ACETOBACTER VINELANDII MCC 4059301
1-IDENTIFIER
1.1
1.1.1-Describe
Azotobacter vinelandii is Gram-negative diazotroph that can fix nitrogen while grown aerobically. These bacteria are easily
cultured and grown.
1.1.2-Names
Azotobacter vinelandii
1.1.3-Supplier
Schwarp biyoteknoloji A.Ş
Saray osmangazi mahallesi sarsılmaz caddesi no :2 daire 6 Pursaklar Ankara
0-312 5143724 www.schwarp.com
1.2-IDENTIFY NUMBERS
1.2.1 -Milicard number: 868182336-02792
1.2.2 -EA Codex number : 8681823363965
1.2.3 -Cas number :
1.2.4 -EC number :
1.2.5 -Permit License number :
1.2.6 -Patent and License number : NA
1.3-STRUCTURE
1.3.1
1.3.2
1.3.3
1.3.4
1.4-CHEMICAL&PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| 1.4.1-ID NAMES | : Azotobacter Vinelandii |
| 1.4.2 TAXONOMY | |
| 1.4.2.1-DOMAIN | : Bacteria |
| 1.4.2.2-PHYLLUM | : Pseudomonadota |
| 1.4.2.3-CLASS | : Gammaproteobacteria |
| 1.4.2.4-ORDER | : Pseudomonadales |
| 1.4.2.5-FAMILY | : Pseudomonadaceae |
| 1.4.2.6-GENUS | : Azotobacter |
| 1.4.2.7-SPECIES | : Azotobacter Vinelandii |
| 1.4.2.8-BINOMINAL NAMES | : Azotobacter Vinelandii |
| 1.4.3-TYPE | : Gram-negative diazotroph |
| 1.4.4.-SIZE | : 2.7 to 6.6 microns |
| 1.4.5-CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1.4.5.1-ODOUR | : Not available |
| 1.4.5.2-COLOUR | : Not available |
| 1.4.5.3.-TYPE | : Not available |
| 1.4.5.4-pH VALUE | : 6.8 |
| 1.4.5.5-MELTING POINT | : Not available |
| 1.4.5.6-BOILING POINT | : Not available |
| 1.4.5.7-VAPOUR PRESSURE | : Not available |
| 1.4.5.8-DENSITY | : Not available |
| 1.4.5.9-VISCOSITY | : Not available |
| 1.4.5.10-PURITY,COUNT | : 1.10^10 cfu/gr |
| 1.4.5.10.1-PURE CULTURE | : 1.10^10 cfu/gr |
| 1.4.5.10.2-LIQUID SUSPENSION | : Not available |
| 1.4.5.10.3-FINAL CULTURE | : Not available |
| 1.4.5.11-STEAM RESISTANCE | : Not available |
| 1.4.5.12-FLASH POINT | : Not available |
| 1.4.5.13-AUTO IGNITION TEMP. | : Not available |
| 1.4.6-INSTRUCTION FOR USE,Vials | : Not available |
| 1.4.7-MEDIUM | : Medium 12: Azotobacter Supplement |
| 1.4.8-GROWTH CONDITIONS | : Temperature : 36°C, |
| 1.4.9.1-BIOSAFETY LEVEL | : 1 |
| 1.4.10.1-LD 50 ORAL RAT | |
| 1.4.10.2-LC 50 ACUTE RESPIRATORY | : Not available |
2-ORO
3-TOT
4-DOCUMENTER
4.1-MSDS
4.1.1-MSDS Material Info
| Product Name | : AZOTOBACTER VINELANDII |
| Producer Name | : Fermo Crysta™ Fermantasyon Kristalleri Üretim Gıda San. Ve Tic. LTD. ŞTİ. |
| Saray Osmangazi Mahallesi Sarsılmaz Cad.No: 2/15 Pursaklar/ANKARA 0312 5143724 | |
| MILICARD NO | : 868182336-02792 |
| CODEX NUMBER | : 8681823363965 |
| CAS NUMBER | : MCC 1997 |
Acil durum telefon numarası Ulusal Zehir Danışma Merkezi (UZEM):
114 CHEMTREC Turkey (Istanbul): +(90)-212-7055340
4.1.2-Hazard Identification
Emergency overview
KEEP OUT OF REACH OF CHILDREN.
Potential sensitizer.
Avoid contact with the skin, eyes and clothing
Avoid inhalation of dusts/mists/vapours
Wash thoroughly after handling
Potential health effects
Acute toxicity:
Virtually nontoxic after a single ingestion. Virtually nontoxic by inhalation. Virtually nontoxic after a single skin contact
Irritation / corrosion :Not irritating to the skin. Not irritating to the eyes.
Sensitization:There is no evidence of a skin-sensitizing potential
Carcinogenicity: The product has not been tested. The statement has been derived from the properties of the
individual components. The results of various animal studies gave no indication of a carcinogenic effect.
Repeated dose toxicity: The product has not been tested. The statement has been derived from the properties
of the individual components. No substance-specific organtoxicity was observed after repeated administration to animals.
Reproductive toxicity: The product has not been tested. The statement has been derived from the properties
of the individual components. The results of animal studies gave no indication of a fertility impairing effect
Teratogenicity: The product has not been tested. The statement has been derived from the properties of the
individual components. Animal studies gave no indication of a developmental toxic effect at doses that were not
toxic to the parental animals.
Genotoxicity: The product has not been tested. The statement has been derived from the properties of the individual
components. Mutagenicity tests revealed no genotoxic potential.
Signs and symptoms of overexposure:No significant reaction of the human body to the product known.
Potential environmental effects
Aquatic toxicity:There is a high probability that the product is not acutely harmful to aquatic organisms
Degradation / environmental fate:
The product has not been tested. The statement has been derived from the properties of the individual components.
Colourants are by their nature very stable and are therefore not readily biodegradable under conditions prevailing
in surface water or in effluent treatment plants.
