GIBBERELLIN A-1
1-IDENTIFIER
1.1
1.1.1-Describe
Gibberellin A1 is a C19-gibberellin, initially identified in Gibberella fujikuroi.
1.1.2-Names
(1R,2R,5S,8S,9S,10R,11S,12S)-5,12-dihydroxy-11-methyl-6-methylidene-16-oxo-15-oxapentacyclo[9.3.2.15,8.01,
10.02,8]heptadecane-9-carboxylic acid
1.1.3-Supplier
Schwarp biyoteknoloji A.Ş
Saray osmangazi mahallesi sarsılmaz caddesi no :2 daire 6 Pursaklar Ankara
0-312 5143724 www.schwarp.com
1.2-IDENTIFY NUMBERS
1.2.1 -Milicard number : 868182336-02645
1.2.2 -EA Codex number : 8681823363538
1.2.3 -Cas number : 545-97-1
1.2.4 -EC number :
1.2.5 -Permit License number :
1.2.6 -Patent and License number :
1.3-STRUCTURE
1.3.1
1.3.2
1.3.3
1.3.4
1.4-CHEMICAL&PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| 1.4.1-CHEMICAL FORMULA: | C19H24O6 |
| 1.4.2-TYPE/STATE/FORM : | Powder |
| 1.4.3-COLOUR : | White |
| 1.4.4-ODOUR : | Not available. |
| 1.4.5-TASTE : | Not available. |
| 1.4.6-PARTICLE SIZE: | Not available. |
| 1.4.7-DENSITY : | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
| 1.4.8-MELTING POINT : | 230 °C |
| 1.4.9-BOILING POINT : | 619.7±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| 1.4.10-FLASH POINT : | Not available. |
| 1.4.11-VAPOUR PRESSURE : | Not available. |
| 1.4.12-VISCOSITY : | Not available. |
| 1.4.13-REFRACTIVE IDEX: | 1.639 |
| 1.4.14-IGNITION TEMP: | Not available. |
| 1.4.15-DISSOCIATION CONSTANTS : | Not available. |
| 1.4.16-SOLUBILITY : | 3.93 g/L in H2O |
| 1.4.17-pH VALUE : | Not available. |
| 1.4.18-ACIDITY pKa : | 4.10±0.70 |
| 1.4.19-Log P : | 0.24 |
| 1.4.20-CHIRAL ROTATION : | Not available. |
| 1.4.21-MOLAR MASS : | 348.4 g/mol |
| 1.4.22-PURITY : | |
| 1.4.22.1-CARRIER : | None. |
| 1.4.23-METALS : | Chloride <%0,02,Sulphate <%0.01 Heavy Metals <%0.0001 Arsenic <%0.00001 |
| Calcium <%0.001 Cobalt< %0.000001 Fe <%0.0005 K <%0.0003 Mg <%0.0002 | |
| Amonium N<%0.01 Na <%0.01 | |
| 1.4.24-LD 50 ORAL RAT | |
| 1.4.25-GHS: | Not available. |
| 1.4.26-WGK: | Not available. |
| 1.4.27-OTHER DETALIS: | |
2-ORO
3-TOT
4-DOCUMENTER
4.1-MSDS
4.1.1-MSDS Material Info
| Product Name | : GIBBERELLIN A-1 |
| Producer Name | : Milicard Seri Standartlar LTD ŞTİ |
| Saray Osmangazi Mahallesi Sarsılmaz Cad.No: 2/15 Pursaklar/ANKARA 0312 5143724 | |
| MILICARD NO | : 868182336-02645 |
| CODEX NUMBER | : 8681823363538 |
| CAS NUMBER | : 545-97-1 |
Acil durum telefon numarası Ulusal Zehir Danışma Merkezi (UZEM):
114 CHEMTREC Turkey (Istanbul): +(90)-212-7055340
4.1.2-Hazard Identification
Toxicological Data on Ingredients: Gibberellin A-1 LD50: Not available. LC50: Not available.
Potential Acute Health Effects: Slightly hazardous in case of skin contact, of eye contact (irritant), of ingestion, of inhalation.
Potential Chronic Health Effects: CARCINOGENIC EFFECTS: Not . MUTAGENIC EFFECTS: Mutagenic for mammalian somatic CELLS
TERATOGENIC EFFECTS: Not DEVELOPMENTAL TOXICITY: Not. Prolonged exposure is not known to aggravate medical condition.
GHS.Warning,Eye,Irritation,Category 2,H319,P305,P351,P338
Bu madde, Avrupa Birliği yönetmeliklerine göre tehlikeli olarak sınıflandırılmamıştır.
(EC) No 1272/2008 Yönetmeliğine göre tehlikeli madde ya da karışım değildir
1907/2006 No’lu AB Düzenlemesine göre tehlikeli içerikler yoktur
1907/2006 No’lu Yönetmeliğe (AB) (Zararlı Maddeler ve Karışımlara İlişkin Güvenlik Bilgi Formları Hakkında Yönetmelik
(R.G. 13.12.2014-29204)) göre hazırlanmıştır.
4.1.3-First Aid Measurement
EyeContact: Check for and remove any contact lenses. In case of contact,immediately flush eyes with plenty of water for at least
15 minutes Cold water may be used. Get medical attention if irritation occurs.
Skin Contact: Wash with soap and water. Cover the irritated skin with an emollient. Get medical attention if irritation develops.
Cold water may be used.
Serious Skin Contact: Not available.
Inhalation: If inhaled, remove to fresh air. If not breathing, give artificial respiration. If breathing is difficult, give oxygen.
Serious Inhalation: Not available.
Ingestion: DoNOT induce vomiting unless directed to do so by medical personnel. Never give anything by mouth to an
unconscious person. If large quantities of this material are swallowed, call a physician immediately. Loosen tight clothing
such as a collar, tie,belt or waistband.
Serious Ingestion: Not available.
Teneffüs ettikten sonra: temiz hava.
Deriyle teması halinde: Hemen tüm bulaşmış giyisileri çıkarınız. Deriyi suyla yıkayınız.
Göz temasından sonra: bol su ile yıkayın. Kontakt lensleri çıkarınız.
Yuttuktan sonra hemen 2 bardak su içirin. Kötü hissediliyorsa doktora başvurun.
Akut ve sonradan görülen önemli belirtiler ve etkiler Herhangi bir toksik semptom tanımımız yoktur.
Tıbbi müdahale ve özel tedavi gereği için ilk işaretler Bilgi bulunmamaktadır.
