1.2.25-Pseudobactin | 0,00% |
| 1.5.1.16-ANTIBIOSIS, METABOLITES | 1,35% |
2-ORO
3-TOT
4-DOCUMENTER
4.1-MSDS
4.1.1-MSDS Material Info
| Product Name | : SEAVITAL 4000p ™ |
| Producer Name | : SEAWEAN ™ Makroalg ve marin bitkileri özütleri GM Saray osmangazi mahallesi sarsılmaz caddesi no :2 daire 6 Pursaklar Ankara 0-312-5143724 |
| MILICARD NO | : 868182336-02508 |
| CODEX NUMBER | : 8681823363200 |
| CAS NUMBER |
Acil durum telefon numarası Ulusal Zehir Danışma Merkezi (UZEM):
114 CHEMTREC Turkey (Istanbul): +(90)-212-7055340
4.1.2-Hazard Identification
Emergency overview
KEEP OUT OF REACH OF CHILDREN.
Potential sensitizer.
Avoid contact with the skin, eyes and clothing
Avoid inhalation of dusts/mists/vapours
Wash thoroughly after handling
Potential health effects
Acute toxicity:
Virtually nontoxic after a single ingestion. Virtually nontoxic by inhalation. Virtually nontoxic after a single skin contact
Irritation / corrosion :Not irritating to the skin. Not irritating to the eyes.
Sensitization:There is no evidence of a skin-sensitizing potential
Carcinogenicity: The product has not been tested. The statement has been derived from the properties of the
individual components. The results of various animal studies gave no indication of a carcinogenic effect.
Repeated dose toxicity: The product has not been tested. The statement has been derived from the properties
of the individual components. No substance-specific organtoxicity was observed after repeated administration to animals.
Reproductive toxicity: The product has not been tested. The statement has been derived from the properties
of the individual components. The results of animal studies gave no indication of a fertility impairing effect
Teratogenicity: The product has not been tested. The statement has been derived from the properties of the
individual components. Animal studies gave no indication of a developmental toxic effect at doses that were not
toxic to the parental animals.
Genotoxicity: The product has not been tested. The statement has been derived from the properties of the individual
components. Mutagenicity tests revealed no genotoxic potential.
Signs and symptoms of overexposure:No significant reaction of the human body to the product known.
Potential environmental effects
Aquatic toxicity:There is a high probability that the product is not acutely harmful to aquatic organisms
Degradation / environmental fate:
The product has not been tested. The statement has been derived from the properties of the individual components.
Colourants are by their nature very stable and are therefore not readily biodegradable under conditions prevailing
in surface water or in effluent treatment plants.
Bioaccumulation / bioconcentration:The Product has not been tested
Special Remarks on Fire Hazards: Not available.
Special Remarks on Explosion Hazards: Not available.
4.1.3-Accidental Release Measures
General Advice :Remove contaminated clothing
If Inhaled :Keep Patient Calm,remove to fresh air,seek medical attention.
If on skin :was thoroughly with soap and water
If in eyes :Wash affected eyes for at least 15 minutes under running water with eyelids held open
If swallowed :Immediately rinse mouth and then drink 200-300 ml of water, seek medical attention
Not to physician :Treat according to symptoms (decontamination, vital functions), no known specific antidote
EyeContact: Check for and remove any contact lenses. In case of contact,immediately flush eyes with plenty of water for at least
15 minutes Cold water may be used. Get medical attention if irritation occurs.
Skin Contact: Wash with soap and water. Cover the irritated skin with an emollient. Get medical attention if irritation develops.
Cold water may be used.
Serious Skin Contact: Not available.
Inhalation: If inhaled, remove to fresh air. If not breathing, give artificial respiration. If breathing is difficult, give oxygen.
Serious Inhalation: Not available.
Ingestion: DoNOT induce vomiting unless directed to do so by medical personnel. Never give anything by mouth to an
unconscious person. If large quantities of this material are swallowed, call a physician immediately. Loosen tight clothing
such as a collar, tie,belt or waistband.
Serious Ingestion: Not available.
Engineering Controls: Use process enclosures, local exhaust ventilation,other engineering controls to keep airborne levels
below recommended exposure limits.
If user operations generate dust, fume,mist, use ventilation to keep exposure to airborne contaminants below the exposure
limit.
Personal Protection: Safety glasses. Lab coat. Dust respirator. Be sure to use an approved/certified respirator or equivalent.
Gloves.
PersonalProtection in Case of a LargeSpill:Splash goggles.Full suit.Dust respirator. Boots. Gloves. A self contained breathing
apparatus should be used to avoid inhalation of the product. Suggested protective clothing might not be sufficient; consult a
specialist BEFORE handling this product.
Exposure Limits: Not available.
4.1.4-Fire And Explosion Data
Flash Point: Not applicable
Lower Explosion Limit :As a result of our experience with this product and our knowledge of its composition
we do not expect any hazard as long as the ,product is used appropriately and in accordance with the intended use
Upper Explosion Limit :As a result of our experience with this product and our knowledge of its composition
we do not expect any hazard as long as the ,product is used appropriately and in accordance with the intended use
Flammability:Not applicable
Suitable extinguishing media:water spray, dry powder, foam, carbon dioxide
Hazards during fire-fighting:carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides
The substances/groups of substances mentioned can be released in case of fire
Protective equipment for fire-fighting:Wear self-contained breathing apparatus and chemical-protective clothing.
Further Info:Keep containers cool by spraying with water if exposed to fire. In case of fire and/or explosion do not breathe
fumes. Collect contaminated extinguishing water separately, do not allow to reach sewage or effluent systems.
Dispose of fire debris and contaminated extinguishing water in accordance with official regulations.
4.1.5-Accidental Release Measures
Personal precautions:Do not breathe vapour/spray.Use personal protective clothing.Avoid contact with the skin,eyes and clothing.
Environmental precautions:Do not discharge into the subsoil/soil. Do not discharge into drains/surface waters/groundwater.