Bioaccumulation / bioconcentration:The Product has not been tested
4.1.3-First Aid Measurement
General Advice :Remove contaminated clothing
If Inhaled :Keep Patient Calm,remove to fresh air,seek medical attention.
If on skin :was thoroughly with soap and water
If in eyes :Wash affected eyes for at least 15 minutes under running water with eyelids held open
If swallowed :Immediately rinse mouth and then drink 200-300 ml of water, seek medical attention
Not to physician :Treat according to symptoms (decontamination, vital functions), no known specific antidote
EyeContact: Check for and remove any contact lenses. In case of contact,immediately flush eyes with plenty of water for at least
15 minutes Cold water may be used. Get medical attention if irritation occurs.
Skin Contact: Wash with soap and water. Cover the irritated skin with an emollient. Get medical attention if irritation develops.
Cold water may be used.
Serious Skin Contact: Not available.
Inhalation: If inhaled, remove to fresh air. If not breathing, give artificial respiration. If breathing is difficult, give oxygen.
Serious Inhalation: Not available.
Ingestion: DoNOT induce vomiting unless directed to do so by medical personnel. Never give anything by mouth to an
unconscious person. If large quantities of this material are swallowed, call a physician immediately. Loosen tight clothing
such as a collar, tie,belt or waistband.
Serious Ingestion: Not available.
4.1.4-Fire And Explosion Data
Flash Point: Not applicable
Lower Explosion Limit :As a result of our experience with this product and our knowledge of its composition
we do not expect any hazard as long as the ,product is used appropriately and in accordance with the intended use
Upper Explosion Limit :As a result of our experience with this product and our knowledge of its composition
we do not expect any hazard as long as the ,product is used appropriately and in accordance with the intended use
Flammability:Not applicable
Suitable extinguishing media:water spray, dry powder, foam, carbon dioxide
Hazards during fire-fighting:carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides
The substances/groups of substances mentioned can be released in case of fire
Protective equipment for fire-fighting:Wear self-contained breathing apparatus and chemical-protective clothing.
Further Info:Keep containers cool by spraying with water if exposed to fire. In case of fire and/or explosion do not breathe
fumes. Collect contaminated extinguishing water separately, do not allow to reach sewage or effluent systems.
Dispose of fire debris and contaminated extinguishing water in accordance with official regulations.
4.1.5-Accidental Release Measures
Personal precautions:Do not breathe vapour/spray.Use personal protective clothing.Avoid contact with the skin,eyes and clothing.
Environmental precautions:Do not discharge into the subsoil/soil. Do not discharge into drains/surface waters/groundwater.
Cleanup:Dispose of absorbed material in accordance with regulations. Collect waste in suitable containers, which can be
labeled and sealed.Clean contaminated floors and objects thoroughly with water and detergents,observing enviromental
regulations.For small amounts: Pick up with suitable absorbent material (e.g. sand, sawdust, general-purpose binder,
For large amounts: Dike spillage. Pump off product.
4.1.6-Handling And Storage
Handling
General Advice :
No special measures necessary if stored and handled correctly. Ensure thorough ventilation of stores and work areas.
When using do not eat, drink or smoke. Hands and/or face should be washed before breaks and at the end of shit.
Protection against fire and explosion :
No special precautions necessary. The substance/product is non-combustible. Product is not explosive
Storage
General Advice :Keep away from heat. Protect from direct sunlight.
4.1.7- Exposure Controls/Personal Protection
Personel Protective Equipment
Respiratory protection :Wear respiratory protection if ventilation is inadequate. Wear a NIOSH-certified (or equivalent) TC23C
Chemical/Mechanical type filter system to remove a combination of particles, gas and vapours. For situations where
the airborne concentrations may exceed the level for which an air purifying respirator is effective, or where the levels are
unknown or Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health (IDLH), use NIOSH-certified full facepiece pressure demand self contained
breathing apparatus (SCBA) or a full facepiece pressure demand supplied-air respirator (SAR) with escape provisions.
Eye protection:Safety glasses with side-shields. Tightly fitting safety goggles (chemical goggles). Wear face shield if splashing
hazard exists.
Body protection :Body protection must be chosen depending on activity and possible exposure, e.g. head protection, apron,
protective boots, chemical-protection suit.
General safety and hygiene measures:Handle in accordance with good industrial hygiene and safety practice.Wearing of closed
work clothing is recommended. Store work clothing separately. Keep away from food, drink and animal feeding stuff
4.1.8-Physical and Chemical Properties
Form : Not available
Odour : Not available
Colour : Not available
pH Value : 6.8
Density : Not available
Melting Point : Not available
Solubility in Water : Disperse soluble
Vapour Density : Not available
Viscosity : Not available
Boiling Point : Not available
Vapour Pressure : Not available
4.1.9-Stability and Reactivity Data
Conditions to avoid :See MSDS section – Handling and storage.
Substances to avoid:strong acids, strong bases, strong oxidizing agents
Hazardous reactions:No hazardous reactions if stored and handled as prescribed/indicated
Decomposition products:Hazardous decomposition products: No hazardous decomposition products if stored and handled as
prescribed/indicated.
Thermal decomposition :No decomposition if stored and handled as prescribed/indicated.
Oxidizing properties:Based on its structural properties the product is not classified as oxidizing.
4.1.10-Toxicological Information
4.1.10.1-Acute toxicity
No data available
4.1.10.2-Skin corrosion/irritation
No data available
4.1.10.3-Serious eye damage/eye irritation
No data available
4.1.10.4-Respiratory or skin sensitization
No data available
4.1.10.5-Germ cell mutagenicity
No data available
4.1.10.6-Carcinogenicity
No data available
4.1.10.7-Reproductive toxicity
No data available
4.1.10.8-Specific target organ toxicity – single exposure
No data available
4.1.10.9-Specific target organ toxicity – repeated exposure
No data available
4.1.10.10-Aspiration hazard
No data available
4.1.10.11- Additional Information
To the best of our knowledge, the chemical, physical, and toxicological properties have not been thoroughly investigated.