4.1.4-Fire And Explosion Data
Yangın söndürücüler
Uygun yangın söndürücüler
Su, Köpük, Karbon dioksit (CO2), Kuru toz
Uygun olmayan söndürme aracı
Bu madde/karışım için söndürme maddelerine yönelik bir sınırlama yoktur.
Madde veya karışımdan kaynaklanan özel zararlar
Yangın durumunda tehlikeli yanıcı gazlar veya buharlar gelişebilir.
Yangın şu maddelerin açığa çıkmasına neden olabilir: AZOT OKSİT
Yangın söndürme ekibi için özel koruyucu ekipmanlar.
Tehlikeli bölgede solunum aparatı olmaksızın durmayınız. Cilt ile temasını engellemek için güvenli uzaklıkta durun ve uygun
koruyucu kıyafet giyin.
Gaz/buhar/tozu, su fışkırtarak hapsediniz (kontrol altına alınız). Yangın söndürme sularının yeryüzü veya yeraltı sularına
karışmasını önleyiniz.
Flammability of the Product: May be combustible at high temperature.
Auto-Ignition Temperature: Not available.
Flash Points: Not available.
Flammable Limits: Not available.
Products of Combustion: These products are carbon oxides (CO, CO2), nitrogen oxides (NO, NO2…).
Fire Hazards in Presence of Various Substances: Slightly flammable to flammable in presence of heat. Non-flammable in
presence of shocks.
Explosion Hazards in Presence of Various Substances: Risks of explosion of the product in presence of mechanical impact: Not
Risks of explosion of the product in presence of static discharge: Not available.
Fire Fighting Media and Instructions: SMALL FIRE: Use DRY chemical powder. LARGE FIRE: Use water spray, fog or foam.
Do Not Use water jet.
Special Remarks on Fire Hazards: Not available.
Special Remarks on Explosion Hazards: Not available.
4.1.5-Accidental Release Measures
Acil durum personeli olmayan personeli uyarın tozları teneffüs ettikten sonra. Tehlike bölgesini boşaltın
acil durum prosedürlerini uygulayın, bir uzmana danışın.
Kanalizasyona karışmamasına dikkat ediniz.
Drenaj kanallarını kapatın. Dökülmeleri toplayın, sarın ve pompalayarak uzaklaştırın. Olası malzeme kısıtlamalarına uyun
Kuru alın. Atılması için gönderin. Etkilenmiş bölgeyi temizleyin. Tozların çoğalmasını engelleyin.
Small Spill: Use appropriate tools to put the spilled solid in a convenient waste disposal container.Finish cleaning by
spreading water on the contaminated surface and dispose of according to local and regional authority requirements.
Large Spill: Use a shovel to put the material into a convenient waste disposal container. Finish cleaning by spreading water
on the contaminated surface and allow to evacuate through the sanitary system.
4.1.6-Handling And Storage
1907/2006 No’lu Yönetmeliğe (AB) (Zararlı Maddeler ve Karışımlara İlişkin Güvenlik Bilgi Formları Hakkında Yönetmelik
(R.G. 13.12.2014-29204)) göre Hazırlama Tarihi: 12.04.2019 Yeni Düzenleme Tarihi :19.09.2020
Precautions: Keep locked up.. Keep away from heat. Keep away from sources of ignition. Empty containers pose a fire risk,
evaporate the residue under a fume hood. Ground all equipment containing material. Do not breathe dust. Wear suitable
protective clothing.
If you feel unwell, seek medical attention ,show thelabel when possible.Keepaway from incompatibles such as oxidizing agents.
Storage: Light sensitive. Store in light resistant containers. Keep container tightly closed. Keep container in a cool,
well-ventilated area.
Do not store above 24°C (75.2°F).
Genel Önlemlere Uyunuz.
Hijyen önlemleri
Kirlenen giysiyi değiştirin. Madde ile çalıştıktan sonra ellerinizi yıkayın.
Uyuşmazlıkları da içeren güvenli depolama için koşullar
Saklama koşulları
Sıkıca kapatılmış. Kuru.
Önerilen saklama sıcaklığı, ürün etiketine bakın
Belirli son kullanımlar
Bölüm 1.2’de belirtilen kullanımlar dışında, başka bir belirli kullanım öngörülmemiştir
4.1.7- Exposure Controls/Personal Protection
Engineering Controls: Use process enclosures, local exhaust ventilation,other engineering controls to keep airborne levels
below recommended exposure limits.
If user operations generate dust, fume,mist, use ventilation to keep exposure to airborne contaminants below the exposure
limit.
Personal Protection: Safety glasses. Lab coat. Dust respirator. Be sure to use an approved/certified respirator or equivalent.
Gloves.
PersonalProtection in Case of a LargeSpill:Splash goggles.Full suit.Dust respirator. Boots. Gloves. A self contained breathing
apparatus should be used to avoid inhalation of the product. Suggested protective clothing might not be sufficient; consult a
specialist BEFORE handling this product.
Exposure Limits: Not available.
Kontrol parametreleri
Maruz kalma limiti bulunan hiçbir madde içermez
Uygun Mühendislik Kontrolleri
Teknik önlemlere ve uygun iş operasyonlarına, kişisel koruyucu ekipman k ullanımı karşısında öncelik verilmelidir.
Bireysel Koruyucu Önlemler
Koruyucu giysi, kullanılan tehlikeli madde konsantrasyonu ve miktarına bağlı olarak , işyerine özgüsel olarak seçilmelidir.
Kimyasallardan korunmak için, koruyucu giysilerde bulunan resistanslar her bir tedarikçi tarafından saptanmalıdır.
Göz/yüz koruması :Güvenlik Gözlükleri
Ellerin korunması
Tam Temas
Eldiven malzemesi: Nitril kauçuk
Eldiven kalınlığı: 0,11 mm
delinme süresi: > 480 dakika
1907/2006 No’lu Yönetmeliğe (AB) (Zararlı Maddeler ve Karışımlara İlişkin Güvenlik Bilgi Formları Hakkında Yönetmelik
(R.G. 13.12.2014-29204)) göre
sıçrama ile temas:
Eldiven malzemesi: Nitril kauçuk
Solunum sisteminin korunması
Tavsiye edilen Filtre tipi: Asal maddelerin katı tanecikleri için P 1 Filtresi (DIN 3181’e uygun)
Girişimci, solunum koruma cihazlarının, cihaz üreticisinin talimatlarınca bakım yapıldığı,temizlendiği ve test edildiğini temin
etmelidir.