Cleanup:Dispose of absorbed material in accordance with regulations. Collect waste in suitable containers, which can be
labeled and sealed.Clean contaminated floors and objects thoroughly with water and detergents,observing enviromental
regulations.For small amounts: Pick up with suitable absorbent material (e.g. sand, sawdust, general-purpose binder,
For large amounts: Dike spillage. Pump off product.
4.1.6-Handling And Storage
Handling
General Advice :
No special measures necessary if stored and handled correctly. Ensure thorough ventilation of stores and work areas.
When using do not eat, drink or smoke. Hands and/or face should be washed before breaks and at the end of shit.
Protection against fire and explosion :
No special precautions necessary. The substance/product is non-combustible. Product is not explosive
Storage
General Advice :Keep away from heat. Protect from direct sunlight.
4.1.7- Exposure Controls/Personal Protection
Personel Protective Equipment
Respiratory protection :Wear respiratory protection if ventilation is inadequate. Wear a NIOSH-certified (or equivalent) TC23C
Chemical/Mechanical type filter system to remove a combination of particles, gas and vapours. For situations where
the airborne concentrations may exceed the level for which an air purifying respirator is effective, or where the levels are
unknown or Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health (IDLH), use NIOSH-certified full facepiece pressure demand self contained
breathing apparatus (SCBA) or a full facepiece pressure demand supplied-air respirator (SAR) with escape provisions.
Eye protection:Safety glasses with side-shields. Tightly fitting safety goggles (chemical goggles). Wear face shield if splashing
hazard exists.
Body protection :Body protection must be chosen depending on activity and possible exposure, e.g. head protection, apron,
protective boots, chemical-protection suit.
General safety and hygiene measures:Handle in accordance with good industrial hygiene and safety practice.Wearing of closed
work clothing is recommended. Store work clothing separately. Keep away from food, drink and animal feeding stuff
4.1.8-Physical and Chemical Properties
| Form | :FLAKE | |||
| Odour | :CHARACTERISTIC MARINE | |||
| Colour | : DARK BLACK | |||
| pH Value | :8.5 | |||
| Density | : Not available | |||
| Melting Point | : Not available | |||
| Solubility in Water | : Disperse soluble | |||
| Vapour Density | : Not available | |||
| Viscosity | : Not available | |||
| Boiling Point | : Not available | |||
| Vapour Pressure | : Not available | |||
4.1.9-Stability and Reactivity Data
Conditions to avoid :See MSDS section – Handling and storage.
Substances to avoid:strong acids, strong bases, strong oxidizing agents
Hazardous reactions:No hazardous reactions if stored and handled as prescribed/indicated
Decomposition products:Hazardous decomposition products: No hazardous decomposition products if stored and handled as
prescribed/indicated.
Thermal decomposition :No decomposition if stored and handled as prescribed/indicated.
Oxidizing properties:Based on its structural properties the product is not classified as oxidizing.
4.1.10-Toxicological Information
4.1.10.1-Acute toxicity
No data available
4.1.10.2-Skin corrosion/irritation
No data available
4.1.10.3-Serious eye damage/eye irritation
No data available
4.1.10.4-Respiratory or skin sensitization
No data available
4.1.10.5-Germ cell mutagenicity
No data available
4.1.10.6-Carcinogenicity
No data available
4.1.10.7-Reproductive toxicity
No data available
4.1.10.8-Specific target organ toxicity – single exposure
No data available
4.1.10.9-Specific target organ toxicity – repeated exposure
No data available
4.1.10.10-Aspiration hazard
No data available
4.1.10.11- Additional Information
To the best of our knowledge, the chemical, physical, and toxicological properties have not been thoroughly investigated.
4.1.11-Ecological Information
4.1.11.1-Fish
Not available
4.1.11.2-Aquatic invertebrates
Not available
4.1.11.3-Aquatic plants
Not available
4.1.11.4-Biodegradation :Significant accumulation in organisms is not to be expected.
Not available
4.1.11.5-Bioaccumulation :Significant accumulation in organisms is not to be expected.
Not available
4.1.12.-Disposal Considerations
Waste disposal of substance:
See product label for disposal and recycling instructions
Container disposal:
Rinse the container or liner as needed for disposal. Add rinsate to spray tank. Recommend crushing, puncturing
or other means to prevent unauthorized use of used containers. Consult the product label for additional details
4.1.13-Transpot Information
Land transport-TDG
Not classified as a dangerous good under transport regulations
Sea transport IMDG
Not classified as a dangerous good under transport regulations
Air transport IATA
Not classified as a dangerous good under transport regulations
4.1.14-Regulatory Information
Registration status
Chemical DSL, CA blocked / not listed
Crop Protection DSL, CA released / exemp
WHMIS does not apply to this product
THIS PRODUCT HAS BEEN CLASSIFIED IN ACCORDANCE WITH THE HAZARD CRITERIA OF THE CPR AND THE MSDS CONTAINS
ALL THE INFORMATION REQUIRED BY THE CPR.