4.1.11-Ecological Information
4.1.11.1-Fish
Not available
4.1.11.2-Aquatic invertebrates
Not available
4.1.11.3-Aquatic plants
Not available
4.1.11.4-Biodegradation :Significant accumulation in organisms is not to be expected.
4.1.11.5-Bioaccumulation :Significant accumulation in organisms is not to be expected.
4.1.12.-Disposal Considerations
Waste disposal of substance:
See product label for disposal and recycling instructions
Container disposal:
Rinse the container or liner as needed for disposal. Add rinsate to spray tank. Recommend crushing, puncturing
or other means to prevent unauthorized use of used containers. Consult the product label for additional details
4.1.13-Transpot Information
Land transport-TDG Not classified as a dangerous good under transport regulations
Sea transport IMDG Not classified as a dangerous good under transport regulations
Air transport IATA Not classified as a dangerous good under transport regulations
4.1.14-Regulatory Information
Registration status
Chemical DSL, CA blocked / not listed
Crop Protection DSL, CA released / exemp
WHMIS does not apply to this product
THIS PRODUCT HAS BEEN CLASSIFIED IN ACCORDANCE WITH THE HAZARD CRITERIA OF THE CPR AND THE MSDS CONTAINS
ALL THE INFORMATION REQUIRED BY THE CPR.
4.1.15-Safe&Hazard Symbols

4.2-RISK REPORT
4.2.1-Toxıcology Study
4.2.2-Toxicity Data
5-TEST STANDARTS&RESULTS
5.1-SPECTRAL ANALYSIS
5.1.1-Circular Genome
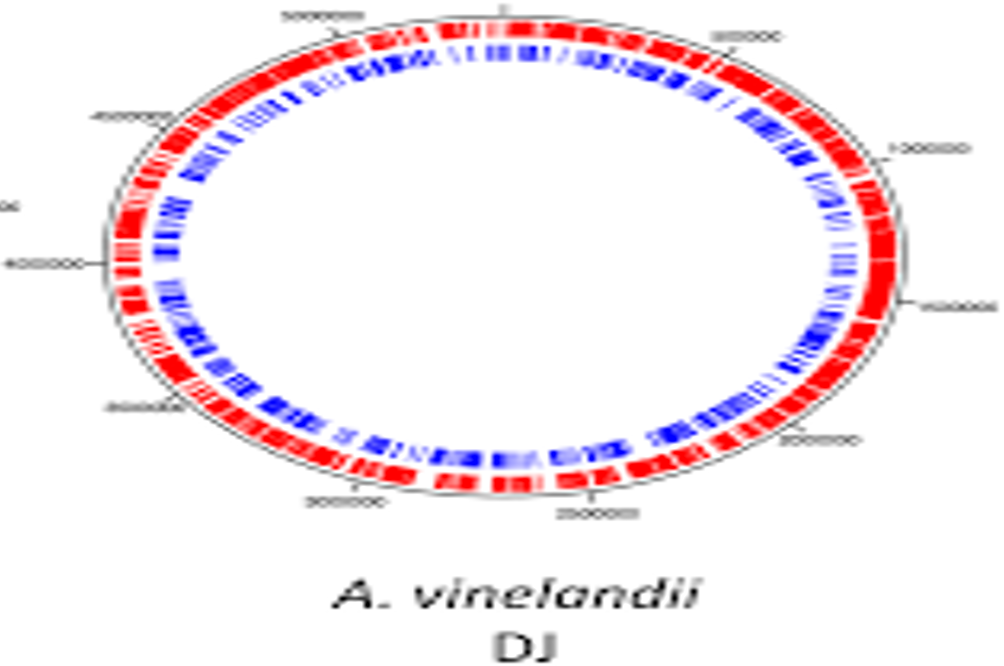
5.1.2-MiliGenome
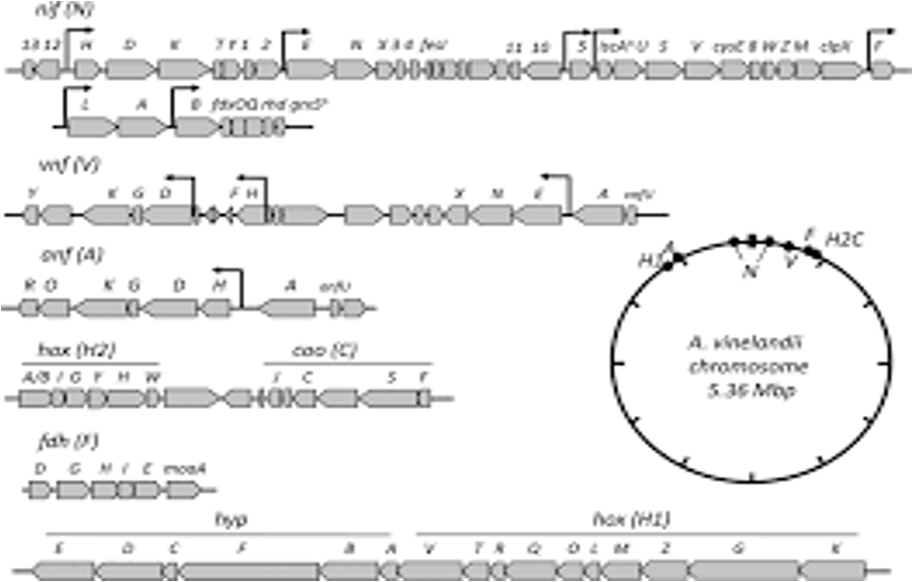
5.1.3-Genome Pathway
6. APPLICATION/PLANT NUTRITION, FERTIGATION, HEALTH AND PESTS
6.2
| 6.2.1-Potato Application /Fertigation,Crop Protection | |
| 6.2.1.1-Turbo Spray | : Sprays 100-300 g /da |
| 6.2.1.2-Drip Irrıgation | : 1:1000 dilute |
| 6.2.1.3-30 days after planting | : 100 g/d |
| 6.2.1.4-45 days after planting | : 250 g/d |
| 6.2.1.5-90 days after planting | : 100 g/d |
| 6.2.1.6-Aerial Uses | : 200-400g/d |
| 6.2.1.7-Roat Soak | : 200-500 g/d |
| 6.2.1.8-Seed Treatment | : 3-5 g/kg of seed |
| 6.2.1.9-Alternaria diseaes | : 1 kg/ha |
| 6.2.1.10-Dry rot diseaes | : 220 g/d |
| 6.2.1.11-Potato Virus | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.1.12-Verticillium | : 60 g/d |
| 6.2.1.13-Skin Spot | : 80 g /d |
| 6.2.1.14-Powdery Scab | : 110 g/d |
| 6.2.1.15-Gangrene | : 190 g/d |
| 6.2.1.16-Viral and viroid diseaes | : 180 g/d |
| 6.2.1.17-Nematode parasitic | : 380 g/d |
| 6.2.1.18-Miscellaneous diseaes | : 35 g/d |
| 6.2.1.19-Bacterial soft rot | : 80 g/d |
| 6.2.1.20-Botrytis gray mold | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.1.21-Charcoal rot | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.1.22-Fusarium | : 700 g/d |
| 6.2.1.23-Pysyllid yellows | : 210 g/d |
| 6.2.1.24-Air pollution damage | : 130 g/d |
| 6.2.1.25-Fertilizer burn | : 108 g/d |
| 6.2.1.26-Freezing necros | : 190 g/d |
| 6.2.1.27-Hollow heart | : 33 g/d |
| 6.2.1.28-Lightning injury | : 78 g /d |
| 6.2.1.29-Second growth | : 90 g/d |
| 6.2.1.30-Greening | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.1.31-Xylem ring discoloration | : 260 g/d |
| 6.2.1.32-Tipburn | : 25 g/d |
| 6.2.1.33-Sunscald | : 106 g/d |
| 6.2.1.34-Stem streak necrosis | : 188 g/d |
| 6.2.1.35-Sprout tubers | : 102 g/d |
| 6.2.1.36-Spinding sprout | : 180 g/d |
| 6.2.1.37-Internal brown spot | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.1.38-Internal brown spot | : 112 g/d |
| 6.2.1.39-Heat and drought necrosis | : 190 g/d |
| 6.2.1.40-Feather and scald | : 110 g/d |
| 6.2.1.41-Enlarged lenticels | : 40 g/d |
| 6.2.1.42-Rootling | : 290 g/d |
| 6.2.1.43-Rootling | : 130 g/d |
| 6.2.1.44-Maturating | : 70 g/d |
| 6.2.1.45-Maturating | : 100 g/d |
| 6.2.1.46-Antifreezing and preventing cold stress | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.1.47Antifreezing and preventing cold stress | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.2-Apple Application /Fertigation,Crop Protection | |
| 6.2.2.1-Apple Scab-the fungus Venturia inaequalis | : 230 g/d |
| 6.2.2.2-Alternaria leaf and fruit blotch | : 177 g/d |
| 6.2.2.3-Bitter rot | : 55 g/d |
| 6.2.2.4-Powdery mildew | : 102 g/d |
| 6.2.2.5-White root rot-Rosellinia necatrix | : 380 g/d |
| 6.2.2.6-Sclerotium collar root -Sclerotium spp | : 310 g/d |
| 6.2.2.7-Black rot canker | : 74 g/d |
| 6.2.2.8-Collar rot | : 192 g/d |
| 6.2.2.9-Apple virus diseaes | : 450 g/d |
| 6.2.2.10-Brown rot | : 214 g/d |