4.1.8-Physical and Chemical Properties
Physical state and appearance: Powder.
Chemical Formula : C19H24O6
Odor: Not available.
Taste: Not available.
Molecular Weight: 348.4 g/mol
Cas Number : 545-97-1
EC Number : Not available.
Melting Point: 230 °C
Color: White.
Dispersion Properties: Not available.
Solubility: 3.93 g/L in h2O
Temel fiziksel ve kimyasal özellikler hakkında bilgi
Görünüm : Toz Renk: Beyaz Koku : Uygun veri yoktur.
Kütle yoğunluğu yaklaşık Yüzey gerilimi yaklaşık: Uygun veri yoktur.
pH yaklaşık : Uygun veri yoktur. Ayrışma sabiti : Uygun veri yoktur.
Erime noktası: 230 °C Patlama Sınırı :Uygun veri yoktur
Başlangıç Kaynama Noktası ve AralIğı :619.7±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg Buhar Basıncı: Uygun veri yoktur.
Parlama noktası : Uygun veri yoktur. Buharlaşma oranı :Uygun veri yoktur.
Su içinde çözünürlüğü : 3.93 g/L Parçacık büyüklüğü : Uygun veri yoktur.
Dağılım katsayısı log Pow: -1,52 – (Kaynak), Uygun veri yoktur.
Bağıl yoğunluk: Uygun veri yoktur. Buhar yoğunluğu: Uygun veri yoktur.
Oksitleyici özellikler : Uygun veri yoktur.
Bozunma sıcaklığı : Uygun veri yoktur. Patlayıcılık özellikleri:Uygun veri yoktur.
4.1.9-Stability and Reactivity Data
Stability: The product is stable.
Instability Temperature: Not available.
Conditions of Instability: Excess heat, light
Incompatibility with various substances: Reactive with oxidizing agents.
Corrosivity: Non-corrosive in presence of glass.
Special Remarks on Reactivity: Light sensitive.
Special Remarks on Corrosivity: Not available.
Polymerization: Will not occur.
Tepkime
Aşağıdakiler genelde yanıcı organik maddelere ve preparatlar için geçerl idir:uygun ince bir dağılımda, ve havaya kaldırıldığında
bir toz patlam ası riski genelde beklenebilir.
Kimyasal kararlılık
Ürün, standart ortam koşulları (oda sıcaklığı) altında kimyasal olarak stabildir.
Zararlı tepkime olasılığı
Kuvvetli oksitleyici maddeler
Kaçınılması gereken durumlar
Zararlı bozunma ürünleri
yangın durumunda: Bölüm 5’e bakınız
4.1.10-Toxicological Information
Routes of Entry: Inhalation. Ingestion.
Toxicity to Animals: LD50: Not available. LC50: Not available.
Chronic Effects on Humans: MUTAGENIC EFFECTS: Mutagenic for mammalian somatic cells.
Other Toxic Effects on Humans: Slightly hazardous in case of skin contact (irritant), of ingestion, of inhalation.
Special Remarks on Toxicity to Animals: Not available.
Special Remarks on Chronic Effects on Humans: May affect genetic material. Some Laboratory experiments have resulted in
mutagenic effects.
Although some dietary studies in animals have demonstrated that arginine deficiency can impair reproductive organ
development as well as having adverse effects on gestation and lactation,we did not locate any literature on possible adverse
reproductive effects of supplemental arginine during human pregnancy.
Special Remarks on other Toxic Effects on Humans: Acute Potential Health Effects: Skin: May cause skin irritation.
Eyes: May cause eye irritation.
Inhalation: May cause respiratory tract irritation. Ingestion: May cause gastrointestinal tract irritation with nausea, vomiting,
and diarrhea.
The toxicological properties of this substance have not been fully investigated.
Akut oral toksisite
LD50 Oral – Sıçan – erkek ve dişi – > 2.000 mg/kg
Cilt tahrişi
Tavşan
Sonuç: negatif
Göz tahrişi
Tavşan
Sonuç: negatif
Eşey hücre mutajenitesi
İn vitro genotoksisite
Mutajenite (memeli hücre testi): kromozom
İnsan Lenfositleri
Sonuç: negatif
Ames testi
Escherichia coli/Salmonella typhimurium
Sonuç: negatif
Kanserojenite :Bilgi Yok
Üreme sistemi toksisitesi :Bilgi Yok
Teratojenisite (gelişimsel sakatlıklara neden olabilirlik) :Bilgi Yok
4.1.11-Ecological Information
Ecotoxicity: Not available.
BOD5 and COD: Not available.
ProductsofBiodegradation:Possibly hazardous shortterm degradation products are not likely.
However,longterm degradation products may arise.
Toxicity of the Products of Biodegradation: The product itself and its products of degradation are not toxic.
Special Remarks on the Products of Biodegradation: Not available.
Balıklar üzerinde toksisite
Semi-statik test LC50 Danio rerio (zebra balığı):10.000 mg/l; 96 sa OECD Test Kılavuzu 203
Analitik gözlem: hayır
Daphnia ve diğer suda yaşayan omurgasızlar üzerinde toksisite
Statik test EC50 Daphnia magna (Defne): 10.000 mg/l; 24 sa OECD Test Kılavuzu 202
Analitik gözlem: hayır
Bakteriler üzerinde toksisite
statik test EC10 Pseudomonas Putida:> 9.900 mg/l; 16 sa
Belirli Hedef Organ Toksisitesi – Tek maruz kalma
Bu bilgi mevcut değildir.
Aspirasyon toksisitesi
Tekrarlanan doz toksisitesi – Sıçan – erkek ve dişi – Oral – 90 d – Ters etkinin olmadığı düzey – 3.330 – 3.840 mg/kgN
Subkronik zehirlilik
4.1.12.-Disposal Considerations
Waste Disposal: Waste must be disposed of in accordance with federal, state and local environmental control regulations.
Identification: Not applicable.
Kalıcılık ve bozunabilirlik
Biyolojik bozunma
Oksijenli ( aerobik ) – Maruziyet süresi 28 d Sonuç: 83 % – Kolay bozunabilir
Kendiliğinden doğada kolaylıkla çözünür.
Biyobirikim potansiyeli
Dağılım katsayısı ( n-oktanol/su)
log Pow :-4,20
Kimyasal güvenlik değerlendirmesi gerekmediği/yapılmadığı için, PBT/vPvB değerlendirmesi yapılmamıştır.
4.1.13-Transpot Information
Kara taşımacılığı (ADR/RID)
Taşımacılık kurallarına göre tehlikeli maddeler sınıfına girmez.