4.1.15-Safe&Hazard Symbols

5-TEST STANDARTS&RESULTS
5.1-SPECTRAL ANALYSIS
5.1.1- Alginic Acid Analysis Protocols& Test Methods
5.1.1.1-Alginic Acid- Refractive Index Detector (RID) HPLC Methods Protocol MCC 12.04.5009
Standart Solutions
Individual standard stock solutions were obtained by dissolving 10 mg in 10 ml NaOH 0.10 M for Alginic acid and ultrapure
water for SEAWEED, Mannitol and glycerol to a final concentration of 1000 mg/l. The intermediate solutions were prepared
by diluting the stock solution in ultrapure water to obtain concentrations of 5,10,25,50,100,200 mg/l and 50 mg/l of glycerol
5.1.2- Polyol Analysis Protocols& Test Methods
5.1.2.1-Mannitol-Refractive Index Detector (RID) HPLC Methods Protocol MCC 10.04.4053
5.1.2.2-Sorbitol-Refractive Index Detector (RID) HPLC Methods Protocol MCC 10.04.9021
Standart Solutions
Individual standard stock solutions were obtained by dissolving 10 mg in 10 ml NaOH 0.10 M for Alginic acid and ultrapure
water for SEAWEED, Mannitol and glycerol to a final concentration of 1000 mg/l. The intermediate solutions were prepared
by diluting the stock solution in ultrapure water to obtain concentrations of 5,10,25,50,100,200 mg/l and 50 mg/l of glycerol
5.1.3- Fatty Acid Analysis Protocols& Test Methods
5.1.3.1-Fatty Acid Refractive Index Detector (RID) HPLC Methods Protocol MCC 10.04.4053
Standart Solutions
Milicard Serial Standarts ,Protocol MCC 09.101.20.009 DHA Spectral ,Hexane Volumetric Flask,Methyl Undecanoate,
1,2,3-triundecanoylglycerol,methyl 4,7,10,13,16,19-docosahexaenoate,methyl octadecenoate, methyl hexadecanoate
6. APPLICATION/PLANT NUTRITION, FERTIGATION, HEALTH AND PESTS
6.1
6.2
6.2.1-Potato Application /Fertigation,Crop Protection
| 6.2.1.1-Turbo Spray | : Sprays 100-300 g /da |
| 6.2.1.2-Drip Irrıgation | : 1:1000 dilute |
| 6.2.1.3-30 days after planting | : 100 g/d |
| 6.2.1.4-45 days after planting | : 250 g/d |
| 6.2.1.5-90 days after planting | : 100 g/d |
| 6.2.1.6-Aerial Uses | : 200-400g/d |
| 6.2.1.7-Roat Soak | : 200-500 g/d |
| 6.2.1.8-Seed Treatment | : 3-5 g/kg of seed |
| 6.2.1.9-Alternaria diseaes | : 1 kg/ha |
| 6.2.1.10-Dry rot diseaes | : 220 g/d |
| 6.2.1.11-Potato Virus | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.1.12-Verticillium | : 60 g/d |
| 6.2.1.13-Skin Spot | : 80 g /d |
| 6.2.1.14-Powdery Scab | : 110 g/d |
| 6.2.1.15-Gangrene | : 190 g/d |
| 6.2.1.16-Viral and viroid diseaes | : 180 g/d |
| 6.2.1.17-Nematode parasitic | : 380 g/d |
| 6.2.1.18-Miscellaneous diseaes | : 35 g/d |
| 6.2.1.19-Bacterial soft rot | : 80 g/d |
| 6.2.1.20-Botrytis gray mold | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.1.21-Charcoal rot | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.1.22-Fusarium | : 700 g/d |
| 6.2.1.23-Pysyllid yellows | : 210 g/d |
| 6.2.1.24-Air pollution damage | : 130 g/d |
| 6.2.1.25-Fertilizer burn | : 108 g/d |
| 6.2.1.26-Freezing necros | : 190 g/d |
| 6.2.1.27-Hollow heart | : 33 g/d |
| 6.2.1.28-Lightning injury | : 78 g /d |
| 6.2.1.29-Second growth | : 90 g/d |
| 6.2.1.30-Greening | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.1.31-Xylem ring discoloration | : 260 g/d |
| 6.2.1.32-Tipburn | : 25 g/d |
| 6.2.1.33-Sunscald | : 106 g/d |
| 6.2.1.34-Stem streak necrosis | : 188 g/d |
| 6.2.1.35-Sprout tubers | : 102 g/d |
| 6.2.1.36-Spinding sprout | : 180 g/d |
| 6.2.1.37-Internal brown spot | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.1.38-Internal brown spot | : 112 g/d |
| 6.2.1.39-Heat and drought necrosis | : 190 g/d |
| 6.2.1.40-Feather and scald | : 110 g/d |
| 6.2.1.41-Enlarged lenticels | : 40 g/d |
| 6.2.1.42-Rootling | : 290 g/d |
| 6.2.1.43-Rootling | : 130 g/d |
| 6.2.1.44-Maturating | : 70 g/d |
| 6.2.1.45-Maturating | : 100 g/d |
| 6.2.1.46-Antifreezing and preventing cold stress | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.1.47Antifreezing and preventing cold stress | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.2-Apple Application /Fertigation,Crop Protection | |
| 6.2.2.1-Apple Scab-the fungus Venturia inaequalis | : 230 g/d |
| 6.2.2.2-Alternaria leaf and fruit blotch | : 177 g/d |
| 6.2.2.3-Bitter rot | : 55 g/d |
| 6.2.2.4-Powdery mildew | : 102 g/d |
| 6.2.2.5-White root rot-Rosellinia necatrix | : 380 g/d |
| 6.2.2.6-Sclerotium collar root -Sclerotium spp | : 310 g/d |
| 6.2.2.7-Black rot canker | : 74 g/d |
| 6.2.2.8-Collar rot | : 192 g/d |
| 6.2.2.9-Apple virus diseaes | : 450 g/d |
| 6.2.2.10-Brown rot | : 214 g/d |
| 6.2.2.11-Seedling blight | : 190 g/d |
| 6.2.2.12-Fire blight | : 600 g/d |
| 6.2.2.13-Poor Fruiting | : 250-300 g/d |
| 6.2.2.14-Root Decay | : 80-120 g/d |
| 6.2.2.15-Grey-coloured crusty growth | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.2.16-Grey-coloured crusty growth | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.2.17-Bird Damage on Flowers | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.2.18-Waterlogging | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.2.19-Waterlogging | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.2.20-Calcium uptake | : 120-300 g/d |