| 6.2.2.11-Seedling blight | : 190 g/d |
| 6.2.2.12-Fire blight | : 600 g/d |
| 6.2.2.13-Poor Fruiting | : 250-300 g/d |
| 6.2.2.14-Root Decay | : 80-120 g/d |
| 6.2.2.15-Grey-coloured crusty growth | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.2.16-Grey-coloured crusty growth | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.2.17-Bird Damage on Flowers | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.2.18-Waterlogging | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.2.19-Waterlogging | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.2.20-Calcium uptake | : 120-300 g/d |
| 6.2.2.21-Calcium uptake | : 120-300 g/d |
| 6.2.2.22-Poor growing conditions | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.2.23-Poor growing conditions | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.2.24-Unproductive trees | : 10 g/tree |
| 6.2.2.25-Pollinating Partner | : 80 g/d |
| 6.2.2.26-Mussel Scale | : 340 g/d |
| 6.2.2.27-Aphid Attack | : 280-370 g/d |
| 6.2.2.28-Caterpillars | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.2.29-Capsid Bugs | : 90 g/d |
| 6.2.2.30-Summer pruning | : 230 g/d |
| 6.2.2.31-Blossom wilt | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.2.32-Codling Moth | : 380 g/d |
| 6.2.2.33-Coral Spot | : 160 g/d |
| 6.2.2.34-Silver Leaf | : 100 g/d |
| 6.2.2.35-Flyspeck | : 170 g/d |
| 6.2.2.36-Low N requirement varieties | : 100-200 g/d |
| 6.2.2.37-Low N requirement varieties | : 100-200 g/d |
| 6.2.2.38-High N requirement varieties | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.2.39-High N requirement varieties | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.2.40-Vigor of Shoot Growth | : 240-300 g/d |
| 6.2.2.41-Fruit Size and firmness | : 80-120 g/d |
| 6.2.2.42-Terminal growth | : 230 g/d |
| 6.2.2.43-Leaf size growth | : 300-400 g/d |
| 6.2.2.44-Fruit setting | : 30-110 g/d |
| 6.2.2.45-Fruit setting and maturating | : 30-110 g/d |
| 6.2.2.46-Fruit maturity | : 180-270 g/d |
| 6.2.3.1-Growing Excessively Large Fruit | : 110-205 g/d |
| 6.2.3.2-Growing Excessively Large Fruit | : 110-205 g/d |
| 6.2.3.3-Encouraging Good pollination | : 50-90 g/d |
| 6.2.3.4-Encouraging Good pollination | : 50-90 g/d |
| 6.2.3.5-General Soil Application | : 500-700 g/d |
| 6.2.3.6-General Soil Application | : 500-700 g/d |
| 6.2.3.7-General Foliar Application | : 100-400 g/d |
| 6.2.3.8-General Foliar Application | : 100-400 g/d |
| 6.2.3.9-Pre-Bloom | : 20-60 g/d |
| 6.2.3.10-Pre-Bloom | : 20-60 g/d |
| 6.2.3.11-Post-Bloom | : 30-50 g/d |
| 6.2.3.12-Post-Bloom | : 30-50 g/d |
| 6.2.3.13-Plant Population 60-80 trees /d | : 200-500 g/d |
| 6.2.3.14-Plant Population 60-80 trees /d | : 200-500 g/d |
| 6.2.3.15-Plant Population 140-250 trees/d | : 400-600 g/d |
| 6.2.3.16-Plant Population 140-250 trees/d | : 400-600 g/d |
| 6.2.3.17-Spring to early summer | : 100-300 g/d |
| 6.2.3.18-Spring to early summer | : 100-300 g/d |
| 6.2.3.19-Post Harvest | : 200-250 g/d |
| 6.2.3.20-Post Harvest | : 200-250 g/d |
| 6.2.3.21-Antifreezing and preventing cold stress | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.3.22-Antifreezing and preventing cold stress | : 400 g/d |
| 3.2.4-Grape Application/ Fertigation | |
| 6.2.4.1-Soil pH near 6.5 | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.4.2-Soil pH near 6.5 | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.4.3-Soil pH 5.0-6.0 | : 300-500 g/d |
| 6.2.4.4-Soil pH 5.0-6.0 | : 300-500 g/d |
| 6.2.4.5-New plantings | : 100-180 g/d |
| 6.2.4.6-New plantings | : 100-180 g/d |
| 6.2.4.7-Coarse textured ,Acid Soil | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.4.8-Pre-Bloom,upper mature leaf/petiole | : 90-110 g/d |
| 6.2.4.9-Bloom and Fruiting ,leaf /petiole opposite cluster | : 170-220 g/d |
| 6.2.4.10-Fruit maturating | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.4.11-Sandy Soil | : 200-300 g/d |
| 6.2.4.12-Sandy Soil | : 200-300 g/d |
| 6.2.4.13-Beginning 2 weeks before bloom | : 30-60 g/d |
| 6.2.4.14-Beginning 2 weeks before bloom | : 30-60 g/d |
| 6.2.4.15-Root damage | : 250 g/d |
| 6.2.4.16-Bud Burst stage | : 40-70 g/d |
| 6.2.4.17-Bud Burst stage | : 40-70 g/d |
| 6.2.4.18-Early Shoot stage | : 70-110 g/d |
| 6.2.4.19-Early Shoot stage | : 70-110 g/d |
| 6.2.4.20-Mid Shoot stage | : 100 g/d |
| 6.2.4.21-Mid Shoot stage | : 100 g/d |
| 6.2.5.1-Post Harvest | : 90-200 g/d |
| 6.2.5.2-Post Harvest | : 90-200 g/d |
| 6.2.5.3-Downy Mildew | : 130-300 g/d |