Hava taşımacılığı (IATA)
Taşımacılık kurallarına göre tehlikeli maddeler sınıfına girmez.
Deniz taşımacılığı (IMDG)
Taşımacılık kurallarına göre tehlikeli maddeler sınıfına girmez.
4.1.14-Regulatory Information
Bu ürün için 1907/2006 numaralı EU REACH Mevzuatı’na uygun olarak bir kimyasal güvenlik değerlendirmesi
Depolama sınıfı 10 – 13
EINECS: This product is on the European Inventory of Existing Commercial Chemical Substances.
DSCL (EEC): R40- Possible risks of irreversible effects. S2- Keep out of the reach of children.
S36/37- Wear suitable protective clothing and gloves.
Health Hazard: 1
Fire Hazard: 1
Reactivity: 0
Personal Protection: E
National Fire Protection Association (U.S.A.):
Health: 1
Flammability: 1
Reactivity: 0
Specific hazard:
Protective Equipment: Gloves. Lab coat. Dust respirator. Be sure to use an approved/certified respirator or equivalent.
4.1.15-Safe&Hazard Symbols
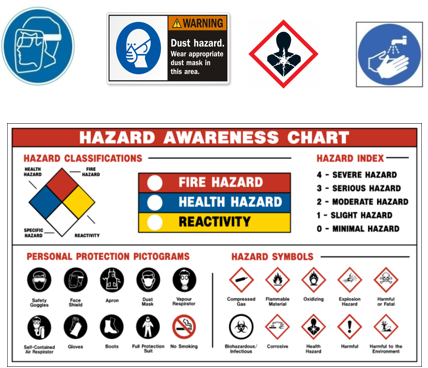
4.2-RISK REPORT
5-TEST STANDARTS&RESULTS
5.1-SPECTRAL ANALYSIS
5.1.1.1-1 D NMR Spectrum
5.1.1.2.1- 1H NMR Spectrum
5.1.1.2.2- 13C NMR Spectrum
5.1.1.2.3- 15N NMR Spectrum
5.1.1.2.4- 2D NMR Spectrum
5.1.2.1.1- Mass Spectrum
5.1.2.1.2- GC-MS Spectrum
5.1.2.1.2.1- GC-MS Spectrum TOF
5.1.2.1.3- MS-MS Spectrum
5.1.2.1.4- LC-MS Spectrum

6. APPLICATION/PLANT NUTRITION, FERTIGATION, HEALTH AND PESTS
6.2
| 6.2.1-Potato Application /Fertigation,Crop Protection | |
| 6.2.1.1-Turbo Spray | : Sprays 100-300 g /da |
| 6.2.1.2-Drip Irrıgation | : 1:1000 dilute |
| 6.2.1.3-30 days after planting | : 100 g/d |
| 6.2.1.4-45 days after planting | : 250 g/d |
| 6.2.1.5-90 days after planting | : 100 g/d |
| 6.2.1.6-Aerial Uses | : 200-400g/d |
| 6.2.1.7-Roat Soak | : 200-500 g/d |
| 6.2.1.8-Seed Treatment | : 3-5 g/kg of seed |
| 6.2.1.9-Alternaria diseaes | : 1 kg/ha |
| 6.2.1.10-Dry rot diseaes | : 220 g/d |
| 6.2.1.11-Potato Virus | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.1.12-Verticillium | : 60 g/d |
| 6.2.1.13-Skin Spot | : 80 g /d |
| 6.2.1.14-Powdery Scab | : 110 g/d |
| 6.2.1.15-Gangrene | : 190 g/d |
| 6.2.1.16-Viral and viroid diseaes | : 180 g/d |
| 6.2.1.17-Nematode parasitic | : 380 g/d |
| 6.2.1.18-Miscellaneous diseaes | : 35 g/d |
| 6.2.1.19-Bacterial soft rot | : 80 g/d |
| 6.2.1.20-Botrytis gray mold | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.1.21-Charcoal rot | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.1.22-Fusarium | : 700 g/d |
| 6.2.1.23-Pysyllid yellows | : 210 g/d |
| 6.2.1.24-Air pollution damage | : 130 g/d |
| 6.2.1.25-Fertilizer burn | : 108 g/d |
| 6.2.1.26-Freezing necros | : 190 g/d |
| 6.2.1.27-Hollow heart | : 33 g/d |
| 6.2.1.28-Lightning injury | : 78 g /d |
| 6.2.1.29-Second growth | : 90 g/d |
| 6.2.1.30-Greening | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.1.31-Xylem ring discoloration | : 260 g/d |
| 6.2.1.32-Tipburn | : 25 g/d |
| 6.2.1.33-Sunscald | : 106 g/d |
| 6.2.1.34-Stem streak necrosis | : 188 g/d |
| 6.2.1.35-Sprout tubers | : 102 g/d |
| 6.2.1.36-Spinding sprout | : 180 g/d |
| 6.2.1.37-Internal brown spot | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.1.38-Internal brown spot | : 112 g/d |
| 6.2.1.39-Heat and drought necrosis | : 190 g/d |
| 6.2.1.40-Feather and scald | : 110 g/d |
| 6.2.1.41-Enlarged lenticels | : 40 g/d |
| 6.2.1.42-Rootling | : 290 g/d |
| 6.2.1.43-Rootling | : 130 g/d |
| 6.2.1.44-Maturating | : 70 g/d |
| 6.2.1.45-Maturating | : 100 g/d |
| 6.2.1.46-Antifreezing and preventing cold stress | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.1.47Antifreezing and preventing cold stress | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.2-Apple Application /Fertigation,Crop Protection | |
| 6.2.2.1-Apple Scab-the fungus Venturia inaequalis | : 230 g/d |
| 6.2.2.2-Alternaria leaf and fruit blotch | : 177 g/d |
| 6.2.2.3-Bitter rot | : 55 g/d |
| 6.2.2.4-Powdery mildew | : 102 g/d |
| 6.2.2.5-White root rot-Rosellinia necatrix | : 380 g/d |
| 6.2.2.6-Sclerotium collar root -Sclerotium spp | : 310 g/d |
| 6.2.2.7-Black rot canker | : 74 g/d |
| 6.2.2.8-Collar rot | : 192 g/d |
| 6.2.2.9-Apple virus diseaes | : 450 g/d |
| 6.2.2.10-Brown rot | : 214 g/d |
| 6.2.2.11-Seedling blight | : 190 g/d |
| 6.2.2.12-Fire blight | : 600 g/d |
| 6.2.2.13-Poor Fruiting | : 250-300 g/d |
| 6.2.2.14-Root Decay | : 80-120 g/d |
| 6.2.2.15-Grey-coloured crusty growth | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.2.16-Grey-coloured crusty growth | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.2.17-Bird Damage on Flowers | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.2.18-Waterlogging | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.2.19-Waterlogging | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.2.20-Calcium uptake | : 120-300 g/d |
| 6.2.2.21-Calcium uptake | : 120-300 g/d |
| 6.2.2.22-Poor growing conditions | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.2.23-Poor growing conditions | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.2.24-Unproductive trees | : 10 g/tree |
| 6.2.2.25-Pollinating Partner | : 80 g/d |
| 6.2.2.26-Mussel Scale | : 340 g/d |
| 6.2.2.27-Aphid Attack | : 280-370 g/d |
| 6.2.2.28-Caterpillars | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.2.29-Capsid Bugs | : 90 g/d |