| 6.2.2.21-Calcium uptake | : 120-300 g/d |
| 6.2.2.22-Poor growing conditions | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.2.23-Poor growing conditions | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.2.24-Unproductive trees | : 10 g/tree |
| 6.2.2.25-Pollinating Partner | : 80 g/d |
| 6.2.2.26-Mussel Scale | : 340 g/d |
| 6.2.2.27-Aphid Attack | : 280-370 g/d |
| 6.2.2.28-Caterpillars | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.2.29-Capsid Bugs | : 90 g/d |
| 6.2.2.30-Summer pruning | : 230 g/d |
| 6.2.2.31-Blossom wilt | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.2.32-Codling Moth | : 380 g/d |
| 6.2.2.33-Coral Spot | : 160 g/d |
| 6.2.2.34-Silver Leaf | : 100 g/d |
| 6.2.2.35-Flyspeck | : 170 g/d |
| 6.2.2.36-Low N requirement varieties | : 100-200 g/d |
| 6.2.2.37-Low N requirement varieties | : 100-200 g/d |
| 6.2.2.38-High N requirement varieties | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.2.39-High N requirement varieties | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.2.40-Vigor of Shoot Growth | : 240-300 g/d |
| 6.2.2.41-Fruit Size and firmness | : 80-120 g/d |
| 6.2.2.42-Terminal growth | : 230 g/d |
| 6.2.2.43-Leaf size growth | : 300-400 g/d |
| 6.2.2.44-Fruit setting | : 30-110 g/d |
| 6.2.2.45-Fruit setting and maturating | : 30-110 g/d |
| 6.2.2.46-Fruit maturity | : 180-270 g/d |
| 6.2.3.1-Growing Excessively Large Fruit | : 110-205 g/d |
| 6.2.3.2-Growing Excessively Large Fruit | : 110-205 g/d |
| 6.2.3.3-Encouraging Good pollination | : 50-90 g/d |
| 6.2.3.4-Encouraging Good pollination | : 50-90 g/d |
| 6.2.3.5-General Soil Application | : 500-700 g/d |
| 6.2.3.6-General Soil Application | : 500-700 g/d |
| 6.2.3.7-General Foliar Application | : 100-400 g/d |
| 6.2.3.8-General Foliar Application | : 100-400 g/d |
| 6.2.3.9-Pre-Bloom | : 20-60 g/d |
| 6.2.3.10-Pre-Bloom | : 20-60 g/d |
| 6.2.3.11-Post-Bloom | : 30-50 g/d |
| 6.2.3.12-Post-Bloom | : 30-50 g/d |
| 6.2.3.13-Plant Population 60-80 trees /d | : 200-500 g/d |
| 6.2.3.14-Plant Population 60-80 trees /d | : 200-500 g/d |
| 6.2.3.15-Plant Population 140-250 trees/d | : 400-600 g/d |
| 6.2.3.16-Plant Population 140-250 trees/d | : 400-600 g/d |
| 6.2.3.17-Spring to early summer | : 100-300 g/d |
| 6.2.3.18-Spring to early summer | : 100-300 g/d |
| 6.2.3.19-Post Harvest | : 200-250 g/d |
| 6.2.3.20-Post Harvest | : 200-250 g/d |
| 6.2.3.21-Antifreezing and preventing cold stress | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.3.22-Antifreezing and preventing cold stress | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.4-Grape Application/ Fertigation | |
| 6.2.4.1-Soil pH near 6.5 | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.4.2-Soil pH near 6.5 | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.4.3-Soil pH 5.0-6.0 | : 300-500 g/d |
| 6.2.4.4-Soil pH 5.0-6.0 | : 300-500 g/d |
| 6.2.4.5-New plantings | : 100-180 g/d |
| 6.2.4.6-New plantings | : 100-180 g/d |
| 6.2.4.7-Coarse textured ,Acid Soil | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.4.8-Pre-Bloom,upper mature leaf/petiole | : 90-110 g/d |
| 6.2.4.9-Bloom and Fruiting ,leaf /petiole opposite cluster | : 170-220 g/d |
| 6.2.4.10-Fruit maturating | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.4.11-Sandy Soil | : 200-300 g/d |
| 6.2.4.12-Sandy Soil | : 200-300 g/d |
| 6.2.4.13-Beginning 2 weeks before bloom | : 30-60 g/d |
| 6.2.4.14-Beginning 2 weeks before bloom | : 30-60 g/d |
| 6.2.4.15-Root damage | : 250 g/d |
| 6.2.4.16-Bud Burst stage | : 40-70 g/d |
| 6.2.4.17-Bud Burst stage | : 40-70 g/d |
| 6.2.4.18-Early Shoot stage | : 70-110 g/d |
| 6.2.4.19-Early Shoot stage | : 70-110 g/d |
| 6.2.4.20-Mid Shoot stage | : 100 g/d |
| 6.2.4.21-Mid Shoot stage | : 100 g/d |
| 6.2.5.1-Post Harvest | : 90-200 g/d |
| 6.2.5.2-Post Harvest | : 90-200 g/d |
| 6.2.5.3-Downy Mildew | : 130-300 g/d |
| 6.2.5.4-Anthracnose | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.5.5-Grey Mold | : 230-290 g/d |
| 6.2.5.6-Viruses | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.5.7-Greenaria bitter rot | : 90-110 g/d |
| 6.2.5.8-Bacterial leaf spot | : 280 g/d |
| 6.2.5.9-Alternaria blight | : 200-300 g/d |
| 6.2.5.10-Black Rot | : 30-80 g/d |
| 6.2.5.11-Black Rot | : 30-80 g/d |
| 6.2.5.12-Rhizopus rot | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.5.13-Rhizopus rot | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.5.14-Botrytis bunch rot | : 230-290 g/d |
| 6.2.5.15-Color,size,taste improving | : 240-340 g/d |
| 6.2.5.16-Color,size,taste improving | : 240-340 g/d |
| 6.2.5.17-Chemical damage | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.5.18-Nutritional Imbalances | : 100-600 g/d |