| 6.2.5.4-Anthracnose | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.5.5-Grey Mold | : 230-290 g/d |
| 6.2.5.6-Viruses | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.5.7-Greenaria bitter rot | : 90-110 g/d |
| 6.2.5.8-Bacterial leaf spot | : 280 g/d |
| 6.2.5.9-Alternaria blight | : 200-300 g/d |
| 6.2.5.10-Black Rot | : 30-80 g/d |
| 6.2.5.11-Black Rot | : 30-80 g/d |
| 6.2.5.12-Rhizopus rot | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.5.13-Rhizopus rot | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.5.14-Botrytis bunch rot | : 230-290 g/d |
| 6.2.5.15-Color,size,taste improving | : 240-340 g/d |
| 6.2.5.16-Color,size,taste improving | : 240-340 g/d |
| 6.2.5.17-Chemical damage | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.5.18-Nutritional Imbalances | : 100-600 g/d |
| 6.2.5.19-Nutritional Imbalances | : 100-600 g/d |
| 6.2.5.20-Sanitation with biocide | : 20 g/10 L H2O |
| 6.2.5.21-Pruning | : 30 g/100 L H2O |
| 6.2.5.22-Boron deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.23-Boron deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.24-Calcium deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.25-Calcium deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.26-Copper deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.27-Copper deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.28-Iron deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.29-Iron deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.30-Magnesium deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.31-Magnesium deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.32-Manganase deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.33-Manganase deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.34-Zinc deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.35-Zinc deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.36-Antifreezing and preventing cold stress | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.5.37-Antifreezing and preventing cold stress | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.5.38-Flowering | : 60-90 g/d |
| 6.2.5.39-Fruit Set | : 100-240 g/d |
| 6.2.6-Corn Application /Crop Protection | |
| 6.2.6.1-Seed rots and seeding blights | : 100-200 g/d |
| 6.2.6.2-Stalk rots | : 120 g/d |
| 6.2.6.3-Ear rots | : 130-180 g/d |
| 6.2.6.4-Boil and Head smut | : 200-300 g/d |
| 6.2.6.5-Downy mildew | : 80-130 g/d |
| 6.2.6.6-Fusairum | : 240 g/d |
| 6.2.6.7-Virus | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.6.8-Blanking | : 100-120 g/d |
| 6.2.6.9-Blanking | : 100-120 g/d |
| 6.2.6.10-Boron deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.11-Boron deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.12-Calcium deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.13-Calcium deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.14-Copper deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.15-Copper deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.16-Iron deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.17-Iron deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.18-Magnesium deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.19-Magnesium deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.20-Manganase deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.21-Manganase deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.22-Zinc deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.23-Zinc deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.24-Uneven germination | : 100-300 g/d |
| 6.2.6.25-Uneven germination | : 100-300 g/d |
| 6.2.6.26-Aphid | : 800 g/d |
| 6.2.6.27-Cricket | : 600 g/d |
| 6.2.6.28-Cutworm | : 300-500 g/d |
| 6.2.6.29-Earwig | : 200-500 g/d |
| 6.2.6.30-Mite | : 300-700 g/d |
| 6.2.6.31-Heliothis | : 200-270 g/d |
| 6.2.6.32-Maize leafhopper | : 100-300 g/d |
| 6.2.6.33-Parasitoid wasps | : 100-230 g/d |
| 6.2.6.34-Flies | : 200-300 g/d |
| 6.2.6.35-Fungal Systemic diseaes | : 200-450 g/d |
| 6.2.6.36-Smutting diseaes | : 80-190 g/d |
| 6.2.6.37-Herbicide injury symptoms | : 160-210 g/d |
| 6.2.6.38-Trigger symptoms | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.6.39-Trigger symptoms | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.6.40-Nutrient defiency symptoms | : 40-400 g/d |
| 6.2.6.41-Nutrient defiency symptoms | : 40-400 g/d |
| 6.2.6.42-Leaf Diseaes | : 300-400 g/d |