| 6.2.2.30-Summer pruning | : 230 g/d |
| 6.2.2.31-Blossom wilt | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.2.32-Codling Moth | : 380 g/d |
| 6.2.2.33-Coral Spot | : 160 g/d |
| 6.2.2.34-Silver Leaf | : 100 g/d |
| 6.2.2.35-Flyspeck | : 170 g/d |
| 6.2.2.36-Low N requirement varieties | : 100-200 g/d |
| 6.2.2.37-Low N requirement varieties | : 100-200 g/d |
| 6.2.2.38-High N requirement varieties | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.2.39-High N requirement varieties | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.2.40-Vigor of Shoot Growth | : 240-300 g/d |
| 6.2.2.41-Fruit Size and firmness | : 80-120 g/d |
| 6.2.2.42-Terminal growth | : 230 g/d |
| 6.2.2.43-Leaf size growth | : 300-400 g/d |
| 6.2.2.44-Fruit setting | : 30-110 g/d |
| 6.2.2.45-Fruit setting and maturating | : 30-110 g/d |
| 6.2.2.46-Fruit maturity | : 180-270 g/d |
| 6.2.3.1-Growing Excessively Large Fruit | : 110-205 g/d |
| 6.2.3.2-Growing Excessively Large Fruit | : 110-205 g/d |
| 6.2.3.3-Encouraging Good pollination | : 50-90 g/d |
| 6.2.3.4-Encouraging Good pollination | : 50-90 g/d |
| 6.2.3.5-General Soil Application | : 500-700 g/d |
| 6.2.3.6-General Soil Application | : 500-700 g/d |
| 6.2.3.7-General Foliar Application | : 100-400 g/d |
| 6.2.3.8-General Foliar Application | : 100-400 g/d |
| 6.2.3.9-Pre-Bloom | : 20-60 g/d |
| 6.2.3.10-Pre-Bloom | : 20-60 g/d |
| 6.2.3.11-Post-Bloom | : 30-50 g/d |
| 6.2.3.12-Post-Bloom | : 30-50 g/d |
| 6.2.3.13-Plant Population 60-80 trees /d | : 200-500 g/d |
| 6.2.3.14-Plant Population 60-80 trees /d | : 200-500 g/d |
| 6.2.3.15-Plant Population 140-250 trees/d | : 400-600 g/d |
| 6.2.3.16-Plant Population 140-250 trees/d | : 400-600 g/d |
| 6.2.3.17-Spring to early summer | : 100-300 g/d |
| 6.2.3.18-Spring to early summer | : 100-300 g/d |
| 6.2.3.19-Post Harvest | : 200-250 g/d |
| 6.2.3.20-Post Harvest | : 200-250 g/d |
| 6.2.3.21-Antifreezing and preventing cold stress | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.3.22-Antifreezing and preventing cold stress | : 400 g/d |
| 3.2.4-Grape Application/ Fertigation | |
| 6.2.4.1-Soil pH near 6.5 | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.4.2-Soil pH near 6.5 | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.4.3-Soil pH 5.0-6.0 | : 300-500 g/d |
| 6.2.4.4-Soil pH 5.0-6.0 | : 300-500 g/d |
| 6.2.4.5-New plantings | : 100-180 g/d |
| 6.2.4.6-New plantings | : 100-180 g/d |
| 6.2.4.7-Coarse textured ,Acid Soil | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.4.8-Pre-Bloom,upper mature leaf/petiole | : 90-110 g/d |
| 6.2.4.9-Bloom and Fruiting ,leaf /petiole opposite cluster | : 170-220 g/d |
| 6.2.4.10-Fruit maturating | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.4.11-Sandy Soil | : 200-300 g/d |
| 6.2.4.12-Sandy Soil | : 200-300 g/d |
| 6.2.4.13-Beginning 2 weeks before bloom | : 30-60 g/d |
| 6.2.4.14-Beginning 2 weeks before bloom | : 30-60 g/d |
| 6.2.4.15-Root damage | : 250 g/d |
| 6.2.4.16-Bud Burst stage | : 40-70 g/d |
| 6.2.4.17-Bud Burst stage | : 40-70 g/d |
| 6.2.4.18-Early Shoot stage | : 70-110 g/d |
| 6.2.4.19-Early Shoot stage | : 70-110 g/d |
| 6.2.4.20-Mid Shoot stage | : 100 g/d |
| 6.2.4.21-Mid Shoot stage | : 100 g/d |
| 6.2.5.1-Post Harvest | : 90-200 g/d |
| 6.2.5.2-Post Harvest | : 90-200 g/d |
| 6.2.5.3-Downy Mildew | : 130-300 g/d |
| 6.2.5.4-Anthracnose | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.5.5-Grey Mold | : 230-290 g/d |
| 6.2.5.6-Viruses | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.5.7-Greenaria bitter rot | : 90-110 g/d |
| 6.2.5.8-Bacterial leaf spot | : 280 g/d |
| 6.2.5.9-Alternaria blight | : 200-300 g/d |
| 6.2.5.10-Black Rot | : 30-80 g/d |
| 6.2.5.11-Black Rot | : 30-80 g/d |
| 6.2.5.12-Rhizopus rot | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.5.13-Rhizopus rot | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.5.14-Botrytis bunch rot | : 230-290 g/d |
| 6.2.5.15-Color,size,taste improving | : 240-340 g/d |
| 6.2.5.16-Color,size,taste improving | : 240-340 g/d |
| 6.2.5.17-Chemical damage | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.5.18-Nutritional Imbalances | : 100-600 g/d |
| 6.2.5.19-Nutritional Imbalances | : 100-600 g/d |
| 6.2.5.20-Sanitation with biocide | : 20 g/10 L H2O |
| 6.2.5.21-Pruning | : 30 g/100 L H2O |
| 6.2.5.22-Boron deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.23-Boron deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.24-Calcium deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.25-Calcium deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.26-Copper deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.27-Copper deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.28-Iron deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.29-Iron deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.30-Magnesium deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.31-Magnesium deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.32-Manganase deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.33-Manganase deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.34-Zinc deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.35-Zinc deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.5.36-Antifreezing and preventing cold stress | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.5.37-Antifreezing and preventing cold stress | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.5.38-Flowering | : 60-90 g/d |