| 6.2.5.19-Nutritional Imbalances | : 100-600 g/d |
| 6.2.5.20-Sanitation with biocide | : 20 g/10 L H2O |
| 6.2.5.21-Pruning | : 30 g/100 L H2O |
| 6.2.5.22-Boron deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.23-Boron deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.24-Calcium deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.25-Calcium deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.26-Copper deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.27-Copper deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.28-Iron deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.29-Iron deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.30-Magnesium deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.31-Magnesium deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.32-Manganase deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.33-Manganase deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.34-Zinc deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.35-Zinc deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.36-Antifreezing and preventing cold stress | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.5.37-Antifreezing and preventing cold stress | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.5.38-Flowering | : 60-90 g/d |
| 6.2.5.39-Fruit Set | : 100-240 g/d |
| 6.2.6-Corn Application /Crop Protection | |
| 6.2.6.1-Seed rots and seeding blights | : 100-200 g/d |
| 6.2.6.2-Stalk rots | : 120 g/d |
| 6.2.6.3-Ear rots | : 130-180 g/d |
| 6.2.6.4-Boil and Head smut | : 200-300 g/d |
| 6.2.6.5-Downy mildew | : 80-130 g/d |
| 6.2.6.6-Fusairum | : 240 g/d |
| 6.2.6.7-Virus | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.6.8-Blanking | : 100-120 g/d |
| 6.2.6.9-Blanking | : 100-120 g/d |
| 6.2.6.10-Boron deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.11-Boron deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.12-Calcium deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.13-Calcium deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.14-Copper deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.15-Copper deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.16-Iron deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.17-Iron deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.18-Magnesium deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.19-Magnesium deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.20-Manganase deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.21-Manganase deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.22-Zinc deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.23-Zinc deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.24-Uneven germination | : 100-300 g/d |
| 6.2.6.25-Uneven germination | : 100-300 g/d |
| 6.2.6.26-Aphid | : 800 g/d |
| 6.2.6.27-Cricket | : 600 g/d |
| 6.2.6.28-Cutworm | : 300-500 g/d |
| 6.2.6.29-Earwig | : 200-500 g/d |
| 6.2.6.30-Mite | : 300-700 g/d |
| 6.2.6.31-Heliothis | : 200-270 g/d |
| 6.2.6.32-Maize leafhopper | : 100-300 g/d |
| 6.2.6.33-Parasitoid wasps | : 100-230 g/d |
| 6.2.6.34-Flies | : 200-300 g/d |
| 6.2.6.35-Fungal Systemic diseaes | : 200-450 g/d |
| 6.2.6.36-Smutting diseaes | : 80-190 g/d |
| 6.2.6.37-Herbicide injury symptoms | : 160-210 g/d |
| 6.2.6.38-Trigger symptoms | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.6.39-Trigger symptoms | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.6.40-Nutrient defiency symptoms | : 40-400 g/d |
| 6.2.6.41-Nutrient defiency symptoms | : 40-400 g/d |
| 6.2.6.42-Leaf Diseaes | : 300-400 g/d |
| 6.2.6.43-Leaf Diseaes | : 300-400 g/d |
| 6.2.6.44-Unfavorable soil conditions | : 200-600 g/d |
| 6.2.6.45-Unfavorable soil conditions | : 200-600 g/d |
| 6.2.6.46-Poor Seed-soil contact | : 130-180 g/d |
| 6.2.6.47-Poor Seed-soil contact | : 130-180 g/d |
| 6.2.6.48-Fertilizer injury | : 220-260 g/d |
| 6.2.6.49-Fertilizer injury | : 220-260 g/d |
| 6.2.7.1-Seed planted to deep | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.7.2-Seed planted to deep | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.7.3-Bird and rodent damage | : 450 g/d |
| 6.2.7.4-Bird and rodent damage | : 450 g/d |
| 6.2.7.5-Insects attacking roots | : 340-380 g/d |
| 6.2.7.6-Insects attacking roots | : 340-380 g/d |
| 6.2.7.7-Nematodes | : 500 g/d |
| 6.2.7.8-Nematodes | : 500 g/d |
| 6.2.7.9-Non-uniform planting | : 200-600 g/d |
| 6.2.7.10-Non-uniform planting | : 200-600 g/d |
| 6.2.7.11-Failure of roots develop | : 300-460 g/d |
| 6.2.7.12-Failure of roots develop | : 300-460 g/d |
| 6.2.7.13-Wind damage | : 50-80 g/d |
| 6.2.7.14-Wind damage | : 50-80 g/d |
| 6.2.7.15-Freeze damage | : 100-120 g/d |
| 6.2.7.16-Freeze damage | : 100-120 g/d |