| 6.2.6.43-Leaf Diseaes | : 300-400 g/d |
| 6.2.6.44-Unfavorable soil conditions | : 200-600 g/d |
| 6.2.6.45-Unfavorable soil conditions | : 200-600 g/d |
| 6.2.6.46-Poor Seed-soil contact | : 130-180 g/d |
| 6.2.6.47-Poor Seed-soil contact | : 130-180 g/d |
| 6.2.6.48-Fertilizer injury | : 220-260 g/d |
| 6.2.6.49-Fertilizer injury | : 220-260 g/d |
| 6.2.7.1-Seed planted to deep | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.7.2-Seed planted to deep | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.7.3-Bird and rodent damage | : 450 g/d |
| 6.2.7.4-Bird and rodent damage | : 450 g/d |
| 6.2.7.5-Insects attacking roots | : 340-380 g/d |
| 6.2.7.6-Insects attacking roots | : 340-380 g/d |
| 6.2.7.7-Nematodes | : 500 g/d |
| 6.2.7.8-Nematodes | : 500 g/d |
| 6.2.7.9-Non-uniform planting | : 200-600 g/d |
| 6.2.7.10-Non-uniform planting | : 200-600 g/d |
| 6.2.7.11-Failure of roots develop | : 300-460 g/d |
| 6.2.7.12-Failure of roots develop | : 300-460 g/d |
| 6.2.7.13-Wind damage | : 50-80 g/d |
| 6.2.7.14-Wind damage | : 50-80 g/d |
| 6.2.7.15-Freeze damage | : 100-120 g/d |
| 6.2.7.16-Freeze damage | : 100-120 g/d |
| 6.2.7.17-Antifreezing and preventing cold stress | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.7.18-Antifreezing and preventing cold stress | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.8-Tomato Application/Crop Protection | |
| 6.2.8.1-Failure to set fruit,poor fruit set | : 120-340 g/d |
| 6.2.8.2-Failure to set fruit,poor fruit set | : 120-340 g/d |
| 6.2.8.3-Cold soil stress | : 40-70 g/d |
| 6.2.8.4-Cold soil stress | : 40-70 g/d |
| 6.2.8.5-Root initiatives | : 50-80 g/d |
| 6.2.8.6-Root initiatives | : 50-80 g/d |
| 6.2.8.7-Early blight | : 90-310 g/d |
| 6.2.8.8-Septoria leaf spot | : 60-100 g/d |
| 6.2.8.9-Bacterial spot and speck | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.8.10-Spider mites | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.8.11-Fusarium & Verticillium | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.8.12-Bacterial canker | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.8.13-Late blight | : 100 g/d |
| 6.2.8.14-Hornworms | : 130 g/d |
| 6.2.8.15-Root-Knot nematodes | : 180-240 g/d |
| 6.2.8.16-Gray Leaf Spot | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.8.17-Anthracnose | : 200-240 g/d |
| 6.2.8.18-Blossom end rot | : 50 g/d |
| 6.2.8.19-Buckeye rot | : 60-90 g/d |
| 6.2.8.20-Buckeye rot | : 60-90 g/d |
| 6.2.8.21-Botrytis Gray Mold | : 230-310 g/d |
| 6.2.8.22-Spotty Leaves | : 290-370 g/d |
| 6.2.8.23-Spotty Leaves | : 290-370 g/d |
| 6.2.8.24-Fixing Fruit | : 300-600 g/d |
| 6.2.8.25-Fixing Fruit | : 300-600 g/d |
| 6.2.9-Tomato Application/Crop Protection | |
| 6.2.9.1-Catfacing | : 100-300 g/d |
| 6.2.9.2-Catfacing | : 100-300 g/d |
| 6.2.9.3-Leaf Roll | : 120-340 g/d |
| 6.2.9.4-Leaf Roll | : 120-340 g/d |
| 6.2.9.5-Puffiness | : 80-130 g/d |
| 6.2.9.6-Puffiness | : 80-130 g/d |
| 6.2.9.7-Powdery Mildew | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.9.8-Cutworms | : 80-110 g/d |
| 6.2.9.9-Flea beetles | : 100-130 g/d |
| 6.2.9.10-Tuta Absoluta | : 200-700 g/d |
| 6.2.9.11-Whiteflies | : 100-190 g/d |
| 6.2.9.12-Parasitic plants | : 200-340 g/d |
| 6.2.9.13-Apical Stunt | : 300-500 g/d |
| 6.2.9.14-Hail Damage | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.9.15-Small holes in leaves of seedlings | : 30-50 g/d |
| 6.2.9.16-Small holes in leaves of seedlings | : 30-50 g/d |
| 6.2.9.17-Water-soaked spots on leaves | : 40-80 g/d |
| 6.2.9.18-Water-soaked spots on leaves | : 40-80 g/d |
| 6.2.9.19-Trails and tunnels in leaves | : 40-80 g/d |
| 6.2.9.20-Trails and tunnels in leaves | : 40-80 g/d |
| 6.2.9.21-Small to large holes in fruits | : 100-190 g/d |
| 6.2.9.22-Sunken water-soaked areas on fruit | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.9.23-Worm tunnels into fruit | : 190-230 g/d |
| 6.2.9.24-Fruit is distorted | : 40-90 g/d |
| 6.2.9.25-Fruit is distorted | : 40-90 g/d |
| 6.2.9.26-Psyllids | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.9.27-Roots discolored ,mushy | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.9.28-Roots discolored ,mushy | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.9.29-Ring spots on fruit | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.9.30-Uniforming fruit | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.9.31-Preplant,vegetative growth stage | : 100-400 g/d |