| 6.2.5.39-Fruit Set | : 100-240 g/d |
| 6.2.6-Corn Application /Crop Protection | |
| 6.2.6.1-Seed rots and seeding blights | : 100-200 g/d |
| 6.2.6.2-Stalk rots | : 120 g/d |
| 6.2.6.3-Ear rots | : 130-180 g/d |
| 6.2.6.4-Boil and Head smut | : 200-300 g/d |
| 6.2.6.5-Downy mildew | : 80-130 g/d |
| 6.2.6.6-Fusairum | : 240 g/d |
| 6.2.6.7-Virus | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.6.8-Blanking | : 100-120 g/d |
| 6.2.6.9-Blanking | : 100-120 g/d |
| 6.2.6.10-Boron deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.11-Boron deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.12-Calcium deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.13-Calcium deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.14-Copper deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.15-Copper deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.16-Iron deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.17-Iron deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.18-Magnesium deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.19-Magnesium deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.20-Manganase deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.21-Manganase deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.22-Zinc deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.23-Zinc deficiency | : 30-70 g/d |
| 6.2.6.24-Uneven germination | : 100-300 g/d |
| 6.2.6.25-Uneven germination | : 100-300 g/d |
| 6.2.6.26-Aphid | : 800 g/d |
| 6.2.6.27-Cricket | : 600 g/d |
| 6.2.6.28-Cutworm | : 300-500 g/d |
| 6.2.6.29-Earwig | : 200-500 g/d |
| 6.2.6.30-Mite | : 300-700 g/d |
| 6.2.6.31-Heliothis | : 200-270 g/d |
| 6.2.6.32-Maize leafhopper | : 100-300 g/d |
| 6.2.6.33-Parasitoid wasps | : 100-230 g/d |
| 6.2.6.34-Flies | : 200-300 g/d |
| 6.2.6.35-Fungal Systemic diseaes | : 200-450 g/d |
| 6.2.6.36-Smutting diseaes | : 80-190 g/d |
| 6.2.6.37-Herbicide injury symptoms | : 160-210 g/d |
| 6.2.6.38-Trigger symptoms | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.6.39-Trigger symptoms | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.6.40-Nutrient defiency symptoms | : 40-400 g/d |
| 6.2.6.41-Nutrient defiency symptoms | : 40-400 g/d |
| 6.2.6.42-Leaf Diseaes | : 300-400 g/d |
| 6.2.6.43-Leaf Diseaes | : 300-400 g/d |
| 6.2.6.44-Unfavorable soil conditions | : 200-600 g/d |
| 6.2.6.45-Unfavorable soil conditions | : 200-600 g/d |
| 6.2.6.46-Poor Seed-soil contact | : 130-180 g/d |
| 6.2.6.47-Poor Seed-soil contact | : 130-180 g/d |
| 6.2.6.48-Fertilizer injury | : 220-260 g/d |
| 6.2.6.49-Fertilizer injury | : 220-260 g/d |
| 6.2.7.1-Seed planted to deep | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.7.2-Seed planted to deep | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.7.3-Bird and rodent damage | : 450 g/d |
| 6.2.7.4-Bird and rodent damage | : 450 g/d |
| 6.2.7.5-Insects attacking roots | : 340-380 g/d |
| 6.2.7.6-Insects attacking roots | : 340-380 g/d |
| 6.2.7.7-Nematodes | : 500 g/d |
| 6.2.7.8-Nematodes | : 500 g/d |
| 6.2.7.9-Non-uniform planting | : 200-600 g/d |
| 6.2.7.10-Non-uniform planting | : 200-600 g/d |
| 6.2.7.11-Failure of roots develop | : 300-460 g/d |
| 6.2.7.12-Failure of roots develop | : 300-460 g/d |
| 6.2.7.13-Wind damage | : 50-80 g/d |
| 6.2.7.14-Wind damage | : 50-80 g/d |
| 6.2.7.15-Freeze damage | : 100-120 g/d |
| 6.2.7.16-Freeze damage | : 100-120 g/d |
| 6.2.7.17-Antifreezing and preventing cold stress | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.7.18-Antifreezing and preventing cold stress | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.8-Tomato Application/Crop Protection | |
| 6.2.8.1-Failure to set fruit,poor fruit set | : 120-340 g/d |
| 6.2.8.2-Failure to set fruit,poor fruit set | : 120-340 g/d |
| 6.2.8.3-Cold soil stress | : 40-70 g/d |
| 6.2.8.4-Cold soil stress | : 40-70 g/d |
| 6.2.8.5-Root initiatives | : 50-80 g/d |
| 6.2.8.6-Root initiatives | : 50-80 g/d |
| 6.2.8.7-Early blight | : 90-310 g/d |
| 6.2.8.8-Septoria leaf spot | : 60-100 g/d |
| 6.2.8.9-Bacterial spot and speck | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.8.10-Spider mites | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.8.11-Fusarium & Verticillium | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.8.12-Bacterial canker | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.8.13-Late blight | : 100 g/d |
| 6.2.8.14-Hornworms | : 130 g/d |
| 6.2.8.15-Root-Knot nematodes | : 180-240 g/d |
| 6.2.8.16-Gray Leaf Spot | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.8.17-Anthracnose | : 200-240 g/d |
| 6.2.8.18-Blossom end rot | : 50 g/d |
| 6.2.8.19-Buckeye rot | : 60-90 g/d |
| 6.2.8.20-Buckeye rot | : 60-90 g/d |
| 6.2.8.21-Botrytis Gray Mold | : 230-310 g/d |
| 6.2.8.22-Spotty Leaves | : 290-370 g/d |
| 6.2.8.23-Spotty Leaves | : 290-370 g/d |
| 6.2.8.24-Fixing Fruit | : 300-600 g/d |
| 6.2.8.25-Fixing Fruit | : 300-600 g/d |