| 6.2.7.17-Antifreezing and preventing cold stress | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.7.18-Antifreezing and preventing cold stress | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.8-Tomato Application/Crop Protection | |
| 6.2.8.1-Failure to set fruit,poor fruit set | : 120-340 g/d |
| 6.2.8.2-Failure to set fruit,poor fruit set | : 120-340 g/d |
| 6.2.8.3-Cold soil stress | : 40-70 g/d |
| 6.2.8.4-Cold soil stress | : 40-70 g/d |
| 6.2.8.5-Root initiatives | : 50-80 g/d |
| 6.2.8.6-Root initiatives | : 50-80 g/d |
| 6.2.8.7-Early blight | : 90-310 g/d |
| 6.2.8.8-Septoria leaf spot | : 60-100 g/d |
| 6.2.8.9-Bacterial spot and speck | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.8.10-Spider mites | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.8.11-Fusarium & Verticillium | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.8.12-Bacterial canker | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.8.13-Late blight | : 100 g/d |
| 6.2.8.14-Hornworms | : 130 g/d |
| 6.2.8.15-Root-Knot nematodes | : 180-240 g/d |
| 6.2.8.16-Gray Leaf Spot | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.8.17-Anthracnose | : 200-240 g/d |
| 6.2.8.18-Blossom end rot | : 50 g/d |
| 6.2.8.19-Buckeye rot | : 60-90 g/d |
| 6.2.8.20-Buckeye rot | : 60-90 g/d |
| 6.2.8.21-Botrytis Gray Mold | : 230-310 g/d |
| 6.2.8.22-Spotty Leaves | : 290-370 g/d |
| 6.2.8.23-Spotty Leaves | : 290-370 g/d |
| 6.2.8.24-Fixing Fruit | : 300-600 g/d |
| 6.2.8.25-Fixing Fruit | : 300-600 g/d |
| 6.2.9-Tomato Application/Crop Protection | |
| 6.2.9.1-Catfacing | : 100-300 g/d |
| 6.2.9.2-Catfacing | : 100-300 g/d |
| 6.2.9.3-Leaf Roll | : 120-340 g/d |
| 6.2.9.4-Leaf Roll | : 120-340 g/d |
| 6.2.9.5-Puffiness | : 80-130 g/d |
| 6.2.9.6-Puffiness | : 80-130 g/d |
| 6.2.9.7-Powdery Mildew | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.9.8-Cutworms | : 80-110 g/d |
| 6.2.9.9-Flea beetles | : 100-130 g/d |
| 6.2.9.10-Tuta Absoluta | : 200-700 g/d |
| 6.2.9.11-Whiteflies | : 100-190 g/d |
| 6.2.9.12-Parasitic plants | : 200-340 g/d |
| 6.2.9.13-Apical Stunt | : 300-500 g/d |
| 6.2.9.14-Hail Damage | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.9.15-Small holes in leaves of seedlings | : 30-50 g/d |
| 6.2.9.16-Small holes in leaves of seedlings | : 30-50 g/d |
| 6.2.9.17-Water-soaked spots on leaves | : 40-80 g/d |
| 6.2.9.18-Water-soaked spots on leaves | : 40-80 g/d |
| 6.2.9.19-Trails and tunnels in leaves | : 40-80 g/d |
| 6.2.9.20-Trails and tunnels in leaves | : 40-80 g/d |
| 6.2.9.21-Small to large holes in fruits | : 100-190 g/d |
| 6.2.9.22-Sunken water-soaked areas on fruit | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.9.23-Worm tunnels into fruit | : 190-230 g/d |
| 6.2.9.24-Fruit is distorted | : 40-90 g/d |
| 6.2.9.25-Fruit is distorted | : 40-90 g/d |
| 6.2.9.26-Psyllids | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.9.27-Roots discolored ,mushy | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.9.28-Roots discolored ,mushy | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.9.29-Ring spots on fruit | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.9.30-Uniforming fruit | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.9.31-Preplant,vegetative growth stage | : 100-400 g/d |
| 6.2.9.32-Preplant,vegetative growth stage | : 100-400 g/d |
| 6.2.9.33-Flowering&Fruit Set | : 80-120 g/d |
| 6.2.9.34-Flowering&Fruit Set | : 80-120 g/d |
| 6.2.9.35-Ripening&Maturity | : 80-140 g/d |
| 6.2.9.36-Ripening&Maturity | : 80-140 g/d |
| 6.2.9.37-Over-pruning | : 120 g/d |
| 6.2.9.38-Fruit cracks | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.9.39-Poor fruit set | : 400-450 g/d |
| 6.2.10-Cabbage Application/Fertigation | |
| 6.2.10.1-Adjusting the spacing | : 310-340 g/d |
| 6.2.10.2-Adjusting the spacing | : 310-340 g/d |
| 6.2.10.3-Pre-drilling | : 1000 g/d |
| 6.2.10.4-Pre-drilling | : 1000 g/d |
| 6.2.10.5-Transplanting | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.10.6-Transplanting | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.10.7-4-6 leaf stage | : 80-130 g/d |
| 6.2.10.8-4-6 leaf stage | : 80-130 g/d |
| 6.2.11.1-Cutworms | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.11.2-Cabbage worms | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.11.3-Root maggots | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.11.4-Flea Beetles | : 100-400 g/d |
| 6.2.11.5-Aphids | : 100-200 g/d |
| 6.2.11.6-Slugs and Snails | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.11.7-Damping off seedlings | : 100 g/d |
| 6.2.11.8-Clubroot | : 80-100 g/d |
| 6.2.11.9-Caterpillars | : 230 g/d |
| 6.2.11.10-Downy mildew | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.11.11-Sclerotinia rot | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.11.12-Tipburn | : 100-180 g/d |
| 6.2.11.13-Seedlings fail to emerge from soil | : 200-300 g/d |