| 6.2.9.32-Preplant,vegetative growth stage | : 100-400 g/d |
| 6.2.9.33-Flowering&Fruit Set | : 80-120 g/d |
| 6.2.9.34-Flowering&Fruit Set | : 80-120 g/d |
| 6.2.9.35-Ripening&Maturity | : 80-140 g/d |
| 6.2.9.36-Ripening&Maturity | : 80-140 g/d |
| 6.2.9.37-Over-pruning | : 120 g/d |
| 6.2.9.38-Fruit cracks | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.9.39-Poor fruit set | : 400-450 g/d |
| 6.2.10-Cabbage Application/Fertigation | |
| 6.2.10.1-Adjusting the spacing | : 310-340 g/d |
| 6.2.10.2-Adjusting the spacing | : 310-340 g/d |
| 6.2.10.3-Pre-drilling | : 1000 g/d |
| 6.2.10.4-Pre-drilling | : 1000 g/d |
| 6.2.10.5-Transplanting | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.10.6-Transplanting | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.10.7-4-6 leaf stage | : 80-130 g/d |
| 6.2.10.8-4-6 leaf stage | : 80-130 g/d |
| 6.2.11.1-Cutworms | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.11.2-Cabbage worms | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.11.3-Root maggots | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.11.4-Flea Beetles | : 100-400 g/d |
| 6.2.11.5-Aphids | : 100-200 g/d |
| 6.2.11.6-Slugs and Snails | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.11.7-Damping off seedlings | : 100 g/d |
| 6.2.11.8-Clubroot | : 80-100 g/d |
| 6.2.11.9-Caterpillars | : 230 g/d |
| 6.2.11.10-Downy mildew | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.11.11-Sclerotinia rot | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.11.12-Tipburn | : 100-180 g/d |
| 6.2.11.13-Seedlings fail to emerge from soil | : 200-300 g/d |
| 6.2.11.14-Young sprouts fail to grow | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.11.15-Young plants flower | : 300 g/ d |
| 6.2.11.16-Small holes in leaves | : 200-500 g/d |
| 6.2.11.17-Leaves are pitted | : 100-220 g/d |
| 6.2.11.18-Root nematodes | : 200-300 g/d |
| 6.2.11.19-Bacterial Soft rot | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.11.20-Blackleg | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.11.21-White rust | : 120-220 g/d |
| 6.2.11.22-Yellow patches | : 300-550 g/d |
| 6.2.11.23-Turnip mosaic | : 80-130 g/d |
| 6.2.11.24-Cracking of heads | : 200-290 g/d |
| 6.2.11.25-Cracking of heads | : 200-290 g/d |
| 6.2.11.26-Poor heading | : 120-180 g/d |
| 6.2.11.27-Poor heading | : 120-180 g/d |
| 6.2.11.28-Discolored heads | : 130-180 g/d |
| 6.2.11.29-Discolored heads | : 130-180 g/d |
| 6.2.11.30-V-shaped lesions on leaf margin | : 60-80 g/d |
| 6.2.11.31-V-shaped lesions on leaf margin | : 60-80 g/d |
| 6.2.11.32-Heads soft and rotted | : 90-140 g/d |
| 6.2.11.33-Heads soft and rotted | : 90-140 g/d |
| 6.2.11.34-Bolting | : 200-280 g/d |
| 6.2.11.35-Bolting | : 200-280 g/d |
| 6.2.11.36-Curled leaves | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.11.37-Rough leaves | : 300-450 g/d |
| 6.2.11.38-Rough leaves | : 300-450 g/d |
| 6.2.11.39-Poorly developed roots | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.11.40-Poorly developed roots | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.11.41-Wind damage | : 50-80 g/d |
| 6.2.11.42-Wind damage | : 50-80 g/d |
| 6.2.11.43-Freeze damage | : 100-120 g/d |
| 6.2.11.44-Freeze damage | : 100-120 g/d |
| 6.2.11.45-Antifreezing and preventing cold stress | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.11.46-Antifreezing and preventing cold stress | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.11.47-Breaking the cycle-stage | : 230-290 g/d |
| 6.2.11.48-Breaking the cycle-stage | : 230-290 g/d |
| 6.2.11.49-Vegetative stage | : 120-150 g/d |
| 6.2.11.50-Vegetative stage | : 120-150 g/d |
| 6.2.11.51-Head development | : 100-130 g/d |
| 6.2.11.52-Head development | : 100-130 g/d |
| 6.2.12-Watermelon Application /Crop Protection | |
| 6.2.12.1-Bacterial Fruit Blotch | : 100-300 g/d |
| 6.2.12.2-Gummy Stem Blight | : 450 g/d |
| 6.2.12.3-Anthracnose | : 200-280 g/d |
| 6.2.12.4-Alternaria | : 300-400 g/d |
| 6.2.12.5-Cercospora | : 130-190 g/d |
| 6.2.12.6-Myrothecium Leaf Spot | : 300-500 g/d |
| 6.2.12.7-Leaf Mosaic | : 220-280 g/d |
| 6.2.12.8-Tobacco ring spot | : 130-160 g/d |
| 6.2.12.9-Squash Leaf Curl Virus | : 300-450 g/d |
| 6.2.12.10-Fusarium | : 90-170 g/d |
| 6.2.12.11-Bud necrosis | : 300-400 g/d |
| 6.2.12.12-Phytopthora | : 200-340 g/d |
| 6.2.12.13-Root Knot nematodes | : 300-500 g/d |
| 6.2.12.14-Rotting seeds | : 200g/d |