| 6.2.9-Tomato Application/Crop Protection | |
| 6.2.9.1-Catfacing | : 100-300 g/d |
| 6.2.9.2-Catfacing | : 100-300 g/d |
| 6.2.9.3-Leaf Roll | : 120-340 g/d |
| 6.2.9.4-Leaf Roll | : 120-340 g/d |
| 6.2.9.5-Puffiness | : 80-130 g/d |
| 6.2.9.6-Puffiness | : 80-130 g/d |
| 6.2.9.7-Powdery Mildew | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.9.8-Cutworms | : 80-110 g/d |
| 6.2.9.9-Flea beetles | : 100-130 g/d |
| 6.2.9.10-Tuta Absoluta | : 200-700 g/d |
| 6.2.9.11-Whiteflies | : 100-190 g/d |
| 6.2.9.12-Parasitic plants | : 200-340 g/d |
| 6.2.9.13-Apical Stunt | : 300-500 g/d |
| 6.2.9.14-Hail Damage | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.9.15-Small holes in leaves of seedlings | : 30-50 g/d |
| 6.2.9.16-Small holes in leaves of seedlings | : 30-50 g/d |
| 6.2.9.17-Water-soaked spots on leaves | : 40-80 g/d |
| 6.2.9.18-Water-soaked spots on leaves | : 40-80 g/d |
| 6.2.9.19-Trails and tunnels in leaves | : 40-80 g/d |
| 6.2.9.20-Trails and tunnels in leaves | : 40-80 g/d |
| 6.2.9.21-Small to large holes in fruits | : 100-190 g/d |
| 6.2.9.22-Sunken water-soaked areas on fruit | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.9.23-Worm tunnels into fruit | : 190-230 g/d |
| 6.2.9.24-Fruit is distorted | : 40-90 g/d |
| 6.2.9.25-Fruit is distorted | : 40-90 g/d |
| 6.2.9.26-Psyllids | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.9.27-Roots discolored ,mushy | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.9.28-Roots discolored ,mushy | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.9.29-Ring spots on fruit | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.9.30-Uniforming fruit | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.9.31-Preplant,vegetative growth stage | : 100-400 g/d |
| 6.2.9.32-Preplant,vegetative growth stage | : 100-400 g/d |
| 6.2.9.33-Flowering&Fruit Set | : 80-120 g/d |
| 6.2.9.34-Flowering&Fruit Set | : 80-120 g/d |
| 6.2.9.35-Ripening&Maturity | : 80-140 g/d |
| 6.2.9.36-Ripening&Maturity | : 80-140 g/d |
| 6.2.9.37-Over-pruning | : 120 g/d |
| 6.2.9.38-Fruit cracks | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.9.39-Poor fruit set | : 400-450 g/d |
| 6.2.10-Cabbage Application/Fertigation | |
| 6.2.10.1-Adjusting the spacing | : 310-340 g/d |
| 6.2.10.2-Adjusting the spacing | : 310-340 g/d |
| 6.2.10.3-Pre-drilling | : 1000 g/d |
| 6.2.10.4-Pre-drilling | : 1000 g/d |
| 6.2.10.5-Transplanting | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.10.6-Transplanting | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.10.7-4-6 leaf stage | : 80-130 g/d |
| 6.2.10.8-4-6 leaf stage | : 80-130 g/d |
| 6.2.11.1-Cutworms | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.11.2-Cabbage worms | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.11.3-Root maggots | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.11.4-Flea Beetles | : 100-400 g/d |
| 6.2.11.5-Aphids | : 100-200 g/d |
| 6.2.11.6-Slugs and Snails | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.11.7-Damping off seedlings | : 100 g/d |
| 6.2.11.8-Clubroot | : 80-100 g/d |
| 6.2.11.9-Caterpillars | : 230 g/d |
| 6.2.11.10-Downy mildew | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.11.11-Sclerotinia rot | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.11.12-Tipburn | : 100-180 g/d |
| 6.2.11.13-Seedlings fail to emerge from soil | : 200-300 g/d |
| 6.2.11.14-Young sprouts fail to grow | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.11.15-Young plants flower | : 300 g/ d |
| 6.2.11.16-Small holes in leaves | : 200-500 g/d |
| 6.2.11.17-Leaves are pitted | : 100-220 g/d |
| 6.2.11.18-Root nematodes | : 200-300 g/d |
| 6.2.11.19-Bacterial Soft rot | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.11.20-Blackleg | : 200 g/d |
| 6.2.11.21-White rust | : 120-220 g/d |
| 6.2.11.22-Yellow patches | : 300-550 g/d |
| 6.2.11.23-Turnip mosaic | : 80-130 g/d |
| 6.2.11.24-Cracking of heads | : 200-290 g/d |
| 6.2.11.25-Cracking of heads | : 200-290 g/d |
| 6.2.11.26-Poor heading | : 120-180 g/d |
| 6.2.11.27-Poor heading | : 120-180 g/d |
| 6.2.11.28-Discolored heads | : 130-180 g/d |
| 6.2.11.29-Discolored heads | : 130-180 g/d |
| 6.2.11.30-V-shaped lesions on leaf margin | : 60-80 g/d |
| 6.2.11.31-V-shaped lesions on leaf margin | : 60-80 g/d |
| 6.2.11.32-Heads soft and rotted | : 90-140 g/d |
| 6.2.11.33-Heads soft and rotted | : 90-140 g/d |
| 6.2.11.34-Bolting | : 200-280 g/d |
| 6.2.11.35-Bolting | : 200-280 g/d |
| 6.2.11.36-Curled leaves | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.11.37-Rough leaves | : 300-450 g/d |
| 6.2.11.38-Rough leaves | : 300-450 g/d |
| 6.2.11.39-Poorly developed roots | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.11.40-Poorly developed roots | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.11.41-Wind damage | : 50-80 g/d |
| 6.2.11.42-Wind damage | : 50-80 g/d |
| 6.2.11.43-Freeze damage | : 100-120 g/d |
| 6.2.11.44-Freeze damage | : 100-120 g/d |
| 6.2.11.45-Antifreezing and preventing cold stress | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.11.46-Antifreezing and preventing cold stress | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.11.47-Breaking the cycle-stage | : 230-290 g/d |