| 6.2.11.14-Young sprouts fail to grow | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.11.15-Young plants flower | : 300 g/ d |
| 6.2.11.16-Small holes in leaves | : 200-500 g/d |
| 6.2.11.17-Leaves are pitted | : 100-220 g/d |
| 6.2.11.18-Root nematodes | : 200-300 g/d |
| 6.2.11.19-Bacterial Soft rot | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.11.20-Blackleg | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.11.21-White rust | : 120-220 g/d |
| 6.2.11.22-Yellow patches | : 300-550 g/d |
| 6.2.11.23-Turnip mosaic | : 80-130 g/d |
| 6.2.11.24-Cracking of heads | : 200-290 g/d |
| 6.2.11.25-Cracking of heads | : 200-290 g/d |
| 6.2.11.26-Poor heading | : 120-180 g/d |
| 6.2.11.27-Poor heading | : 120-180 g/d |
| 6.2.11.28-Discolored heads | : 130-180 g/d |
| 6.2.11.29-Discolored heads | : 130-180 g/d |
| 6.2.11.30-V-shaped lesions on leaf margin | : 60-80 g/d |
| 6.2.11.31-V-shaped lesions on leaf margin | : 60-80 g/d |
| 6.2.11.32-Heads soft and rotted | : 90-140 g/d |
| 6.2.11.33-Heads soft and rotted | : 90-140 g/d |
| 6.2.11.34-Bolting | : 200-280 g/d |
| 6.2.11.35-Bolting | : 200-280 g/d |
| 6.2.11.36-Curled leaves | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.11.37-Rough leaves | : 300-450 g/d |
| 6.2.11.38-Rough leaves | : 300-450 g/d |
| 6.2.11.39-Poorly developed roots | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.11.40-Poorly developed roots | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.11.41-Wind damage | : 50-80 g/d |
| 6.2.11.42-Wind damage | : 50-80 g/d |
| 6.2.11.43-Freeze damage | : 100-120 g/d |
| 6.2.11.44-Freeze damage | : 100-120 g/d |
| 6.2.11.45-Antifreezing and preventing cold stress | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.11.46-Antifreezing and preventing cold stress | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.11.47-Breaking the cycle-stage | : 230-290 g/d |
| 6.2.11.48-Breaking the cycle-stage | : 230-290 g/d |
| 6.2.11.49-Vegetative stage | : 120-150 g/d |
| 6.2.11.50-Vegetative stage | : 120-150 g/d |
| 6.2.11.51-Head development | : 100-130 g/d |
| 6.2.11.52-Head development | : 100-130 g/d |
| 6.2.12-Watermelon Application /Crop Protection | |
| 6.2.12.1-Bacterial Fruit Blotch | : 100-300 g/d |
| 6.2.12.2-Gummy Stem Blight | : 450 g/d |
| 6.2.12.3-Anthracnose | : 200-280 g/d |
| 6.2.12.4-Alternaria | : 300-400 g/d |
| 6.2.12.5-Cercospora | : 130-190 g/d |
| 6.2.12.6-Myrothecium Leaf Spot | : 300-500 g/d |
| 6.2.12.7-Leaf Mosaic | : 220-280 g/d |
| 6.2.12.8-Tobacco ring spot | : 130-160 g/d |
| 6.2.12.9-Squash Leaf Curl Virus | : 300-450 g/d |
| 6.2.12.10-Fusarium | : 90-170 g/d |
| 6.2.12.11-Bud necrosis | : 300-400 g/d |
| 6.2.12.12-Phytopthora | : 200-340 g/d |
| 6.2.12.13-Root Knot nematodes | : 300-500 g/d |
| 6.2.12.14-Rotting seeds | : 200g/d |
| 6.2.12.15-Stunted growth | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.12.16-Stunted growth | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.12.17-Blossom end-rot | : 200-300 g/d |
| 6.2.12.18-Blossom end-rot | : 200-300 g/d |
| 6.2.12.19-Internal Cracking | : 120-270 g/d |
| 6.2.12.20-Internal Cracking | : 120-270 g/d |
| 6.2.12.21-Spongy end | : 180-220 g/d |
| 6.2.12.22-Spongy end | : 180-220 g/d |
| 6.2.12.23-Sunburn | : 200-270 g/d |
| 6.2.12.24-Sunburn | : 200-270 g/d |
| 6.2.12.25-Thrips | : 300-500 g/d |
| 6.2.12.26-Flea Beetles | : 100-170 g/d |
| 6.2.12.27-Beet armyworms | : 500 g/d |
| 6.2.12.28-Grasshoppers | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.12.29-Melon Aphids | : 500-600 g/d |
| 6.2.12.30-Silverleaf Whiteflies | : 200-250 g/d |
| 6.2.12.31-Mole crickets | : 180-230 g/d |
| 6.2.12.32-White grubs | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.12.33-Germination | : 300-400 g/d |
| 6.2.12.34-Germination | : 300-400 g/d |
| 6.2.12.35-Vining | : 100-400 g/d |
| 6.2.12.36-Vining | : 100-400 g/d |
| 6.2.12.37-Flowering | : 40-120 g/d |
| 6.2.12.38-Flowering | : 40-120 g/d |
| 6.2.12.39-Fruiting | : 80-140 g/d |
| 6.2.12.40-Fruiting | : 80-140 g/d |
6.3
6.3.1-Mixing and solubility
6.3.1.1-Solubility :Excell Libra is soluble in H2O ,260 gr/L 24 C’ solution
260 gr/L 24 C’
320 gr/L 38 C’
400 gr/L 55 C’
6.3.1.2-Mixability :Excell Libra is soluble in H2O ,260 gr/L 24 C’ solution
260 gr/L 24 C’
320 gr/L 38 C’
400 gr/L 55 C’
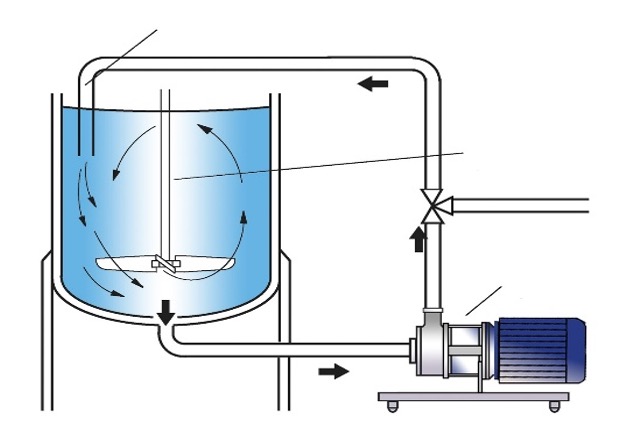
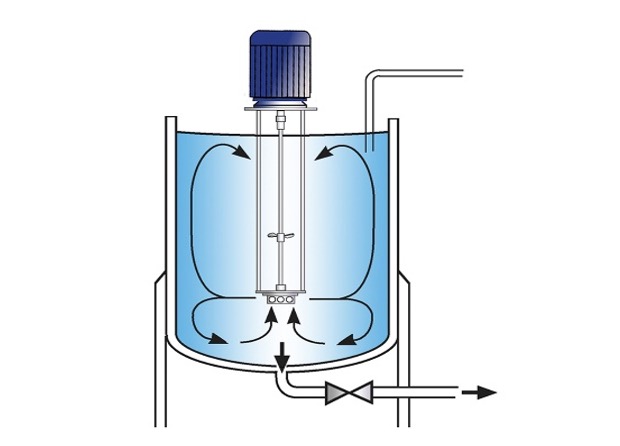
6.3.2-Further process
6.3.1.1-Make product with Excell Libra™
Chealating Zn,Cu,Mn,Fe
7- RESEARCH and ARTICLES
7.1-Content and structure
7.1.1-Algal Polysaccharide
7.1.1.1-Alginic acid binds to and blocks the rizospherial absorption of various TM such as K,Zn,Mn,Mg
7.1.1.2-Laminaran is an elicitor-active
7.1.1.3-Laminaran is stimulating plant defense against phytopathogens
7.1.1.4-Antiviral activity of Algiva sulfated polysaccharides
7.1.1.5-Algiva C4 elicitor-activator of function of plant immunity on viral and parasitic infections.