| 6.2.12.15-Stunted growth | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.12.16-Stunted growth | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.12.17-Blossom end-rot | : 200-300 g/d |
| 6.2.12.18-Blossom end-rot | : 200-300 g/d |
| 6.2.12.19-Internal Cracking | : 120-270 g/d |
| 6.2.12.20-Internal Cracking | : 120-270 g/d |
| 6.2.12.21-Spongy end | : 180-220 g/d |
| 6.2.12.22-Spongy end | : 180-220 g/d |
| 6.2.12.23-Sunburn | : 200-270 g/d |
| 6.2.12.24-Sunburn | : 200-270 g/d |
| 6.2.12.25-Thrips | : 300-500 g/d |
| 6.2.12.26-Flea Beetles | : 100-170 g/d |
| 6.2.12.27-Beet armyworms | : 500 g/d |
| 6.2.12.28-Grasshoppers | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.12.29-Melon Aphids | : 500-600 g/d |
| 6.2.12.30-Silverleaf Whiteflies | : 200-250 g/d |
| 6.2.12.31-Mole crickets | : 180-230 g/d |
| 6.2.12.32-White grubs | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.12.33-Germination | : 300-400 g/d |
| 6.2.12.34-Germination | : 300-400 g/d |
| 6.2.12.35-Vining | : 100-400 g/d |
| 6.2.12.36-Vining | : 100-400 g/d |
| 6.2.12.37-Flowering | : 40-120 g/d |
| 6.2.12.38-Flowering | : 40-120 g/d |
| 6.2.12.39-Fruiting | : 80-140 g/d |
| 6.2.12.40-Fruiting | : 80-140 g/d |
6.3- APPLICATION/Process and production
6.3.1-Mixing and solubility
6.3.1.1-Solubility :Excell Libra is soluble in H2O ,260 gr/L 24 C’ solution
260 gr/L 24 C’
320 gr/L 38 C’
400 gr/L 55 C’
6.3.1.2-Mixability :Excell Libra is soluble in H2O ,260 gr/L 24 C’ solution
260 gr/L 24 C’
320 gr/L 38 C’
400 gr/L 55 C’
6.3.2-Further process
6.3.1.1-Make product with Excell Libra™
Chealating Zn,Cu,Mn,Fe
7- RESEARCH and ARTICLES
7.1-Benefits,Effect and uses
7.1.-Applications
7.1.1.1-L-Arginine Alleviated the Drought-Induced Growth Inhibition of Maize Seedlings
7.1.1.2-Grain-Priming with L-Arginine Improves the Growth Performance of Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Plants under Drought Stress
7.1.1.3-L-arginine promotes the positive effect of IBA on rooting with regard to both root number and root length in both cherry rootstocks
7.1.1.4-L-Arginine Increases Tolerance to Nitrogen Deficiency in Malus hupehensis via Alterations in Photosynthetic Capacity and Amino Acids Metabolism
7.1.1.5-L-Arginine priming increased seed germination at low temperature by relieving inhibition of seed carbon and nitrogen metabolism and improving seed
7.1.1.6-L-Arginine has a significant effect in eliminating zinc chlorosis seen in tomato plants
7.1.1.7-L-Arginine is an effective nitrogen source for pepper development
7.1.1.8-L-Arginine applied to grape leaves together with urea increased yield per decare by 15%
7.1.1.9-L-Arginine enhanced the synthesis of soluble sugars, proline, free amino acids, phenols, and flavonoids in wheat plants under normal or stressed conditions
7.1.1.10- In conclusion, the exogenous use of L-Arginine is beneficial for the growth and development of maize plants, especially under stress conditions.
7.1.1.11-Effect of L-Arginine growth and yield on tomato plants
7.1.1.12-Compensation for delayed growth in vegetable seedlings
7.1.1.13-Reactivating stalled growth
7.1.1.14-Fruit enlargement and growth applications
7.1.1.15-It serves not only as an important nitrogen reserve and recycling, but also as a precursor of the biosynthesis of polyamines, nitric oxide and so on. Polyamines
7.1.1.16-Fruit enlargement and growth applications
7.1.1.17-Postharvest application of the arginine on strawberry fruits leading to inhibiting fruit decay and maintaining fruit quality
7.1.1.18-application of arginine (200 ppm) increased the growth and yield of wheat crop
7.1.1.19-Arginine has surfaced as a non-toxic plant growth governor that augments the resistance of plants to salt stress
7.1.1.20-Arginine enhanced plant development, fruit yield, and quality of tomatoes
7.1.1.21-Plant spraying treatment with arginine at a dosage of 100 mg L-1 was superior to the number of grains per spike and achieved an average
7.1.1.22-The exogenous application of amino acids in crop production has shown promising results, such as the increase in productivity and plant quality
7.1.1.23-By applying Arginine, researchers observed improvements in seed germination, seedling fresh mass, and water content
7.1.1.24-
7.1.1.25-
7.1.1.26-
7.1.1.27-
7.1.1.28-
7.1.1.29-
7.1.1.30-
7.1.2-Action of mechanism
7.1.2.1-Stimulate plant growth
7.1.3-Insight,experiment and facts
7.1.3.1-Stimulate plant growth