| 6.2.11.48-Breaking the cycle-stage | : 230-290 g/d |
| 6.2.11.49-Vegetative stage | : 120-150 g/d |
| 6.2.11.50-Vegetative stage | : 120-150 g/d |
| 6.2.11.51-Head development | : 100-130 g/d |
| 6.2.11.52-Head development | : 100-130 g/d |
| 6.2.12-Watermelon Application /Crop Protection | |
| 6.2.12.1-Bacterial Fruit Blotch | : 100-300 g/d |
| 6.2.12.2-Gummy Stem Blight | : 450 g/d |
| 6.2.12.3-Anthracnose | : 200-280 g/d |
| 6.2.12.4-Alternaria | : 300-400 g/d |
| 6.2.12.5-Cercospora | : 130-190 g/d |
| 6.2.12.6-Myrothecium Leaf Spot | : 300-500 g/d |
| 6.2.12.7-Leaf Mosaic | : 220-280 g/d |
| 6.2.12.8-Tobacco ring spot | : 130-160 g/d |
| 6.2.12.9-Squash Leaf Curl Virus | : 300-450 g/d |
| 6.2.12.10-Fusarium | : 90-170 g/d |
| 6.2.12.11-Bud necrosis | : 300-400 g/d |
| 6.2.12.12-Phytopthora | : 200-340 g/d |
| 6.2.12.13-Root Knot nematodes | : 300-500 g/d |
| 6.2.12.14-Rotting seeds | : 200g/d |
| 6.2.12.15-Stunted growth | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.12.16-Stunted growth | : 400 g/d |
| 6.2.12.17-Blossom end-rot | : 200-300 g/d |
| 6.2.12.18-Blossom end-rot | : 200-300 g/d |
| 6.2.12.19-Internal Cracking | : 120-270 g/d |
| 6.2.12.20-Internal Cracking | : 120-270 g/d |
| 6.2.12.21-Spongy end | : 180-220 g/d |
| 6.2.12.22-Spongy end | : 180-220 g/d |
| 6.2.12.23-Sunburn | : 200-270 g/d |
| 6.2.12.24-Sunburn | : 200-270 g/d |
| 6.2.12.25-Thrips | : 300-500 g/d |
| 6.2.12.26-Flea Beetles | : 100-170 g/d |
| 6.2.12.27-Beet armyworms | : 500 g/d |
| 6.2.12.28-Grasshoppers | : 200-400 g/d |
| 6.2.12.29-Melon Aphids | : 500-600 g/d |
| 6.2.12.30-Silverleaf Whiteflies | : 200-250 g/d |
| 6.2.12.31-Mole crickets | : 180-230 g/d |
| 6.2.12.32-White grubs | : 300 g/d |
| 6.2.12.33-Germination | : 300-400 g/d |
| 6.2.12.34-Germination | : 300-400 g/d |
| 6.2.12.35-Vining | : 100-400 g/d |
| 6.2.12.36-Vining | : 100-400 g/d |
| 6.2.12.37-Flowering | : 40-120 g/d |
| 6.2.12.38-Flowering | : 40-120 g/d |
| 6.2.12.39-Fruiting | : 80-140 g/d |
| 6.2.12.40-Fruiting | : 80-140 g/d |
6.3- APPLICATION/Process and production
6.3.1-Mixing and solubility
6.3.1.1-Solubility :Excell Libra is soluble in H2O ,260 gr/L 24 C’ solution
260 gr/L 24 C’
320 gr/L 38 C’
400 gr/L 55 C’
6.3.1.2-Mixability :Excell Libra is soluble in H2O ,260 gr/L 24 C’ solution
260 gr/L 24 C’
320 gr/L 38 C’
400 gr/L 55 C’
6.3.2-Further process
6.3.1.1-Make product with Excell Libra™
Chealating Zn,Cu,Mn,Fe
7- RESEARCH and ARTICLES
7.1.-Applications
7.1.1.1-L-Arginine Alleviated the Drought-Induced Growth Inhibition of Maize Seedlings
7.1.1.2-Grain-Priming with L-Arginine Improves the Growth Performance of Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Plants under Drought Stress
7.1.1.3-L-arginine promotes the positive effect of IBA on rooting with regard to both root number and root length in both cherry rootstocks
7.1.1.4-L-Arginine Increases Tolerance to Nitrogen Deficiency in Malus hupehensis via Alterations in Photosynthetic Capacity and Amino Acids Metabolism
7.1.1.5-L-Arginine priming increased seed germination at low temperature by relieving inhibition of seed carbon and nitrogen metabolism and improving seed
7.1.1.6-L-Arginine has a significant effect in eliminating zinc chlorosis seen in tomato plants
7.1.1.7-L-Arginine is an effective nitrogen source for pepper development
7.1.1.8-L-Arginine applied to grape leaves together with urea increased yield per decare by 15%
7.1.1.9-L-Arginine enhanced the synthesis of soluble sugars, proline, free amino acids, phenols, and flavonoids in wheat plants under normal or stressed conditions
7.1.1.10- In conclusion, the exogenous use of L-Arginine is beneficial for the growth and development of maize plants, especially under stress conditions.
7.1.1.11-Effect of L-Arginine growth and yield on tomato plants
7.1.1.12-Compensation for delayed growth in vegetable seedlings
7.1.1.13-Reactivating stalled growth
7.1.1.14-Fruit enlargement and growth applications
7.1.1.15-It serves not only as an important nitrogen reserve and recycling, but also as a precursor of the biosynthesis of polyamines, nitric oxide and so on. Polyamines
7.1.1.16-Fruit enlargement and growth applications
7.1.1.17-Postharvest application of the arginine on strawberry fruits leading to inhibiting fruit decay and maintaining fruit quality
7.1.1.18-application of arginine (200 ppm) increased the growth and yield of wheat crop
7.1.1.19-Arginine has surfaced as a non-toxic plant growth governor that augments the resistance of plants to salt stress
7.1.1.20-Arginine enhanced plant development, fruit yield, and quality of tomatoes
7.1.1.21-Plant spraying treatment with arginine at a dosage of 100 mg L-1 was superior to the number of grains per spike and achieved an average
7.1.1.22-The exogenous application of amino acids in crop production has shown promising results, such as the increase in productivity and plant quality
7.1.1.23-By applying Arginine, researchers observed improvements in seed germination, seedling fresh mass, and water content
7.1.1.24-
7.1.1.25-
7.1.1.26-
7.1.1.27-
7.1.1.28-
7.1.1.29-
7.1.1.30-
7.1.2-Action of mechanism
7.1.2.1-Stimulate plant growth
7.1.3-Insight,experiment and facts
7.1.3.1-Stimulate plant growth