7.1.1.6-Elicitor-active oligosaccharide
7.1.1.7-Algal polysaccharide boron complexing formation
7.1.1.8-Pathogenesis-Related (PR) proteins with antifungal and antibacterial activities
7.1.1.9-Sensing “non-self” molecules derived from Macroalgae cell wall components.
7.1.1.10- Algal polysaccharide defense responses leading to protection against pathogens
7.1.1.11-Algal polysaccharides also induce protection against viral, fungal and bacterial infections in plants
7.1.1.12-Activation of salicylic , jasmonic acid and polyphenol signaling pathways at systemic level.
7.1.1.13-Synthesis of terpenes, terpenoids or alkaloids having antimicrobial activities
7.1.1.14-Alginic acid combines with metals in the rizosphere to complexing a metallopolymer.This
polymer retains significiant amounts of moisture ,enhancing the soil’s structure and also aiding with
moisture retention during dry periods.Plant roots have better access to both nutrients and air within
the soil resulting in healthier,stronger growth.”
7.1.1.14-Alginic acid initially reduces the amount of availabile nitrogen.This can slow plant growth and seed
germination.
7.1.1.15-Alginic acids have promotive effects on seed germination and elicitor properties inducing PAL and
peroxidase activity in crops.”
7.1.1.16-Alginate can be chemically modification to obtain polymers with new physicochemical properties of new
plant nutrient materials.For example microencapsulation of many plant nutrient having slowly release activity.
7.1.1.17-Fucoidan hepls to reduce the risk of plant disaeses.”
7.1.1.18- Fucoidan is delayed the development of the Plant Viruses.The effect of fucoidan on the formation of
specific granular and tubular inclusions induce by viruses and consist presumably of the virus-coded
protein components of the viral replicase
7.1.1.19-Fucoidan have biostimulatory effect on plants.”
7.1.1.20-Fucoidan is stimulate to germinating of seed root and rootling growth.
7.1.1.21-Laminaran sulfate inhibit endothelial cell proliferation and elicit several plant defense mechanisms
7.1.1.22-Sulfated Laminaran have potent inhibitory effects on Plant virus infection
7.1.1.23-Laminaran against the Tobacco mosaic virus by induction of the plant defense and signalling pathways
7.1.1.24-Laminaran is a nitrite-nitrate regulator and replacer to nitrogen during growth.
7.1.1.25-Laminarans are Lower molecular mass glucans ,Laminarans can modulate the soil immun systems by
binding to specific microorganism receptors
7.1.1.26-Laminaran is a water-soluble algal polysaccharide that consists of B-(1-3)-glucans with B-(1-6) linkages of
25 units.It is found in the plastids of each algal cell.İts content is influenced by the species and enviromental
conditions.
7.1.2-Algal Polysaccharide
7.1.2.1-Mannitol is a important role in plant responses to pathogen attack and biotic ,abiotic stresses
7.1.2.2-Mannitol benefit is increased tolerance to salt and osmotic stress as a result of mannitol’s function as a
compatible solute.
7.1.2.3-Mannitol advantage is a possible role in plant responses to pathogen attack — thus mannitol metabolism
may play roles in plant responses to both biotic and abiotic stresses.
7.1.2.4-Mannitol can pass through the interstices of the cell wall to induce water stress.
7.1.2.5-Mannitol can change microbial community of soil, hence could be plenty of extra effects
7.1.2.6-Mannitol is essential in pathogenesis to balance cell reinforcements produced by plants
7.1.2.7- Polyol plays a key role in host–pathogen interactions and must be co-localized with pathogen-secreted
mannitol to resist the infection.
7.1.2.8-Mannitol as a store of reducing power as a compatible osmolyte and in osmoregulation
7.1.2.9-Plants polyols are osmolytes and solutes that provide resistance against various abiotic stresses
7.1.2.10-Mannitol protects enzymes against hydroxyl radicals, which are abundant during the oxidative stress
process associated with water stress
7.1.2.11-Under osmotic stress mannitol accumulation is attributable to a reduction in the catabolism of mannitol
in green tissues
7.1.2.12-Mannitol works as an antioxidant osmoprotectants against oxidative stress coming about because of
salt/dry spell push and even sun oriented irradiance
7.1.2.13-Polyols,glycerol and erythritol are the major polyols included in osmoregulation.
7.1.2.14-Mannitol was the most abundant polyol distinguished at low osmotic weight, while arabinitol levels
amassed at higher osmotic weight, with glycerol having a transitory accumulation
7.1.2.15-Mannitol may accumulate in cells cultivated under submerged conditions
7.1.2.16-Mannitol and likely other sugar alcohols may be utilized to protect against plant disease
7.1.2.17-Mannitol for osmoprotection, efficient growth and resistance to pathogens
7.1.3-Algal Polysaccharide
7.1.3.1-Stimulate plant growth
7.1.3.2-Wide range of potential biological activity
7.1.3.3-Seaweeds have been shown as a rich source of different types of polyphenols
